
Child Health
Recognizing the Signs of Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency: How Early Recognition and Advocacy Helped One Family Find Answers
Diane Benke noticed her son Alex’s height concerns starting at age 7, despite his pediatrician’s reassurances. After persistent worries, they consulted an endocrinologist, leading to a diagnosis of Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency (PGHD). Following treatment changes, including a switch to weekly hormone injections, Alex’s growth improved, allowing the family to focus on their well-being.
Last Updated on February 5, 2026 by Daily News Staff
(Family Features) “Our concerns about Alex’s growth began around the age of 7,” said his mother, Diane Benke.
Though Alex measured around the 50th percentile for weight, his height consistently hovered around the 20th percentile. Benke’s instincts told her something wasn’t quite right.
“I kept asking our pediatrician if this could mean something more,” she said. “Each time, I was reassured that everything was fine. After all, I’m only 5 feet tall myself.”
At first, Benke tried setting her worries aside. Alex was one of the youngest in his class, and she wondered if he could simply be a “late bloomer.”
However, as Alex progressed through elementary school, particularly in the 4th and 6th grades, his height percentile dropped into the single digits. The height difference between Alex and his peers became impossible to ignore.
Despite Benke’s growing concerns, their pediatrician continued to assure them Alex was fine.
“We were told as long as he was making some progress on the growth chart, there was no need to worry,” she said, “but we were never actually shown the charts.”
It wasn’t until one of Benke’s friends confided that her own daughter had recently been diagnosed with Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency (PGHD) that she decided to seek an endocrinologist.
“Although it took several months to get an appointment,” Benke said, “we were determined to get more answers.”
Navigating the Diagnosis Process
Getting a diagnosis for many medical conditions can be a long journey. However, early detection and diagnosis of PGHD is important. It can help minimize the impact on overall health and support optimal growth.
Once Alex was seen by a pediatric endocrinologist, he underwent a series of evaluations, including bloodwork, a bone age X-ray to compare his chronological age with his skeletal age and a growth hormone stimulation test, which measures the body’s ability to produce growth hormone. He also had a brain MRI to rule out the potential of any pituitary abnormalities.
The results of these tests confirmed the diagnosis of PGHD, a rare condition that occurs when the pituitary gland does not produce enough growth hormone. PGHD affects an estimated 1 in 4,000-10,000 children.
Some common signs parents might notice include: their child being significantly shorter than other kids their age, slower growth rate over time, delayed puberty, reduced muscle strength or lower energy levels, slower bone development and delayed physical milestones.
“Receiving Alex’s diagnosis was a relief,” Benke said. “It provided clarity and a path forward.”
Moving Forward with Treatment
“While the diagnosis process was exhausting, starting treatment made the process worthwhile,” Benke said.
For decades, daily injections of a drug called somatropin, which is similar to the growth hormone your body produces, have been the standard of care for PGHD. It wasn’t until 2015 that the Growth Hormone Research Society recognized the need for a long-acting growth hormone (LAGH), offering once-weekly dosing as an alternative to daily injections.
Benke explained navigating the insurance approval process was another challenge.
“Our insurance required us to try a daily medication before approving a weekly option,” she said.
Alex spent three months on daily medication, often missing doses, before he was approved to switch to a weekly treatment option.
“The weekly option made such a positive impact,” Benke said. “We now have minimal disruptions to our daily routine and Alex hasn’t missed a single dose since.”
Beyond a more convenient dosing option, the change gave Benke peace of mind.
“We could focus more on being a family again, without the daily worries of his next dose,” she said.
If you’re concerned about your child’s growth, talk to their doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis is important, as treatment becomes less effective once a child’s bones stop growing.
Benke’s advice to other parents: “Trust your instincts. If something feels wrong, seek out a specialist and push for answers and don’t give up, even when faced with hurdles… Stay hopeful and persistent – it’s a journey worth fighting for.”
Visit GHDinKids.com to download a doctor discussion guide to help prepare for your next appointment.
SOURCE:
Skytrofa
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lifestyle
How to reduce gift-giving stress with your kids – a child psychologist’s tips for making magic and avoiding tears
Reduce gift-giving stress with kids: A child psychologist shares practical rules for stress-free gift giving with kids—how many gifts to give, what holds attention, and how to avoid holiday tears.
