The Knowledge
How to avoid seeing disturbing video on social media and protect your peace of mind
How to avoid seeing disturbing video on social media and protect your peace of mind
Last Updated on February 4, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Annie Margaret, University of Colorado Boulder
How to avoid seeing disturbing video on social media and protect your peace of mind
When graphic videos like those of the recent shooting of a protester by federal agents in Minneapolis go viral, it can feel impossible to protect yourself from seeing things you did not consent to see. But there are steps you can take.
Social media platforms are designed to maximize engagement, not protect your peace of mind. The major platforms have also reduced their content moderation efforts over the past year or so. That means upsetting content can reach you even when you never chose to watch it.
You do not have to watch every piece of content that crosses your screen, however. Protecting your own mental state is not avoidance or denial. As a researcher who studies ways to counteract the negative effects of social media on mental health and well-being, I believe it’s a way of safeguarding the bandwidth you need to stay engaged, compassionate and effective.
Why this matters
Research shows that repeated exposure to violent or disturbing media can increase stress, heighten anxiety and contribute to feelings of helplessness. These effects are not just short-term. Over time, they erode the emotional resources you rely on to care for yourself and others.
Protecting your attention is a form of care. Liberating your attention from harmful content is not withdrawal. It is reclaiming your most powerful creative force: your consciousness.
Just as with food, not everything on the table is meant to be eaten. You wouldn’t eat something spoiled or toxic simply because it was served to you. In the same way, not every piece of media laid out in your feed deserves your attention. Choosing what to consume is a matter of health.
And while you can choose what you keep in your own kitchen cabinets, you often have less control over what shows up in your feeds. That is why it helps to take intentional steps to filter, block and set boundaries.
Practical steps you can take
Fortunately, there are straightforward ways to reduce your chances of being confronted with violent or disturbing videos. Here are four that I recommend:
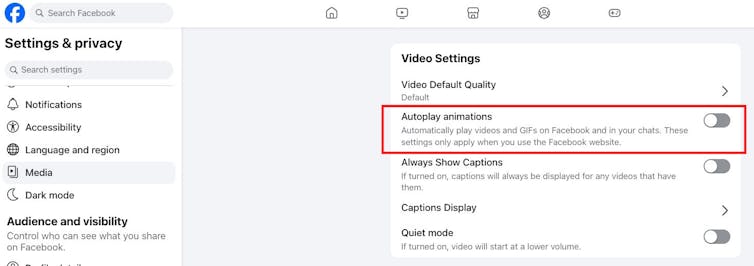
- Turn off autoplay or limit sensitive content. Note that these settings can vary depending on device, operating system and app version, and can change.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/d1deR/2
- Use keyword filters. Most platforms allow you to mute or block specific words, phrases or hashtags. This reduces the chance that graphic or violent content slips into your feed.
- Curate your feed. Unfollow accounts that regularly share disturbing images. Follow accounts that bring you knowledge, connection or joy instead.
- Set boundaries. Reserve phone-free time during meals or before bed. Research shows that intentional breaks reduce stress and improve well-being.
Reclaim your agency
Social media is not neutral. Its algorithms are engineered to hold your attention, even when that means amplifying harmful or sensational material. Watching passively only serves the interests of the social media companies. Choosing to protect your attention is a way to reclaim your agency.
The urge to follow along in real time can be strong, especially during crises. But choosing not to watch every disturbing image is not neglect; it is self-preservation. Looking away protects your ability to act with purpose. When your attention is hijacked, your energy goes into shock and outrage. When your attention is steady, you can choose where to invest it.
You are not powerless. Every boundary you set – whether it is turning off autoplay, filtering content or curating your feed – is a way of taking control over what enters your mind. These actions are the foundation for being able to connect with others, help people and work for meaningful change.
More resources
I’m the executive director of the Post-Internet Project, a nonprofit dedicated to helping people navigate the psychological and social challenges of life online. With my team, I designed the evidence-backed PRISM intervention to help people manage their social media use.
