What we’re seeing is a removing of cooling that’s revealing warming that’s already there. So the air pollution isn’t the cause of the warming. It’s just letting us see stuff that we’ve already done.Listen to the interview on The Conversation Weekly podcast. You can also read an article by Laura Wilcox and her colleague Bjørn H. Samset about their recent research on The Conversation. This episode of The Conversation Weekly was written and produced by Mend Mariwany, Gemma Ware and Katie Flood. Mixing by Michelle Macklem and theme music by Neeta Sarl. Newsclips in this episode from Voice of America, CBC, AP Archive, ABC (News) Australia, WFLA NBC Channel 8 and PBS. Listen to The Conversation Weekly via any of the apps listed above, download it directly via our RSS feed or find out how else to listen here. A transcript of this episode is available via the Apple Podcasts or Spotify apps.
The Earth
Frequency of Extreme Fire Risk in the US has Grown 20X: Deep Sky Research
Last Updated on June 25, 2024 by Daily News Staff
evels of widespread extreme fire risk which used to occur once every 100 years will now occur every 5
MONTREAL /PRNewswire/ — Deep Sky, the Canadian carbon removal project developer, has published original research on wildfire risk in the United States. A new report shares findings from Deep Sky Research and its Wildfire Risk Model on how wildfire risk is changing due to climate change. The model unveiled four key findings:
- Maximum Fire Risk Has Grown Approximately 15X Across North America
- The model shows that Extreme Fire Weather conditions previously seen once every 100 years will now happen on average every 7 years.
- Frequency of Extreme Fire Risk has Grown 20X
- The frequency of Extreme Fire Weather – exceeding the 95th percentile in that area – has grown even more sharply than severity. Levels of widespread extreme fire risk which used to occur once every 100 years will now occur every 5.
- Some Regions Face Even Faster Growing Risks
- Central Colorado and Northern New Mexico are seeing much more extreme fire weather today than in previous years, and Central California is facing staggering increases in extreme fire weather, for example.
- The Increase is Accelerating
- One startling finding from the Wildfire Risk Model is that the increases in Extreme Fire Weather are not linear. These risks are not only growing but have begun accelerating.
One way to understand the increase in wildfire destruction is to look at the underlying conditions that lead to wildfires. Fire Weather Index (FWI) is a measure developed by the Canadian Forestry Service but used globally to assess fire risk. It combines temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation to give a holistic view of landscape flammability.
Climate change, which directly impacts each of these inputs, is causing more frequent and more destructive wildfires. Deep Sky Research analyzed trends in fire weather across North America and found sharp increases in the probability of extreme conditions.
“Deep Sky Research uses a novel approach for predicting the impact of climate change,” said Max Dugan-Knight, Deep Sky Climate Data Scientist. “A risk assessment approach, just like the insurance industry uses, can help us predict disasters ahead of time. In the case of wildfires, an increase in frequency and severity is being driven by changes in extreme fire weather.”
Deep Sky Research developed a map to show how fire weather is changing in each county of the continental US. It shows how Extreme Fire Weather is becoming more frequent and more severe. The darker red the county, the greater the increase in fire weather. The few blue counties are actually seeing decreases in risk.
This is what climate scientists refer to as a “vicious cycle.” Climate change is causing worse fire weather conditions, which cause larger, more destructive wildfires, which cause huge carbon emissions, which themselves contribute to more climate change. If the death and destruction caused by wildfires is not reason enough to act on climate change, avoiding vicious cycles and tipping points surely is.
To read the full report, visit Where Will the Next Extreme Wildfire Be? on deepskyclimate.com/research.
About Deep Sky:
Montreal-based Deep Sky is the world’s first IP agnostic carbon removal project developer aiming to remove gigatons of carbon from the atmosphere and permanently store it underground. As a project developer, Deep Sky brings together the most promising direct air and ocean carbon capture companies under one roof to bring the largest supply of high quality carbon credits to the market and commercialize carbon removal and storage solutions like never before. With $75M in funding, Deep Sky is backed by world class investors including Investissement Québec, Brightspark Ventures, Whitecap Venture Partners, OMERS Ventures, BDC Climate Fund, and more. For more information, visit deepskyclimate.com.
SOURCE Deep Sky
podcasts
How China cleaned up its air pollution – and what that meant for the climate
How China cleaned up its air pollution: Beijing’s air quality went from hazardous to good while Delhi and Lahore still struggle. Discover how China dramatically reduced pollution since 2013—and why cleaner air may have unintended consequences for global warming and climate change.