Last Updated on January 9, 2026 by Daily News Staff

Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
health and wellness
Texas cities have some of the highest preterm birth rates in the US, highlighting maternal health crisis nationwide
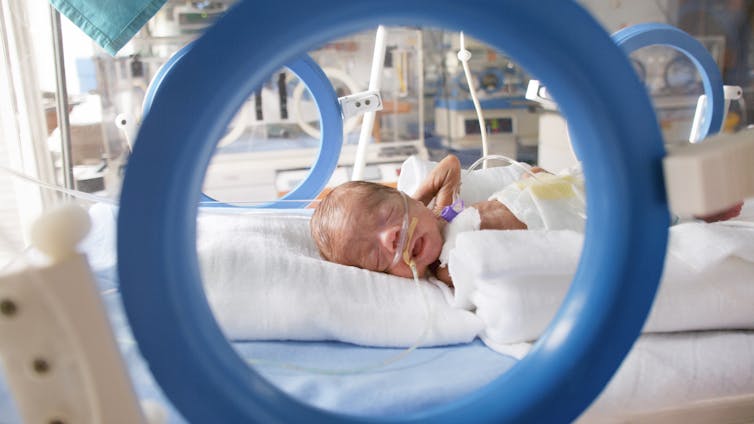
Texas cities have some of the highest preterm birth rates in the US, highlighting maternal health crisis nationwide
Revealing disparities that drive preterm birth rates
The March of Dimes report scored the U.S. overall a D+ grade on preterm birth rate at 10.4%, but states differ dramatically in their scores. New Hampshire, for example, scored an A- with 7.9% of infants born prematurely, while Mississippi, where 15% of infants are born prematurely, scored an F. Texas’ rates aren’t the worst in the country, but it scores notably worse than the national rate of 10.4%, with 11.1% of babies – 43,344 in total – born prematurely in 2024. And Texas has an especially large effect on the low national score because 10 of the 46 cities that receive a D or F grade – defined in the report as a rate higher than the national rate of 10.4% – are located there. In 2023, Texas had the highest number of such cities in the U.S. That may be in part because access to maternal care in Texas is so limited. Close to half of all counties across the state completely lack access to maternity care providers and birthing facilities, compared with one-third of counties across the U.S. Moreover, more counties in Texas are designated as health professional shortage areas, meaning they lack enough doctors for the number of people living in these areas. Shortages exist in 257 areas in Texas for primary care doctors, 149 for dentists and 251 for mental health providers. But even against the backdrop of geographic differences in health care access, the starkest contribution to the state’s preterm birth rates comes from ethnic and racial disparities. Mothers of non-Hispanic Black (14.7%), American Indian/Alaskan Native (12.5%), Pacific Islander (12.3%) and Hispanic (10.1%) descent have babies prematurely much more often than do mothers who are non-Hispanic white (9.5%) or Asian (9.1%). These numbers reflect the broader landscape of maternal health in the U.S. Although nationwide maternal mortality rates decreased from 22.3 to 18.6 deaths per 100,000 live births from 2022 to 2023, Black women died during pregnancy or within one year after childbirth at almost three times the rate (50.3%) of white (14.5%), Hispanic (12.4%) and Asian (10.7%) women.
Preterm birth in context
Having a baby early is not the normal or expected outcome during pregnancy. It occurs due to complex genetic and environmental factors, which are exacerbated by inadequate prenatal care. According to the World Health Organization, women should have eight or more doctor visits during their pregnancy. Without adequate and quality prenatal care, the chances of reversing the preterm birth trends are slim. Yet in Texas, unequal access to prenatal care remains a huge cause for concern. As the March of Dimes report documents, women of color in Texas receive adequate prenatal care at vastly lower rates than do white women – a fact that holds true in several other states as well. In addition, Texas has the highest uninsured rate in the nation, with 17% of women uninsured for health coverage, compared with a national average of 8%. Nationwide, public health experts, community advocates and families are calling for comprehensive health insurance to help cover the costs of prenatal care, particularly for low-income families that primarily rely on Medicaid for childbirth. Cuts to funding for the Affordable Care Act and Medicaid outlined in the 2025 Budget Reconciliation Act make it likely that more Americans will lose access to care or see their health care costs balloon. But state-level action may help reduce access barriers. In Texas, for example, a set of laws passed in 2025 may help improve access to care before, during and after pregnancy. Texas legislators funded initiatives targeted at workforce development in rural areas – particularly for obstetrician-gynecologists, emergency physicians and nurses, women’s preventive safety net programs, and maternal safety and quality improvement initiatives. Rising rates of chronic diseases, such as hypertension, obesity and diabetes, also contribute to women giving birth prematurely. While working with the state maternal mortality and morbidity review committee, my team and I found that cardiovascular conditions contributed to the 85 pregnancy-related deaths that occurred in 2020. An upward trend in obesity, diabetes and hypertension before pregnancy are pressing issues in the state, posing a serious threat to fetal and maternal health.Learning from other countries
These statistics are grim. But proven strategies to reduce these and other causes of maternal mortality and morbidity are available. In Australia, for instance, maternal deaths have significantly declined from 12.7 per 100,000 live births in the early 1970s to 5.3 per 100,000 between 2021 and 2022. The reduction can be linked to several medical interventions that are based on equitable, safe, woman-centered and evidence-based maternal health services. In Texas, some of my colleagues at Texas A&M University use an equitable, woman-centered approach to develop culturally competent care centered on educational health promotion, preventive health care and community services. Utilizing nurses and nonmedical support roles such as community health workers and doulas, my colleagues’ initiatives complement existing state efforts and close critical gaps in health care access for rural and low-income Texas families. Across the country, researchers are using similar models, including the use of doulas, to address the Black maternal health crisis. Research shows the use of doulas can improve access to care during pregnancy and childbirth, particularly for women of color.