Our research-based program emphasizes agency, intention and values alignment as the keys to developing healthier patterns of media consumption. You can try the PRISM process for yourself with an online class I launched through Coursera in October 2025. You can find the course, Values Aligned Media Consumption, on Coursera. The course is aimed at anyone 18 and over, and the videos are free to watch.
This story was updated on Jan. 25, 2026 to include reference to the recent shooting in Minneapolis.
Annie Margaret, Teaching Assistant Professor of Creative Technology & Design, ATLAS Institute, University of Colorado Boulder
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
📺 From Cable to Clicks: How Public Access TV Paved the Way for Social Media
Last Updated on March 11, 2026 by Daily News Staff
“From Public Access to Social Media.” Image: AI
Before there were influencers, viral videos, and billion-view platforms, there was something raw, real, and radically democratic: public access television.
Born in the 1970s, public access TV was one of the first true experiments in community-driven media. And while it may seem like a relic of the analog past, its legacy is alive and well every time someone hits “post” on YouTube, TikTok, or Instagram.
🎤 What Was Public Access Television?
Public access television was part of the “PEG” system—Public, Educational, and Government access channels—mandated by the FCC and local cable providers to serve community needs. The public access arm gave everyday people a platform to create and share their own content, often with free or low-cost equipment provided by local studios.
There were no ads, no executives, and no creative restrictions (aside from legal limitations). Programming ranged from the bizarre to the brilliant—local news, activist messages, drag performances, punk rock shows, religious rants, DIY cooking series, and more. If you had something to say and the courage to get in front of a camera, you could be on the air.
Scrappy, campy and unabashedly queer, public access TV series of the 1980s and 1990s offered a rare glimpse into LGBTQ+ life
🧪 Experimental, Inclusive, and Sometimes Outrageous
Public access TV wasn’t polished. It wasn’t corporate. It wasn’t predictable. And that was exactly the point.
It empowered:
Marginalized voices who couldn’t get airtime elsewhere. Aspiring creatives looking to test out new formats. Communities wanting to share local culture, ideas, and events.
In many ways, it was an open sandbox where media could be weird, wild, and wonderfully honest.
🌐 The Bridge to Social Media
Today, anyone with a smartphone can start a channel, build an audience, or go viral. But the foundation was laid decades earlier by public access.
Public Access TV
Modern Social Media
Community studios
Smartphones, apps, home setups
Broadcast on local cable channels
Global reach via internet
No advertising
Monetized, ad-supported
Free expression, limited censorship
Still a battleground for free speech
Niche, quirky content
Same—just with algorithms
The spirit of user-generated content—amateur, authentic, and accessible—is deeply rooted in the public access ethos. Creators like early YouTubers and digital activists have often cited public access as an inspiration.
🔄 A Full Circle Moment
Today’s digital platforms have expanded the reach and speed of content creation, but they also reintroduce challenges public access once bypassed—like algorithmic bias, platform censorship, and commercialization.
Ironically, as tech giants dominate digital communication, the original values of public access—local control, equal access, and creative freedom—are more relevant than ever.
🧠 Final Thought
Public access television may have existed before likes, shares, or subscribers—but it’s the ancestor of everything we now take for granted in social media. It showed us that the best stories don’t always come from studios, and the most important voices don’t always have a microphone—until they make one.
So next time you scroll through a creator’s feed or stumble on a strange but delightful video, remember:
📼 Public access walked so the internet could run
Related Links:
Public Access Television (Wikipedia): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public-access_television
Cable Communications Policy Act of 1984 (Wikipedia) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cable_Communications_Policy_Act_of_1984
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
How Water Towers Work: The Simple System That Keeps Water Flowing in American Cities
Learn how water towers work in the United States, why they are so tall, and how gravity helps cities maintain water pressure and emergency water supplies.

How Water Towers Work
Water towers are one of the most recognizable pieces of infrastructure across the United States. Rising above towns, suburbs, and cities, these elevated tanks quietly perform a vital function every day: maintaining water pressure and storing emergency water for local communities.