How China cleaned up its air pollution – and what that meant for the climate
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
The Knowledge
Fern Stems Reveal How Evolutionary Constraints Create New Forms in Nature
Evolutionary Constraints: New research on fern vascular systems reveals how developmental constraints don’t just limit evolution—they generate new forms. Discover how leaf placement determines stem structure and what this means for understanding biodiversity and plant breeding.

Fern Stems Reveal How Evolutionary Constraints Create New Forms in Nature
Jacob S. Suissa, University of Tennessee There are few forms of the botanical world as readily identifiable as fern leaves. These often large, lacy fronds lend themselves nicely to watercolor paintings and tricep tattoos alike. Thoreau said it best: “Nature made ferns for pure leaves, to show what she could do in that line.” But ferns are not just for art and gardens. While fern leaves are the most iconic part of their body, these plants are whole organisms, with stems and roots that are often underground or creeping along the soil surface. With over 400 million years of evolutionary history, ferns can teach us a lot about how the diversity of planet Earth came to be. Specifically, examining their inner anatomy can reveal some of the intricacies of evolution.Sums of parts or an integrated whole?
When one structure cannot change without altering the other, researchers consider them constrained by each other. In biology, this linkage between traits is called a developmental constraint. It explains the limits of what possible forms organisms can take. For instance, why there aren’t square trees or mammals with wheels. However, constraint does not always limit form. In my recently published research, I examined the fern vascular system to highlight how changes in one part of the organism can lead to changes in another, which can generate new forms.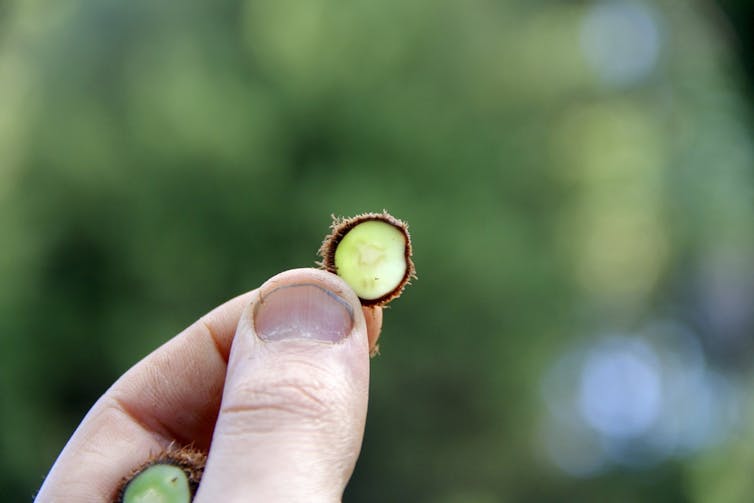
Fern vasculature and the process of evolution
Ferns are one of four lineages of land plants that have vascular tissues – specialized sets of tubes that move water and nutrients through their bodies. These tissues are composed of vascular bundles – clusters of cells that conduct water through the stem. How vascular bundles are arranged in fern stems varies substantially. Some have as many as three to eight or more vascular bundles scattered throughout their stem. Some are arranged symmetrically, while others such as the tobacco fern – Mickelia nicotianifolia – have bundles arranged in a whimsical, smiley-face pattern.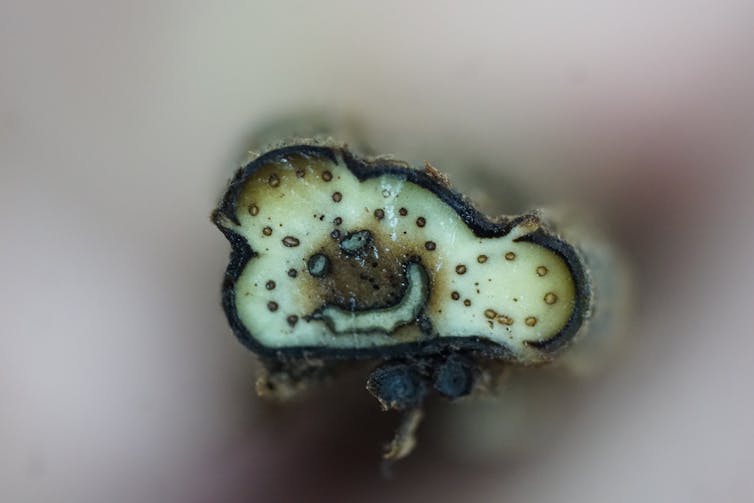
Simple observations and insights into evolution
I wondered how this variation in the number and arrangement of vascular bundles relates to leaf placement around the stem. So I quantified this variation in vascular patterning for 27 ferns representing roughly 30% of all fern species. I found a striking correlation between the number of rows of leaves and the number of vascular bundles within the stem. This relationship was almost 1-to-1 in some cases. For instance, if there were three rows of leaves along the stem, there were three vascular bundles in the stem. What’s more, how leaves were arranged around the stem determined the spatial arrangement of bundles. If the leaves were arranged spirally (on all sides of the stem), the vascular bundles were arranged in a radial pattern. If the leaves were shifted to the dorsal side of the stem, the smiley-face pattern emerged. Importantly, based on our understanding of plant development, there was a directionality here. Specifically, the placement of leaves determines the arrangement of bundles, not the other way around.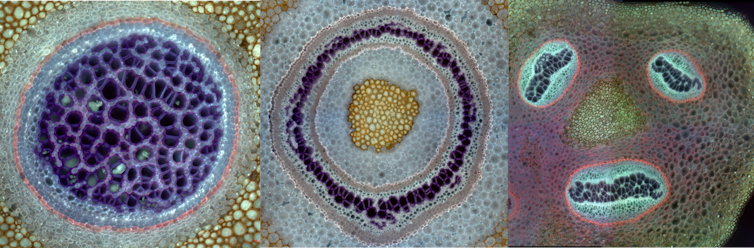
From parochial to existential
