child education
Prince George County Families Meet Independent Schools at School Choice Fair
Last Updated on July 27, 2024 by Daily News Staff
Private school fair to feature STEM carnival, workshops for families
PRINCE GEORGE COUNTY, Md. /PRNewswire/ — Families are invited to explore more than 40 independent school options at Prince George County’s first School Choice Week fair on Saturday, Jan. 21. The inaugural event will be jam-packed with resources and fun, from workshops for parents on admissions and financial aid to face painting and a STEM Carnival for children.
Hosted by the Black Student Fund and Prince George Parents Alliance for Educational Options, the free fair takes place 11 a.m. to 3 p.m. at Bishop McNamara High School. Families will have an opportunity to speak with school representatives, network, and learn about K-12 education options in a positive, supportive environment. While parents “shop” for schools, children can enjoy family-friendly activities and entertainment.
Award-winning influencer Jenny the Voice will be in attendance, covering the event for her 1.2 million followers on TikTok.
The fair is planned to coincide with the celebration of National School Choice Week (Jan. 22-28, 2023), which will feature tens of thousands of school choice celebrations across all 50 states.
“This in person and virtual event will provide Maryland families with information that makes school choice a reality,” said Leroy Nesbitt of the Black Student Fund.
This event is planned by the Black Student Fund, which serves as an advocate for children and strives to assure that all students and their families have equal access to superior educational opportunities, and Prince George Parents Alliance for Educational Options, a not-for-profit organization dedicated to maximizing independent school options and opportunities for all families in Prince George’s County Maryland.
Bishop McNamara High School is located at 6800 Marlboro Pike in Forestville. Register for the free event at eventbrite.com/e/pg-school-choice-fair-2023-tickets-428637435107. A list of participating schools can be found at pgpaeo.org/participating-schools.
National School Choice Week (NSCW) informs, inspires, and empowers parents to discover the K-12 education options available for their children, including traditional public, charter, magnet, online, private, and home schooling. Every January, tens of thousands of schools, organizations, and individuals plan unique events and activities to shine a positive spotlight on effective education options in their communities. The Week is a project of the nonpartisan, nonpolitical National School Choice Awareness Foundation.
SOURCE National School Choice Week
Our Lifestyle section on STM Daily News is a hub of inspiration and practical information, offering a range of articles that touch on various aspects of daily life. From tips on family finances to guides for maintaining health and wellness, we strive to empower our readers with knowledge and resources to enhance their lifestyles. Whether you’re seeking outdoor activity ideas, fashion trends, or travel recommendations, our lifestyle section has got you covered. Visit us today at https://stmdailynews.com/category/lifestyle/ and embark on a journey of discovery and self-improvement.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Entertainment
Smart Gaming: How Parents Can Keep Kids Safe Online
Parents can enhance kids’ safety during online gaming by using privacy settings, researching games, enabling age checks, keeping personal information private, and utilizing parental controls and security tools.
Last Updated on January 21, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Smart Gaming: How Parents Can Keep Kids Safe Online
(Family Features) Playing video games can be a fun, social experience. However, online gaming also poses real risks, especially for kids. As a parent, you don’t necessarily need to be a gamer yourself to help keep your children safe when the controller is in their hands.
Consider taking proactive steps like these to create a healthy online gaming environment for kids of all ages.
Check System Privacy Settings
As a first line of defense – before your child even starts gaming – spend some time in the device or console privacy settings. Here you can turn off sharing, disable location tracking, limit microphone and camera access and restrict how other users can interact with your child’s profile. Similarly, many games and platforms include built-in privacy settings that can be tailored to your child’s age and online experience. These settings may allow you to limit who can view your child’s profile or send a friend request, message or voice chat.