It’s all hands on deck
There isn’t one, single risk factor that leads to a preterm birth, nor is there a universal approach to its prevention. Results from my work with Black mothers who had a preterm birth aligns with what other experts are saying: Addressing the maternal health crisis in the U.S. requires more than policy interventions. It involves the dismantling of system-level and policy-driven inequities that lead to high rates of preterm births and negative pregnancy and childbirth outcomes, particularly for women of color, through funding, research, policy changes and community voices. Although I had my preterm birth in Nigeria, my story and those shared by the Black mothers I have worked with in the U.S. show eerily similar underlying challenges across different settings. Kobi V. Ajayi, Research Assistant Professor of Maternal and Child Health, Texas A&M University This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lifestyle
It’s more than OK for kids to be bored − it’s good for them
A University of Michigan-Dearborn professor explains why boredom can benefit kids—supporting creativity, reflection, and emotional regulation—and why parents don’t need to “fix” it with screens.

It’s more than OK for kids to be bored − it’s good for them
Margaret Murray, University of Michigan-Dearborn Boredom is a common part of life, across time and around the world. That’s because boredom serves a useful purpose: It motivates people to pursue new goals and challenges. I’m a professor who studies communication and culture. I am currently writing a book about modern parenting, and I’ve noticed that many parents try to help their kids avoid boredom. They might see it as a negative emotion that they don’t want their children to experience. Or they might steer them into doing something that they see as more productive. There are various reasons they want to prevent their children from being bored. Many parents are busy with work. They’re stressed about money, child care responsibilities and managing other parts of daily life. Making sure a child is occupied with a game, a TV show or an arts and crafts project at home can help parents work uninterrupted, or make dinner, without their children complaining that they are bored. Parents may also feel pressure for their children to succeed, whether that means getting admitted to a selective school, or becoming a good athlete or an accomplished musician. Children also spend less time playing freely outside and more time participating in structured activities than they did a few decades ago. Easy access to screens has made it possible to avoid boredom more than ever before. Many parents needed to put their children in front of screens throughout the pandemic to keep them occupied during work hours. More recently, some parents have reported feeling social pressure to use screens to keep children quiet in public spaces. That is to say, there are various reasons why parents shy away from their kids being bored. But before striving to eliminate boredom completely, it’s important to know the benefits of boredom.
Benefits of boredom
Although boredom feels bad to experience in the moment, it offers real benefits for personal growth. Boredom is a signal that a change is needed, whether it be a change in scenery, activity or company. Psychologists have found that the experience of boredom can lead to discovering new goals and trying new activities. Harvard public and nonprofit leadership professor Arthur Brooks has found that boredom is necessary for reflection. Downtime leaves room to ask the big questions in life and find meaning. Children who are rarely bored could become adults who cannot cope with boredom. Boredom also offers a brain boost that can cultivate a child’s innate curiosity and creativity. Learning to manage boredom and other negative emotions is an important life skill. When children manage their own time, it can help them develop executive function, which includes the ability to set goals and make plans. The benefits of boredom make sense from an evolutionary perspective. Boredom is extremely common. It affects all ages, genders and cultures, and teens are especially prone to boredom. Natural selection favors traits that offer a leg up, so it is unlikely that boredom would be so prevalent if it did not deliver some advantages. Parents should be wary of treating boredom as a problem they must solve for their children. Psychologists have found that college students with overly involved parents suffer from more depression. Other research shows that young children who were given screens to help them calm down were less equipped to regulate their emotions as they got older.Boredom is uncomfortable
Tolerating boredom is a skill that many children resist learning or do not have the opportunity to develop. Even many adults would rather shock themselves with electricity than experience boredom. It takes practice to learn how to handle boredom. Start with small doses of boredom and work up to longer stretches of unstructured time. Tips for parents include getting kids outside, suggesting a new game or recipe, or simply resting. Creating space for boredom means that there will be some stretches of time when nothing in particular is happening. Younger children might need ideas for what they could do when bored. Parents do not need to play with them every time they are bored, but offering suggestions is helpful. Even five minutes of boredom is a good start for the youngest children. Encouraging older children to solve the problem of boredom themselves is especially empowering. Let them know that boredom is a normal part of life even though it might feel unpleasant.It gets easier
Children are adaptable. As children get used to occasional boredom, it will take them longer to become bored in the future. People find life less boring once they regularly experience boredom. Letting go of the obligation to keep children entertained could also help parents feel less stressed. Approximately 41% of parents in the U.S. said they “are so stressed they cannot function,” and 48% reported that “most days their stress is completely overwhelming,” according to a report from the U.S. surgeon general in 2024. So the next time a kid complains, “I’m bored!” don’t feel guilty or frustrated. Boredom is a healthy part of life. It prompts us to be self-directed, find new hobbies and take on new challenges. Let children know that a little boredom isn’t just OK – in fact, it’s good for them.STM Daily News VlogLink: https://stmdailynews.com/stm-daily-news-vlog/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
