STM Daily News
Better but not stellar: Pollsters faced familiar complaints, difficulties in assessing Trump-Harris race
W. Joseph Campbell, American University School of Communication
An oracle erred badly. The most impressive results were turned in by a little-known company in Brazil. A nagging problem reemerged, and some media critics turned profane in their assessments.
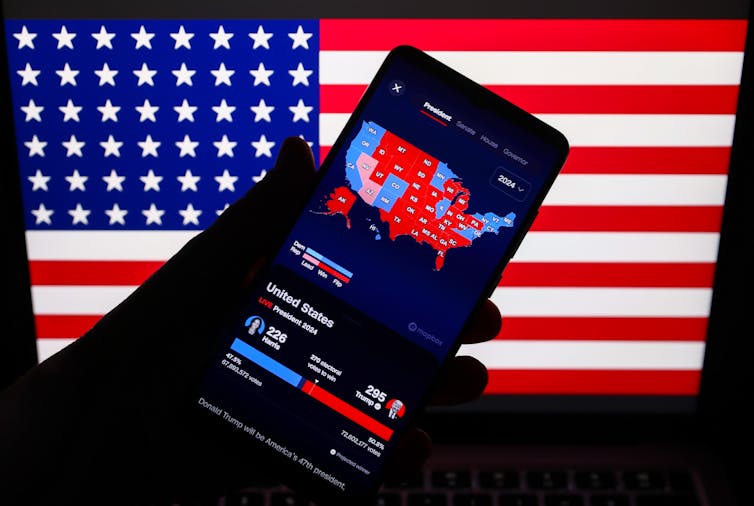
So it went for pollsters in the 2024 presidential election. Their collective performance, while not stellar, was improved from that of four years earlier. Overall, polls signaled a close outcome in the race between former President Donald Trump and Vice President Kamala Harris.
That is what the election produced: a modest win for Trump.
With votes still being counted in California and a few other states more than a week after Election Day, Trump had received 50.1% of the popular vote to Harris’ 48.1%, a difference of 2 points. That margin was closer than Joe Biden’s win by 4.5 points over Trump in 2020. It was closer than Hillary Clinton’s popular vote victory in 2016, closer than Barack Obama’s wins in 2008 and 2012.
There were, moreover, no errors among national pollsters quite as dramatic as CNN’s estimate in 2020 that Biden led Trump by 12 points.
This time, CNN’s final national poll said the race was deadlocked – an outcome anticipated by six other pollsters, according to data compiled by RealClearPolitics.
The most striking discrepancy this year was the Marist College poll, conducted for NPR and PBS. It estimated Harris held a 4-point lead nationally at campaign’s end.
‘Oracle’ of Iowa’s big miss
In any event, a sense lingered among critics that the Trump-Harris election had resulted in yet another polling embarrassment, another entry in the catalog of survey failures in presidential elections, which is the topic of my latest book, “Lost in a Gallup.”
Comedian Jon Stewart gave harsh voice to such sentiments, saying of pollsters on his late-night program on election night, “I don’t ever want to fucking hear from you again. Ever. … You don’t know shit about shit, and I don’t care for you.”
Megyn Kelly, a former Fox News host, also denounced pollsters, declaring on her podcast the day after the election: “Polling is a lie. They don’t know anything.”
Two factors seemed to encourage such derision – a widely discussed survey of Iowa voters released the weekend before the election and Trump’s sweep of the seven states where the outcome turned.
The Iowa poll injected shock and surprise into the campaign’s endgame, reporting that Harris had taken a 3-point lead in the state over Trump. The result was likened to a “bombshell” and its implications seemed clear: If Harris had opened a lead in a state with Iowa’s partisan profile, her prospects of winning elsewhere seemed strong, especially in the Great Lakes swing states of Wisconsin, Michigan and Pennsylvania.
The survey was conducted for the Des Moines Register by J. Ann Selzer, a veteran Iowa-based pollster with an outstanding reputation in opinion research. In a commentary in The New York Times in mid-September, Republican pollster Kristen Soltis Anderson declared Selzer “the oracle of Iowa.” Rachel Maddow of MSNBC praised Selzer’s polls before the election for their “uncanny predictive accuracy.” Ratings released in June by data guru Nate Silver gave Selzer’s polls an A-plus grade.
But this time, Selzer’s poll missed dramatically.
Trump carried Iowa by 13 points, meaning the poll was off by 16 points – a stunning divergence for an accomplished pollster.
“Even the mighty have been humbled” by Trump’s victory, the Times of London said of Selzer’s polling failure.
Selzer said afterward she will “be reviewing data from multiple sources with hopes of learning why that (discrepancy) happened.”
