Iza Lyson/500px Prime via Getty Images
Thousands of genomes reveal the wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA
Audrey T. Lin, Smithsonian Institution and Logan Kistler, Smithsonian Institution
Dogs were the first of any species that people domesticated, and they have been a constant part of human life for millennia. Domesticated species are the plants and animals that have evolved to live alongside humans, providing nearly all of our food and numerous other benefits. Dogs provide protection, hunting assistance, companionship, transportation and even wool for weaving blankets.
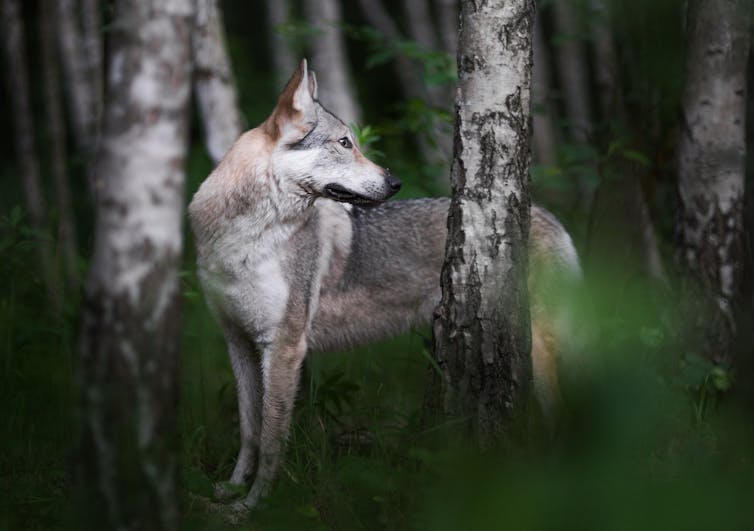
Dogs evolved from gray wolves, but scientists debate exactly where, when and how many times dogs were domesticated. Ancient DNA evidence suggests that domestication happened twice, in eastern and western Eurasia, before the groups eventually mixed. That blended population was the ancestor of all dogs living today.
Molecular clock analysis of the DNA from hundreds of modern and ancient dogs suggests they were domesticated between around 20,000 and 22,000 years ago, when large ice sheets covered much of Eurasia and North America. The first dog identified in the archaeological record is a 14,000-year-old pup found in Bonn-Oberkassel, Germany, but it can be difficult to tell based on bones whether an animal was an early domestic dog or a wild wolf.
Despite the shared history of dogs and wolves, scientists have long thought these two species rarely mated and gave birth to hybrid offspring. As an evolutionary biologist and a molecular anthropologist who study domestic plants and animals, we wanted to take a new look at whether dog-wolf hybridization has really been all that uncommon.
Little interbreeding in the wild
Dogs are not exactly descended from modern wolves. Rather, dogs and wolves living today both derive from a shared ancient wolf population that lived alongside woolly mammoths and cave bears.
In most domesticated species, there are often clear, documented patterns of gene flow between the animals that live alongside humans and their wild counterparts. Where wild and domesticated animals’ habitats overlap, they can breed with each other to produce hybrid offspring. In these cases, the genes from wild animals are folded into the genetic variation of the domesticated population.
For example, pigs were domesticated in the Near East over 10,000 years ago. But when early farmers brought them to Europe, they hybridized so frequently with local wild boar that almost all of their Near Eastern DNA was replaced. Similar patterns can be seen in the endangered wild Anatolian and Cypriot mouflon that researchers have found to have high proportions of domestic sheep DNA in their genomes. It’s more common than not to find evidence of wild and domesticated animals interbreeding through time and sharing genetic material.
That wolves and dogs wouldn’t show that typical pattern is surprising, since they live in overlapping ranges and can freely interbreed.
Dog and wolf behavior are completely different, though, with wolves generally organized around a family pack structure and dogs reliant on humans. When hybridization does occur, it tends to be when human activities – such as habitat encroachment and hunting – disrupt pack dynamics, leading female wolves to strike out on their own and breed with male dogs. People intentionally bred a few “wolf dog” hybrid types in the 20th century, but these are considered the exception.