While this study on ferns and their vascular system may seem parochial, it speaks to the broader question of how variation – the fuel of evolution – arises, and how evolution can proceed. While not all parts of an organism are so tightly linked, considering the individual as a whole – or at least sets of parts as a unit – can help researchers better understand how, and if, observable patterns can evolve in isolation. This insight takes scientists one step closer to understanding the minutia of how evolution works to generate the immense biodiversity on Earth. Understanding these processes is also important for industry. In agricultural settings, plant and animal breeders attempt to increase one aspect of an organism without changing another. By taking a holistic approach and understanding which parts of an organism are developmentally or genetically linked and which are more quasi-independent, breeders may be able to more effectively create organisms with desired traits.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Science
Thousands of genomes reveal the wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA
wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA: New research analyzing 2,693 dog genomes reveals most modern dogs carry wolf DNA from ancient hybridization. Discover how wolf genes helped dogs survive and what this means for breeds from Chihuahuas to sled dogs.
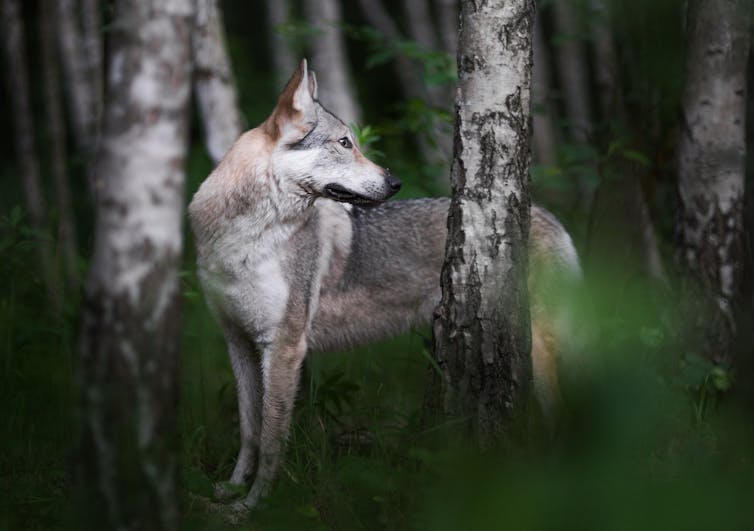

Thousands of genomes reveal the wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA
Audrey T. Lin, Smithsonian Institution and Logan Kistler, Smithsonian Institution Dogs were the first of any species that people domesticated, and they have been a constant part of human life for millennia. Domesticated species are the plants and animals that have evolved to live alongside humans, providing nearly all of our food and numerous other benefits. Dogs provide protection, hunting assistance, companionship, transportation and even wool for weaving blankets. Dogs evolved from gray wolves, but scientists debate exactly where, when and how many times dogs were domesticated. Ancient DNA evidence suggests that domestication happened twice, in eastern and western Eurasia, before the groups eventually mixed. That blended population was the ancestor of all dogs living today. Molecular clock analysis of the DNA from hundreds of modern and ancient dogs suggests they were domesticated between around 20,000 and 22,000 years ago, when large ice sheets covered much of Eurasia and North America. The first dog identified in the archaeological record is a 14,000-year-old pup found in Bonn-Oberkassel, Germany, but it can be difficult to tell based on bones whether an animal was an early domestic dog or a wild wolf. Despite the shared history of dogs and wolves, scientists have long thought these two species rarely mated and gave birth to hybrid offspring. As an evolutionary biologist and a molecular anthropologist who study domestic plants and animals, we wanted to take a new look at whether dog-wolf hybridization has really been all that uncommon.Little interbreeding in the wild
Dogs are not exactly descended from modern wolves. Rather, dogs and wolves living today both derive from a shared ancient wolf population that lived alongside woolly mammoths and cave bears. In most domesticated species, there are often clear, documented patterns of gene flow between the animals that live alongside humans and their wild counterparts. Where wild and domesticated animals’ habitats overlap, they can breed with each other to produce hybrid offspring. In these cases, the genes from wild animals are folded into the genetic variation of the domesticated population. For example, pigs were domesticated in the Near East over 10,000 years ago. But when early farmers brought them to Europe, they hybridized so frequently with local wild boar that almost all of their Near Eastern DNA