Research Games
Because not all games are created equal, look up game ratings through a service such as ESRB before buying or downloading to understand the maturity level of the game and determine if it’s appropriate for your child. To take it a step further, read reviews from other parents or watch gameplay videos to see if you deem not only the content but also the social interaction acceptable.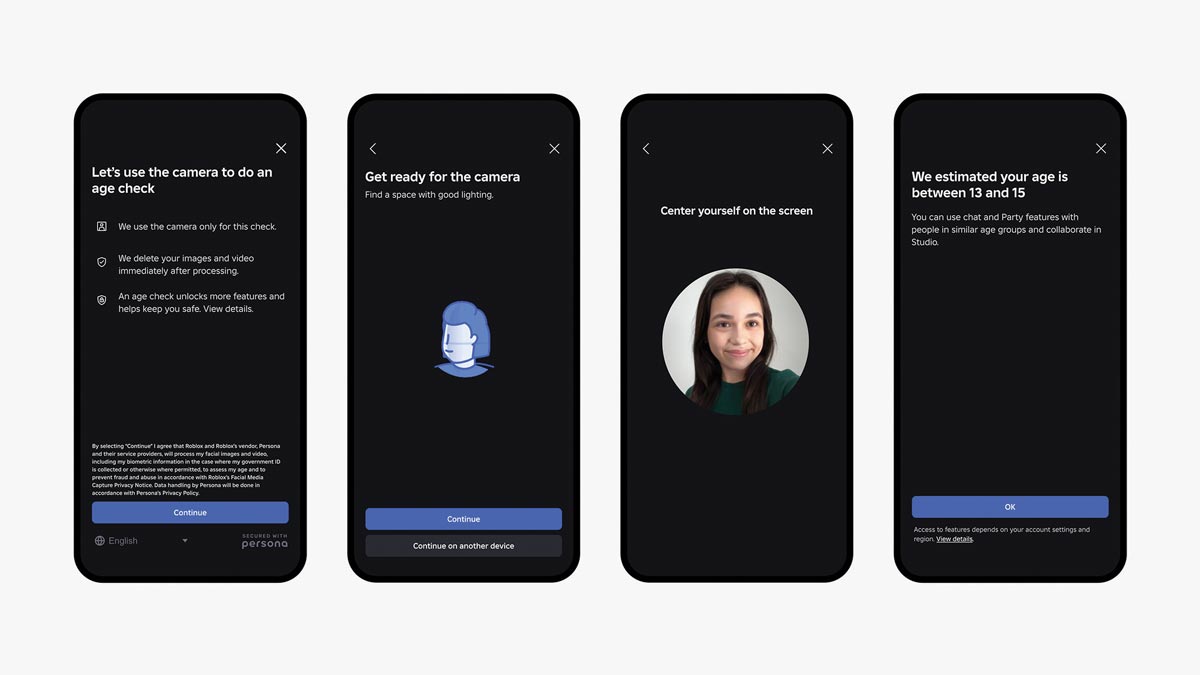
Use Facial Age Estimation
Online platforms are increasingly looking for ways to keep users safe, and that includes added levels of verification. As part of a multilayered approach to safety, Roblox is the first online gaming platform to require age checks for users of all ages to access chat features, enabling age-appropriate communication and limiting conversations between adults and minors. These secure age checks are designed to be fast, easy and secure using Facial Age Estimation technology directly within the app.
“Our commitment to safety is rooted in delivering the highest level of protection for our users,” said Matt Kaufman, chief safety officer at Roblox. “By building proactive, age-based barriers, we can empower users to create and connect in ways that are both safe and appropriate.”
Once age-checked, users are assigned to one of six age groups: under 9, 9-12, 13-15, 16-17, 18-20 or 21 and older, ensuring conversations are safe and age appropriate. Age checks are optional; however, features like chat will not be accessible unless an age check is completed. Chat is also turned off by default for children under age 9, unless a parent provides consent after an age check.
Keep Personal Information Private
It’s seldom a bad idea to be extra cautious when interacting with strangers online, even if they seem friendly enough while playing the game. Teach children what information not to share, including their full name, address, birthday, school name, phone number, email address, passwords or any photos that may contain any personal information (like a house number or school logo) in the background. Also encourage a screen name and generic avatar for added privacy.
Turn on Parental Controls
Designed to allow parents a supervisory role in their child’s online gaming experience, parental controls on many platforms include the ability to set schedules and limit playtime, restrict access to certain content or social features, require a password for purchases or set a spending limit.
Avoid Clicking Unfamiliar Links
Player profiles and in-game chats may include links to external sites, including those promising rewards or cheat codes. Because they can be used to gain access to personal information, remind your children to ask an adult before clicking any unfamiliar links while gaming so they can be verified as trustworthy.
Employ Privacy and Security Tools
While system or console-specific settings allow parents to set content restrictions, approve downloads, manage friends lists and more, additional layers of security are sometimes necessary. Extra safeguards such as antivirus and internet security software, DNS (domain name system) filtering and two-factor authentication can also be enabled to help keep kids safe online.
For more tools to help parents make informed decisions and support their children’s gaming experience, visit corp.roblox.com/safety.
Photo courtesy of Shutterstock (father and daughter playing video game)
SOURCE:
Roblox
Our Lifestyle section on STM Daily News is a hub of inspiration and practical information, offering a range of articles that touch on various aspects of daily life. From tips on family finances to guides for maintaining health and wellness, we strive to empower our readers with knowledge and resources to enhance their lifestyles. Whether you’re seeking outdoor activity ideas, fashion trends, or travel recommendations, our lifestyle section has got you covered. Visit us today at https://stmdailynews.com/category/lifestyle/ and embark on a journey of discovery and self-improvement.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lifestyle
Preparing Students for What’s Next in Work
Preparing Students: Automation, AI and societal economic changes are affecting the workforce and making a significant impact on the employment prospects of future generations. Consider this guidance to put students on the path toward greater earning potential and economic mobility in a rapidly changing economy.

