What we’re seeing is a removing of cooling that’s revealing warming that’s already there. So the air pollution isn’t the cause of the warming. It’s just letting us see stuff that we’ve already done.Listen to the interview on The Conversation Weekly podcast. You can also read an article by Laura Wilcox and her colleague Bjørn H. Samset about their recent research on The Conversation. This episode of The Conversation Weekly was written and produced by Mend Mariwany, Gemma Ware and Katie Flood. Mixing by Michelle Macklem and theme music by Neeta Sarl. Newsclips in this episode from Voice of America, CBC, AP Archive, ABC (News) Australia, WFLA NBC Channel 8 and PBS. Listen to The Conversation Weekly via any of the apps listed above, download it directly via our RSS feed or find out how else to listen here. A transcript of this episode is available via the Apple Podcasts or Spotify apps.
The Earth
The US natural gas industry is leaking way more methane than previously thought. Here’s why that matters
Research reveals that methane emissions from U.S. natural gas operations are significantly underestimated, with a leak rate of 2.3 percent, which poses serious climate concerns and challenges in accurate measurement.

Anthony J. Marchese, Colorado State University and Dan Zimmerle, Colorado State University
Natural gas is displacing coal, which could help fight climate change because burning it produces fewer carbon emissions. But producing and transporting natural gas releases methane, a greenhouse gas that also contributes to climate change. How big is the methane problem?
For the past five years, our research teams at Colorado State University have made thousands of methane emissions measurements at more than 700 separate facilities in the production, gathering, processing, transmission and storage segments of the natural gas supply chain.
This experience has given us a unique perspective regarding the major sources of methane emissions from natural gas and the challenges the industry faces in terms of detecting and reducing, if not eliminating, them.
Our work, along with numerous other research projects, was recently folded into a new study published in the journal Science. This comprehensive snapshot suggests that methane emissions from oil and gas operations are much higher than current EPA estimates.
What’s wrong with methane
One way to quantify the magnitude of the methane leakage is to divide the amount of methane emitted each year by the total amount of methane pumped out of the ground each year from natural gas and oil wells. The EPA currently estimates this methane leak rate to be 1.4 percent. That is, for every cubic foot of natural gas drawn from underground reservoirs, 1.4 percent of it is lost into the atmosphere.
This study synthesized the results from a five-year series of 16 studies coordinated by environmental advocacy group Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), which involved more than 140 researchers from over 40 institutions and 50 natural gas companies.
The effort brought together scholars based at universities, think tanks and the industry itself to make the most accurate estimate possible of the total amount of methane emitted from all U.S. oil and gas operations. It integrated data from a multitude of recent studies with measurements made on the ground and from the air.
All told, based on the results of the new study, the U.S. oil and gas industry is leaking 13 million metric tons of methane each year, which means the methane leak rate is 2.3 percent. This 60 percent difference between our new estimate and the EPA’s current one can have profound climate consequences.
Methane is a highly potent greenhouse gas, with more than 80 times the climate warming impact of carbon dioxide over the first 20 years after it is released.
An earlier EDF study showed that a methane leak rate of greater than 3 percent would result in no immediate climate benefits from retiring coal-fired power plants in favor of natural gas power plants.
That means even with a 2.3 percent leakage rate, the growing share of U.S. electricity powered by natural gas is doing something to slow the pace of climate change. However, these climate benefits could be far greater.
Also, at a methane leakage rate of 2.3 percent, many other uses of natural gas besides generating electricity are conclusively detrimental for the climate. For example, EDF found that replacing the diesel used in most trucks or the gasoline consumed by most cars with natural gas would require a leakage rate of less than 1.4 percent before there would be any immediate climate benefit.
What’s more, some scientists believe that the leakage rate could be even higher than this new estimate.
What causes these leaks
Perhaps you’ve never contemplated the long journey that natural gas travels before you can ignite the burners on the gas stove in your kitchen.
But on top of the 500,000 natural gas wells operating in the U.S. today, there are 2 million miles of pipes and millions of valves, fittings, tanks, compressors and other components operating 24 hours per day, seven days a week to deliver natural gas to your home.
That natural gas that you burn when you whip up a batch of pancakes may have traveled 1,000 miles or more as it wended through this complicated network. Along the way, there were ample opportunities for some of it to leak out into the atmosphere.