Although they may look simple, water towers are an essential part of modern municipal water systems and remain one of the most reliable ways to deliver water to homes and businesses.
The Basic Science Behind Water Towers
Water towers work using a simple principle of physics: gravity.
Water from treatment plants or underground wells is pumped into a storage tank located high above the ground—typically between 100 and 200 feet tall. Because the tank is elevated, gravity naturally pushes the water downward through the city’s pipeline network.
This gravitational force creates the water pressure needed to supply homes, businesses, irrigation systems, and fire hydrants throughout the community.
Most residential plumbing systems in the United States operate best at 40 to 60 PSI (pounds per square inch), which water towers can easily provide through elevation alone.
Why Water Towers Are Built So Tall
The height of a water tower determines how much pressure it can create. Engineers use a common rule:
For example, a water tower standing 120 feet tall can generate roughly 50 PSI of pressure—perfect for delivering water throughout a residential neighborhood.
Why Cities Still Use Water Towers
While modern pumping systems could theoretically move water through pipes continuously, water towers provide several major advantages that make them a preferred design in many municipal systems.
- Stable Water Pressure – Water towers maintain consistent pressure even during peak usage times.
- Energy Efficiency – Pumps can refill towers overnight when electricity demand is lower.
- Emergency Water Supply – If power fails, gravity can continue delivering water.
- Fire Protection – Fire hydrants depend on strong, immediate water pressure.
The Daily Fill-and-Use Cycle
Water towers typically operate on a daily cycle based on community demand.
- Night: Pumps refill the tower while water demand is low.
- Morning: Water levels drop as residents shower and prepare for the day.
- Daytime: Businesses and homes continue drawing water from the tower.
- Evening: The system begins refilling the tank for the next day.
How Much Water Can a Tower Store?
Water towers come in many sizes depending on the population they serve.
- Small towns: 50,000–300,000 gallons
- Suburban communities: 500,000–1 million gallons
- Larger urban systems: up to 2 million gallons or more
Even a single tower holding one million gallons can supply thousands of homes for several hours during peak demand or emergencies.
Modern Technology Inside Water Towers
Today’s water towers are equipped with advanced monitoring systems that help utilities maintain safe and reliable water supplies.
- Digital water level sensors
- Automated pump controls
- Water quality monitoring
- Protective interior coatings
- Regular inspections and maintenance
Landmarks in the American Skyline
Many cities turn their water towers into local landmarks by painting them with city names, mascots, or community slogans. Some towns even design towers shaped like giant objects such as fruit, coffee cups, or sports balls.
Despite their distinctive appearance, water towers remain one of the simplest and most reliable engineering solutions for delivering clean water to millions of Americans every day.
Next time you see a water tower rising above a town skyline, remember: it’s not just a landmark—it’s the gravity-powered system that keeps water flowing.
Related External Coverage
For more information about how water towers and municipal water systems work, explore the following resources:
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency – Drinking Water Regulations
- American Water Works Association – Water Storage and Water Towers
- HowStuffWorks – How Water Distribution Systems Work
- U.S. Geological Survey – Drinking Water and Groundwater Basics
- U.S. Department of Energy – How Water Towers Work
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
unknown
The Unfavorable Semicircle Mystery: The YouTube Channel That Uploaded Tens of Thousands of Cryptic Videos
In 2015, the YouTube channel Unfavorable Semicircle gained attention for its enigmatic and abundant video uploads, totaling over 70,000 before its deletion in 2016. Theories about its purpose vary, from automated content generation to digital art experimentation, leaving its intent unresolved.

In the vast digital landscape of the internet, strange phenomena occasionally emerge that leave investigators, tech enthusiasts, and everyday viewers scratching their heads. One of the most puzzling cases appeared in 2015, when a mysterious YouTube channel called Unfavorable Semicircle began uploading an astonishing number of cryptic videos.
Within months, the channel had published tens of thousands of bizarre clips, many of which seemed random, incomprehensible, and visually chaotic. But as internet detectives began analyzing the content more closely, they discovered that these videos might not have been random at all.