Preparing Students for What’s Next in Work
(Family Features) Automation, AI and societal economic changes are affecting the workforce and making a significant impact on the employment prospects of future generations. More than one-third of today’s college graduates are “underemployed,” meaning they work jobs that don’t require a college degree and may pay less than a living wage, according to data from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. At the same time, a World Economic Forum report explored how advances in AI are threatening to negatively impact access to entry-level and even mid-level jobs for millions of Americans. Looking ahead, research by Georgetown University indicates that by 2031, 70% of jobs will require education or training beyond high school. However, data from the National Center for Education Statistics indicate only one-third of high school graduates go on to complete a college degree with many of those being in fields that are not in high-earning, high-growth professions. These challenges are not lost on today’s students. In a survey by Junior Achievement and Citizens, 57% of teens reported AI has negatively impacted their career outlook, raising concerns about job replacement and the need for new skills. What’s more, a strong majority (87%) expect to earn extra income through side hustles, gig work or social media content creation. “To put students on the path toward greater earning potential and economic mobility in a rapidly changing economy, students need proactive education and exposure to transferable skills and competencies, such as creative and critical thinking, financial literacy, problem-solving, collaboration and career planning,” said Jack Harris, CEO, Junior Achievement. This assertion is consistent with findings from the Camber Collective. This social impact consulting group identified four key life experiences students can consider and explore that positively affect lifetime earnings, including:- Completing secondary education
- Graduating with a degree in a high-paying field of study
- Receiving mentorship during adolescence
- Obtaining a first full-time job with opportunity for advancement
- Learning opportunities that are designed with the future in mind. For example, learning experiences offered through Junior Achievement reflect the skills and competencies needed to promote economic mobility.
- Internships or apprenticeships that provide hands-on experience and exposure to a career field that can’t be found in a textbook.
- Volunteer or extracurricular roles that develop communication and leadership skills. Virtually every career field requires these soft skills for growth and greater earning potential.
- Relationships that provide insight and connection. Networking with individuals who are already excelling in a chosen field, as well as peers who share similar aspirations, offers perspective from those who are where you wish to be and potentially opens future doors for employment.
- Courses that offer introductory insight into a chosen career path. Local trade or technical schools and other training organizations may even offer certifications that align with a student’s area of interest.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Blog
The Substitute Teacher Who Wanted Blueprints of Our House
A fifth-grade assignment took a strange turn when a substitute teacher asked students to draw schematics of their homes. What followed — a wildly fictional floor plan and a priceless reaction from my mom — turned into one of my funniest childhood memories.
Last Updated on December 8, 2025 by Daily News Staff
The Substitute Teacher Who Wanted Blueprints of Our House
Elementary school memories tend to blend together — cafeteria pizza, playground arguments, the eternal struggle of times tables — but every once in a while, something happens that sticks with you for life. For me, that moment came in the fifth grade during a week when our regular teacher was out, and we cycled through substitute teachers like we were testing models for durability. By midweek, in walked a substitute with a mysterious, slightly intense energy — the kind of vibe that suggested he either meditated at dawn or worked a graveyard shift doing something he couldn’t talk about. We settled into our seats, expecting worksheets or quiet reading time. But nope. He had other plans. “Today,” he announced, “we’re going to draw schematics of our houses.” Schematics. Not drawings. Not little houses with smoke coming out of the chimney. Actual blueprint-style schematics. He wanted the layout of our bedrooms, our parents’ rooms, and where the pets slept. Every detail. Now, to be fair, Highlights Magazine did have a feature that month teaching kids how to draw floor plans. So maybe he was just a bit overenthusiastic about cross-curricular learning. Or maybe — and this is my completely rhetorical adult theory — he worked the graveyard shift as a cat burglar gathering intel between heists. Just moonlighting between blueprints. While the rest of the class tried their best to recreate their actual homes, my imagination sprinted in a totally different direction. The house I drew had:- A massive master bedroom with an oversized bathroom for my parents
- Separate bedrooms for us kids on the opposite side of the house
- A kitchen placed right in the center like a command center
- And the dog — the true VIP — had a luxurious two-story doghouse
Enjoy this story?
Check out more nostalgic and humorous stories on STM Daily News and be sure to sign up for our newsletter!Our Lifestyle section on STM Daily News is a hub of inspiration and practical information, offering a range of articles that touch on various aspects of daily life. From tips on family finances to guides for maintaining health and wellness, we strive to empower our readers with knowledge and resources to enhance their lifestyles. Whether you’re seeking outdoor activity ideas, fashion trends, or travel recommendations, our lifestyle section has got you covered. Visit us today at https://stmdailynews.com/category/lifestyle/ and embark on a journey of discovery and self-improvement.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