Natural gas leaks can be accidental, caused by malfunctioning equipment, but a lot of natural gas is also released intentionally to perform process operations such as opening and closing valves. In addition, the tens of thousands of compressors that increase the pressure and pump the gas along through the network are powered by engines that burn natural gas and their exhaust contains some unburned natural gas.
Since the natural gas delivered to your home is 85 to 95 percent methane, natural gas leaks are predominantly methane. While methane poses the greatest threat to the climate because of its greenhouse gas potency, natural gas contains other hydrocarbons that can degrade regional air quality and are bad for human health.
Inventory tallies vs. aircraft surveillance
The EPA Greenhouse Gas Inventory is done in a way experts like us call a “bottom-up” approach. It entails tallying up all of the nation’s natural gas equipment – from household gas meters to wellpads – and estimating an annualized average emission rate for every category and adding it all up.
There are two challenges to this approach. First, there are no accurate equipment records for many of these categories. Second, when components operate improperly or fail, emissions balloon, making it hard to develop an accurate and meaningful annualized emission rate for each source.
“Top-down” approaches, typically requiring aircraft, are the alternative. They measure methane concentrations upwind and downwind of large geographic areas. But this approach has its own shortcomings.
First, it captures all methane emissions, rather than just the emissions tied to natural gas operations – including the methane from landfills, cows and even the leaves rotting in your backyard. Second, these one-time snapshots may get distorted depending on what’s going on while planes fly around capturing methane data.
Historically, top-down approaches estimate emissions that are about twice bottom-up estimates. Some regional top-down methane leak rate estimates have been as high as 8 percent while some bottom-up estimates have been as low as 1 percent.
More recent work, including the Science study, have performed coordinated campaigns in which the on-the-ground and aircraft measurements are made concurrently, while carefully modeling emission events.
Helpful gadgets and sound policy
On a sunny morning in October 2013, our research team pulled up to a natural gas gathering compressor station in Texas. Using an US$80,000 infrared camera, we immediately located an extraordinarily large leak of colorless, odorless methane that was invisible to the operator who quickly isolated and fixed the problem.
We then witnessed the methane emissions decline tenfold – the facility leak rate fell from 9.8 percent to 0.7 percent before our eyes.
It is not economically feasible, of course, to equip all natural gas workers with $80,000 cameras, or to hire the drivers required to monitor every wellpad on a daily basis when there are 40,000 oil and gas wells in Weld County, Colorado, alone.
But new technologies can make a difference. Our team at Colorado State University is working with the Department of Energy to evaluate gadgetry that will rapidly detect methane emissions. Some of these devices can be deployed today, including inexpensive sensors that can be monitored remotely.
Technology alone won’t solve the problem, however. We believe that slashing the nation’s methane leak rate will require a collaborative effort between industry and government. And based on our experience in Colorado, which has developed some of the nation’s strictest methane emissions regulations, we find that best practices become standard practices with strong regulations.
We believe that the Trump administration’s efforts to roll back regulations, without regard to whether they are working or not, will not only have profound climate impacts. They will also jeopardize the health and safety of all Americans while undercutting efforts by the natural gas industry to cut back on the pollution it produces.
Anthony J. Marchese, Associate Dean for Academic and Student Affairs, Walter Scott, Jr. College of Engineering; Director, Engines and Energy Conversion Laboratory; Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Colorado State University and Dan Zimmerle, Senior Research Associate and Director of METEC, Colorado State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
podcasts
How China cleaned up its air pollution – and what that meant for the climate
How China cleaned up its air pollution: Beijing’s air quality went from hazardous to good while Delhi and Lahore still struggle. Discover how China dramatically reduced pollution since 2013—and why cleaner air may have unintended consequences for global warming and climate change.
How China cleaned up its air pollution – and what that meant for the climate
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
Fern Stems Reveal How Evolutionary Constraints Create New Forms in Nature
Evolutionary Constraints: New research on fern vascular systems reveals how developmental constraints don’t just limit evolution—they generate new forms. Discover how leaf placement determines stem structure and what this means for understanding biodiversity and plant breeding.