was replaced. Similar patterns can be seen in the endangered wild Anatolian and Cypriot mouflon that researchers have found to have high proportions of domestic sheep DNA in their genomes. It’s more common than not to find evidence of wild and domesticated animals interbreeding through time and sharing genetic material. That wolves and dogs wouldn’t show that typical pattern is surprising, since they live in overlapping ranges and can freely interbreed. Dog and wolf behavior are completely different, though, with wolves generally organized around a family pack structure and dogs reliant on humans. When hybridization does occur, it tends to be when human activities – such as habitat encroachment and hunting – disrupt pack dynamics, leading female wolves to strike out on their own and breed with male dogs. People intentionally bred a few “wolf dog” hybrid types in the 20th century, but these are considered the exception.
Tiny but detectable wolf ancestry
To investigate how much gene flow there really has been between dogs and wolves after domestication, we analyzed 2,693 previously published genomes, making use of massive publicly available datasets. These included 146 ancient dogs and wolves covering about 100,000 years. We also looked at 1,872 modern dogs, including golden retrievers, Chihuahuas, malamutes, basenjis and other well-known breeds, plus more unusual breeds from around the world such as the Caucasian ovcharka and Swedish vallhund. Finally, we included genomes from about 300 “village dogs.” These are not pets but are free-living animals that are dependent on their close association with human environments. We traced the evolutionary histories of all of these canids by looking at maternal lineages via their mitochondrial genomes and paternal lineages via their Y chromosomes. We used highly sensitive computational methods to dive into the dogs’ and wolves’ nuclear genomes – that is, the genetic material contained in their cells’ nuclei. We found the presence of wild wolf genes in most dog genomes and the presence of dog genes in about half of wild wolf genomes. The sign of the wolf was small but it was there, in the form of tiny, almost imperceptible chunks of continuous wolf DNA in dogs’ chromosomes. About two-thirds of breed dogs in our sample had wolf genes from crossbreeding that took place roughly 800 generations ago, on average. While our results showed that larger, working dogs – such as sled dogs and large guardian dogs that protect livestock – generally have more wolf ancestry, the patterns aren’t universal. Some massive breeds such as the St. Bernard completely lack wolf DNA, but the tiny Chihuahua retains detectable wolf ancestry at 0.2% of its genome. Terriers and scent hounds typically fall at the low end of the spectrum for wolf genes.
The intertwining of dogs and wolves
Because dogs evolved from wolves, all of dogs’ DNA is originally wolf DNA. So when we’re talking about the small pieces of wolf DNA in dog genomes, we’re not referring to that original wolf gene pool that’s been kicking around over the past 20,000 years, but rather evidence for dogs and wolves continuing to interbreed much later in time. A wolf-dog hybrid with one of each kind of parent would carry 50% dog and 50% wolf DNA. If that hybrid then lived and mated with dogs, its offspring would be 25% wolf, and so on, until we see only small snippets of wolf DNA present. The situation is similar to one in human genomes: Neanderthals and humans share a common ancestor around half a million years ago. However, Neanderthals and our species, Homo sapiens, also overlapped and interbred in Eurasia as recently as a few thousand generations ago, shortly before Neanderthals disappeared. Scientists can spot the small pieces of Neanderthal DNA in most living humans in the same way we can see wolf genes within most dogs.