Audrey Lin
Tiny but detectable wolf ancestry
To investigate how much gene flow there really has been between dogs and wolves after domestication, we analyzed 2,693 previously published genomes, making use of massive publicly available datasets.
These included 146 ancient dogs and wolves covering about 100,000 years. We also looked at 1,872 modern dogs, including golden retrievers, Chihuahuas, malamutes, basenjis and other well-known breeds, plus more unusual breeds from around the world such as the Caucasian ovcharka and Swedish vallhund.
Finally, we included genomes from about 300 “village dogs.” These are not pets but are free-living animals that are dependent on their close association with human environments.
We traced the evolutionary histories of all of these canids by looking at maternal lineages via their mitochondrial genomes and paternal lineages via their Y chromosomes. We used highly sensitive computational methods to dive into the dogs’ and wolves’ nuclear genomes – that is, the genetic material contained in their cells’ nuclei.
We found the presence of wild wolf genes in most dog genomes and the presence of dog genes in about half of wild wolf genomes. The sign of the wolf was small but it was there, in the form of tiny, almost imperceptible chunks of continuous wolf DNA in dogs’ chromosomes. About two-thirds of breed dogs in our sample had wolf genes from crossbreeding that took place roughly 800 generations ago, on average.
While our results showed that larger, working dogs – such as sled dogs and large guardian dogs that protect livestock – generally have more wolf ancestry, the patterns aren’t universal. Some massive breeds such as the St. Bernard completely lack wolf DNA, but the tiny Chihuahua retains detectable wolf ancestry at 0.2% of its genome. Terriers and scent hounds typically fall at the low end of the spectrum for wolf genes.
Alexkom000/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY
We were surprised that every single village dog we tested had pieces of wolf DNA in their genomes. Why would this be the case? Village dogs are free-living animals that make up about half the world’s dogs. Their lives can be tough, with short life expectancy and high infant mortality. Village dogs are also associated with pathogenic diseases, including rabies and canine distemper, making them a public health concern.
More often than predicted by chance, the stretches of wolf DNA we found in village dog genomes contained genes related to olfactory receptors. We imagine that olfactory abilities influenced by wolf genes may have helped these free-living dogs survive in harsh, volatile environments.
The intertwining of dogs and wolves
Because dogs evolved from wolves, all of dogs’ DNA is originally wolf DNA. So when we’re talking about the small pieces of wolf DNA in dog genomes, we’re not referring to that original wolf gene pool that’s been kicking around over the past 20,000 years, but rather evidence for dogs and wolves continuing to interbreed much later in time.
A wolf-dog hybrid with one of each kind of parent would carry 50% dog and 50% wolf DNA. If that hybrid then lived and mated with dogs, its offspring would be 25% wolf, and so on, until we see only small snippets of wolf DNA present.
The situation is similar to one in human genomes: Neanderthals and humans share a common ancestor around half a million years ago. However, Neanderthals and our species, Homo sapiens, also overlapped and interbred in Eurasia as recently as a few thousand generations ago, shortly before Neanderthals disappeared. Scientists can spot the small pieces of Neanderthal DNA in most living humans in the same way we can see wolf genes within most dogs.
Westend61 via Getty Images
Our study updates the previously held belief that hybridization between dogs and wolves is rare; interactions between these two species do have visible genetic traces. Hybridization with free-roaming dogs is considered a threat to conservation efforts of endangered wolves, including Iberian, Italian and Himalayan wolves. However, there also is evidence that dog-wolf mixing might confer genetic advantages to wolves as they adapt to environments that are increasingly shaped by humans.
Though dogs evolved as human companions, wolves have served as their genetic lifeline. When dogs encountered evolutionary challenges such as how to survive harsh climates, scavenge for food in the streets or guard livestock, it appears they’ve been able to tap into wolf ancestry as part of their evolutionary survival kit.![]()
Audrey T. Lin, Research Associate in Anthropology, Smithsonian Institution and Logan Kistler, Curator of Archaeobotany and Archaeogenomics, National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.