Fern Stems Reveal How Evolutionary Constraints Create New Forms in Nature
Jacob S. Suissa, University of Tennessee There are few forms of the botanical world as readily identifiable as fern leaves. These often large, lacy fronds lend themselves nicely to watercolor paintings and tricep tattoos alike. Thoreau said it best: “Nature made ferns for pure leaves, to show what she could do in that line.” But ferns are not just for art and gardens. While fern leaves are the most iconic part of their body, these plants are whole organisms, with stems and roots that are often underground or creeping along the soil surface. With over 400 million years of evolutionary history, ferns can teach us a lot about how the diversity of planet Earth came to be. Specifically, examining their inner anatomy can reveal some of the intricacies of evolution.Sums of parts or an integrated whole?
When one structure cannot change without altering the other, researchers consider them constrained by each other. In biology, this linkage between traits is called a developmental constraint. It explains the limits of what possible forms organisms can take. For instance, why there aren’t square trees or mammals with wheels. However, constraint does not always limit form. In my recently published research, I examined the fern vascular system to highlight how changes in one part of the organism can lead to changes in another, which can generate new forms.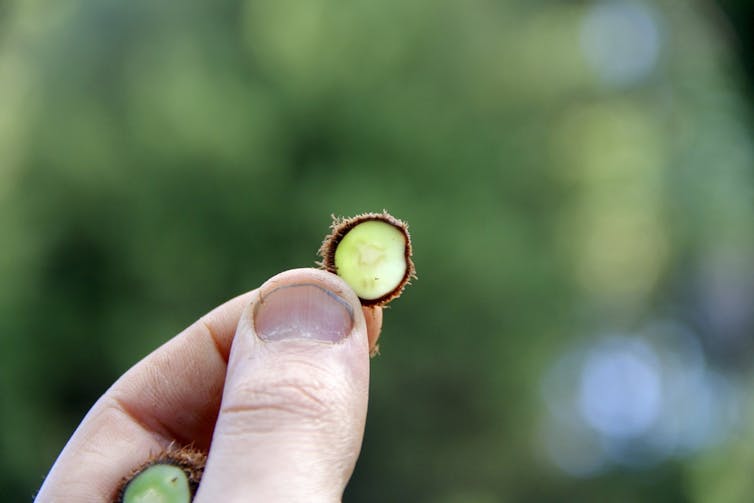
Fern vasculature and the process of evolution
Ferns are one of four lineages of land plants that have vascular tissues – specialized sets of tubes that move water and nutrients through their bodies. These tissues are composed of vascular bundles – clusters of cells that conduct water through the stem. How vascular bundles are arranged in fern stems varies substantially. Some have as many as three to eight or more vascular bundles scattered throughout their stem. Some are arranged symmetrically, while others such as the tobacco fern – Mickelia nicotianifolia – have bundles arranged in a whimsical, smiley-face pattern.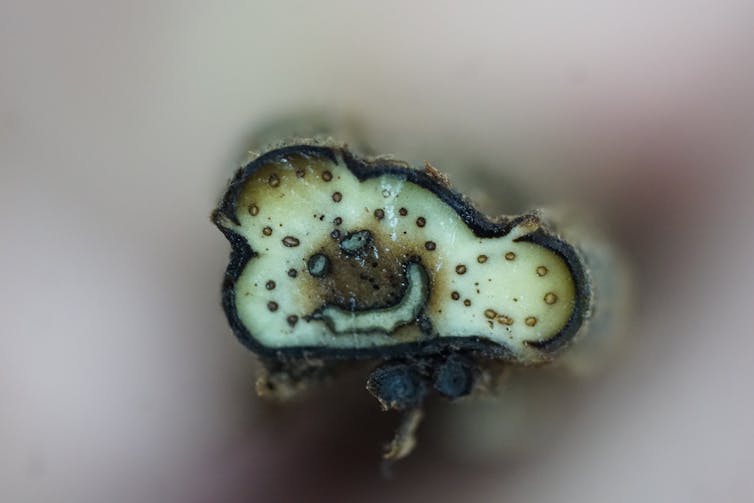
Simple observations and insights into evolution
I wondered how this variation in the number and arrangement of vascular bundles relates to leaf placement around the stem. So I quantified this variation in vascular patterning for 27 ferns representing roughly 30% of all fern species. I found a striking correlation between the number of rows of leaves and the number of vascular bundles within the stem. This relationship was almost 1-to-1 in some cases. For instance, if there were three rows of leaves along the stem, there were three vascular bundles in the stem. What’s more, how leaves were arranged around the stem determined the spatial arrangement of bundles. If the leaves were arranged spirally (on all sides of the stem), the vascular bundles were arranged in a radial pattern. If the leaves were shifted to the dorsal side of the stem, the smiley-face pattern emerged. Importantly, based on our understanding of plant development, there was a directionality here. Specifically, the placement of leaves determines the arrangement of bundles, not the other way around.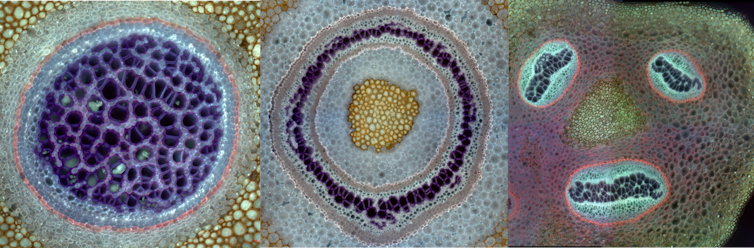
From parochial to existential