The Sudden Appearance of an Internet Mystery
The Unfavorable Semicircle channel reportedly appeared in March 2015, with its first uploads arriving in early April.
Almost immediately, the channel began publishing videos at an incredible pace. Observers estimated that the account uploaded thousands of videos per week, sometimes multiple videos per minute. By the time the channel disappeared in early 2016, researchers believed it had uploaded well over 70,000 videos, possibly far more.
The scale alone made the project seem impossible for a human to manage manually.
Strange Visuals and Cryptic Titles
Most of the videos shared similar characteristics:
- Extremely short or very long runtime
- Abstract visuals such as flashing colors, static, or distorted imagery
- Little or no audio, or heavily distorted sounds
- Titles made of random characters, symbols, or numbers
To casual viewers, the videos looked like pure digital noise. However, online investigators suspected something more deliberate was happening.
Hidden Images Discovered
The mystery deepened when researchers began extracting individual frames from some videos.
When thousands of frames from certain clips were stitched together, the results sometimes formed coherent images. One of the most famous examples involved a video titled “LOCK.” While the footage appeared chaotic at first, combining the frames revealed a recognizable composite image.
This discovery suggested the videos were carefully constructed rather than random uploads.
Theories About the Channel’s Purpose
Because the creator never explained the project, several theories emerged across Reddit, YouTube, and internet forums.
Automated Experiment
Many believe the channel was created using automated software that generated and uploaded content at scale.
Alternate Reality Game (ARG)
Some viewers suspected the channel might be part of a hidden puzzle or digital scavenger hunt.
Encrypted Communication
Others compared the channel to Cold War “numbers stations,” suggesting the videos could contain coded messages.
Digital Art Project
Another theory suggests the channel was an experimental art project exploring algorithms, data, and visual noise.
Despite years of investigation, no single explanation has been confirmed.
Why the Channel Disappeared
In February 2016, YouTube removed the channel, reportedly due to spam or automated activity violations.
By that time, the channel had already become a minor internet legend. Fortunately, some researchers managed to archive a large portion of the videos before they disappeared.
Even today, archived clips continue to circulate online as investigators attempt to decode them.
Other Mysterious YouTube Channels
The Unfavorable Semicircle mystery is not the only strange case on YouTube.
One well-known example is Webdriver Torso, a channel that uploaded hundreds of thousands of videos showing red and blue rectangles with simple beeping sounds. Internet speculation ran wild before Google eventually confirmed it was an internal YouTube testing account.
Another example is AETBX, which posts distorted visuals and unusual audio that some viewers believe contain hidden patterns or encoded information.
These cases highlight how automation, experimentation, and creativity can sometimes blur the line between technology and mystery.
A Digital Mystery That Remains Unsolved
Nearly a decade later, the true purpose behind Unfavorable Semicircle remains unknown.
Was it a sophisticated experiment? A piece of algorithmic art? Or simply an automated test that accidentally captured the internet’s imagination?
Whatever the explanation, the channel stands as a reminder that even in a world filled with billions of videos and endless information, the internet can still produce mysteries that challenge our understanding of technology.
Why Internet Mysteries Still Fascinate Us
Stories like Unfavorable Semicircle capture attention because they combine technology, creativity, and the unknown. They invite people from around the world to collaborate, analyze patterns, and search for meaning hidden in the noise.
And sometimes, the most intriguing part of the mystery is that the answer may never fully be known.
Related Coverage & Further Reading
- Atlas Obscura – The Unsettling Mystery of the Creepiest Channel on YouTube
- Her Campus – Top 5 Most Obscure Internet Mysteries
- Medium – Unfavorable Semicircle: The YouTube Mystery No One Can Solve
- Gazette Review – Top 10 Strangest YouTube Channels Ever
- Decoding the Unknown – Unfavorable Semicircle YouTube Mystery Archive
- Wikipedia – Unfavorable Semicircle
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