While this study on ferns and their vascular system may seem parochial, it speaks to the broader question of how variation – the fuel of evolution – arises, and how evolution can proceed. While not all parts of an organism are so tightly linked, considering the individual as a whole – or at least sets of parts as a unit – can help researchers better understand how, and if, observable patterns can evolve in isolation. This insight takes scientists one step closer to understanding the minutia of how evolution works to generate the immense biodiversity on Earth. Understanding these processes is also important for industry. In agricultural settings, plant and animal breeders attempt to increase one aspect of an organism without changing another. By taking a holistic approach and understanding which parts of an organism are developmentally or genetically linked and which are more quasi-independent, breeders may be able to more effectively create organisms with desired traits.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Science
Thousands of genomes reveal the wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA
wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA: New research analyzing 2,693 dog genomes reveals most modern dogs carry wolf DNA from ancient hybridization. Discover how wolf genes helped dogs survive and what this means for breeds from Chihuahuas to sled dogs.
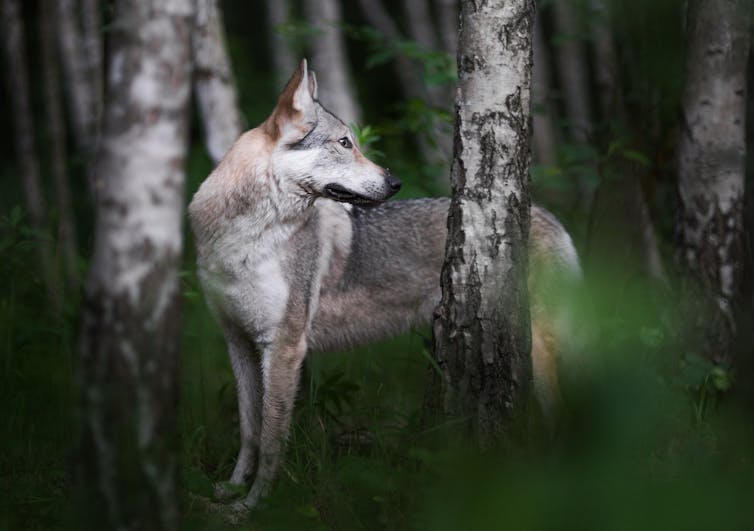

Thousands of genomes reveal the wild wolf genes in most dogs’ DNA
Audrey T. Lin, Smithsonian Institution and Logan Kistler, Smithsonian Institution Dogs were the first of any species that people domesticated, and they have been a constant part of human life for millennia. Domesticated species are the plants and animals that have evolved to live alongside humans, providing nearly all of our food and numerous other benefits. Dogs provide protection, hunting assistance, companionship, transportation and even wool for weaving blankets. Dogs evolved from gray wolves, but scientists debate exactly where, when and how many times dogs were domesticated. Ancient DNA evidence suggests that domestication happened twice, in eastern and western Eurasia, before the groups eventually mixed. That blended population was the ancestor of all dogs living today. Molecular clock analysis of the DNA from hundreds of modern and ancient dogs suggests they were domesticated between around 20,000 and 22,000 years ago, when large ice sheets covered much of Eurasia and North America. The first dog identified in the archaeological record is a 14,000-year-old pup found in Bonn-Oberkassel, Germany, but it can be difficult to tell based on bones whether an animal was an early domestic dog or a wild wolf. Despite the shared history of dogs and wolves, scientists have long thought these two species rarely mated and gave birth to hybrid offspring. As an evolutionary biologist and a molecular anthropologist who study domestic plants and animals, we wanted to take a new look at whether dog-wolf hybridization has really been all that uncommon.Little interbreeding in the wild
Dogs are not exactly descended from modern wolves. Rather, dogs and wolves living today both derive from a shared ancient wolf population that lived alongside woolly mammoths and cave bears. In most domesticated species, there are often clear, documented patterns of gene flow between the animals that live alongside humans and their wild counterparts. Where wild and domesticated animals’ habitats overlap, they can breed with each other to produce hybrid offspring. In these cases, the genes from wild animals are folded into the genetic variation of the domesticated population. For example, pigs were domesticated in the Near East over 10,000 years ago. But when early farmers brought them to Europe, they hybridized so frequently with local wild boar that almost all of their Near Eastern DNA was replaced. Similar patterns can be seen in the endangered wild Anatolian and Cypriot mouflon that researchers have found to have high proportions of domestic sheep DNA in their genomes. It’s more common than not to find evidence of wild and domesticated animals interbreeding through time and sharing genetic material. That wolves and dogs wouldn’t show that typical pattern is surprising, since they live in overlapping ranges and can freely interbreed. Dog and wolf behavior are completely different, though, with wolves generally organized around a family pack structure and dogs reliant on humans. When hybridization does occur, it tends to be when human activities – such as habitat encroachment and hunting – disrupt pack dynamics, leading female wolves to strike out on their own and breed with male dogs. People intentionally bred a few “wolf dog” hybrid types in the 20th century, but these are considered the exception.
Tiny but detectable wolf ancestry
To investigate how much gene flow there really has been between dogs and wolves after domestication, we analyzed 2,693 previously published genomes, making use of massive publicly available datasets. These included 146 ancient dogs and wolves covering about 100,000 years. We also looked at 1,872 modern dogs, including golden retrievers, Chihuahuas, malamutes, basenjis and other well-known breeds, plus more unusual breeds from around the world such as the Caucasian ovcharka and Swedish vallhund. Finally, we included genomes from about 300 “village dogs.” These are not pets but are free-living animals that are dependent on their close association with human environments. We traced the evolutionary histories of all of these canids by looking at maternal lineages via their mitochondrial genomes and paternal lineages via their Y chromosomes. We used highly sensitive computational methods to dive into the dogs’ and wolves’ nuclear genomes – that is, the genetic material contained in their cells’ nuclei. We found the presence of wild wolf genes in most dog genomes and the presence of dog genes in about half of wild wolf genomes. The sign of the wolf was small but it was there, in the form of tiny, almost imperceptible chunks of continuous wolf DNA in dogs’ chromosomes. About two-thirds of breed dogs in our sample had wolf genes from crossbreeding that took place roughly 800 generations ago, on average. While our results showed that larger, working dogs – such as sled dogs and large guardian dogs that protect livestock – generally have more wolf ancestry, the patterns aren’t universal. Some massive breeds such as the St. Bernard completely lack wolf DNA, but the tiny Chihuahua retains detectable wolf ancestry at 0.2% of its genome. Terriers and scent hounds typically fall at the low end of the spectrum for wolf genes.
The intertwining of dogs and wolves
Because dogs evolved from wolves, all of dogs’ DNA is originally wolf DNA. So when we’re talking about the small pieces of wolf DNA in dog genomes, we’re not referring to that original wolf gene pool that’s been kicking around over the past 20,000 years, but rather evidence for dogs and wolves continuing to interbreed much later in time. A wolf-dog hybrid with one of each kind of parent would carry 50% dog and 50% wolf DNA. If that hybrid then lived and mated with dogs, its offspring would be 25% wolf, and so on, until we see only small snippets of wolf DNA present. The situation is similar to one in human genomes: Neanderthals and humans share a common ancestor around half a million years ago. However, Neanderthals and our species, Homo sapiens, also overlapped and interbred in Eurasia as recently as a few thousand generations ago, shortly before Neanderthals disappeared. Scientists can spot the small pieces of Neanderthal DNA in most living humans in the same way we can see wolf genes within most dogs.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