It is possible, other pollsters suggested, that Selzer’s reliance on telephone-based surveying contributed to the polling failure. “Phone polling alone … isn’t going to reach low-propensity voters or politically disengaged nonwhite men,” Tom Lubbock and James Johnson wrote in a commentary for The Wall Street Journal.
These days, few pollsters rely exclusively on the phone to conduct election surveys; many of them have opted for hybrid approaches that combine, for example, phone, text and online sampling techniques.
Surprise sweep of swing states
Trump’s sweep of the seven vigorously contested swing states surely contributed to perceptions that polls had misfired again.
According to RealClearPolitics, Harris held slender, end-of-campaign polling leads in Michigan and Wisconsin, while Trump was narrowly ahead in Arizona, Georgia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina and Nevada.
Trump won them all, an outcome no pollster anticipated – except for AtlasIntel of Sao Paulo, Brazil, a firm “about which little is known,” as The New Republic noted.
AtlasIntel estimated Trump was ahead in all seven swing states by margins that hewed closely to the voting outcomes. In none of the swing states did AtlasIntel’s polling deviate from the final vote tally by more than 1.3 points, an impressive performance.
AtlasIntel did not respond to email requests I sent requesting information about its background and polling technique. The company describes itself as “a leading innovator in online polling” and says it uses “a proprietary methodology,” without revealing much about it.
Its founder and chief executive is Andrei Roman, who earned a doctorate in government at Harvard University. Roman took to X, formerly Twitter, in the election’s aftermath to post a chart that touted AtlasIntel as “the most accurate pollster of the US Presidential Election.”
It was a burst of pollster braggadocio reminiscent of a kind that has emerged periodically since the 1940s. That was when polling pioneer George Gallup placed two-page advertising spreads in the journalism trade publication “Editor & Publisher” to assert the accuracy of his polls in presidential elections.
Underestimating Trump’s support again
A significant question facing pollsters this year – their great known unknown – was whether modifications made to sampling techniques would allow them to avoid underestimating Trump’s support, as they had in 2016 and 2020.
Misjudging Trump’s backing is a nagging problem for pollsters. The results of the 2024 election indicate that the shortcoming persists. By margins ranging from 0.9 points to 2.7 points, polls overall understated Trump’s support in the seven swing states, for example.
Some polls misjudged Trump’s backing by even greater margins. CNN, for example, underestimated Trump’s vote by 4.3 points in North Carolina, by more than 6 points in Michigan and Wisconsin as well as Arizona.
Results that misfire in the same direction suggest that adjustments to sampling methodologies were inadequate or ineffective for pollsters in seeking to reach Trump backers of all stripes.
W. Joseph Campbell, Professor Emeritus of Communication, American University School of Communication
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
STM Daily News is a vibrant news blog dedicated to sharing the brighter side of human experiences. Emphasizing positive, uplifting stories, the site focuses on delivering inspiring, informative, and well-researched content. With a commitment to accurate, fair, and responsible journalism, STM Daily News aims to foster a community of readers passionate about positive change and engaged in meaningful conversations. Join the movement and explore stories that celebrate the positive impacts shaping our world.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
unknown
Why people tend to believe UFOs are extraterrestrial
Last Updated on March 13, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Barry Markovsky, University of South Carolina
Most of us still call them UFOs – unidentified flying objects. NASA recently adopted the term “unidentified anomalous phenomena,” or UAP. Either way, every few years popular claims resurface that these things are not of our world, or that the U.S. government has some stored away.
I’m a sociologist who focuses on the interplay between individuals and groups, especially concerning shared beliefs and misconceptions. As for why UFOs and their alleged occupants enthrall the public, I’ve found that normal human perceptual and social processes explain UFO buzz as much as anything up in the sky.
Historical context
Like political scandals and high-waisted jeans, UFOs trend in and out of collective awareness but never fully disappear. Thirty years of polling find that 25%-50% of surveyed Americans believe at least some UFOs are alien spacecraft. Today in the U.S., over 100 million adults think our galactic neighbors pay us visits.
It wasn’t always so. Linking objects in the sky with visiting extraterrestrials has risen in popularity only in the past 75 years. Some of this is probably market-driven. Early UFO stories boosted newspaper and magazine sales, and today they are reliable clickbait online.
In 1980, a popular book called “The Roswell Incident” by Charles Berlitz and William L. Moore described an alleged flying saucer crash and government cover-up 33 years prior near Roswell, New Mexico. The only evidence ever to emerge from this story was a small string of downed weather balloons. Nevertheless, the book coincided with a resurgence of interest in UFOs. From there, a steady stream of UFO-themed TV shows, films, and pseudo-documentaries has fueled public interest. Perhaps inevitably, conspiracy theories about government cover-ups have risen in parallel.
Some UFO cases inevitably remain unresolved. But despite the growing interest, multiple investigations have found no evidence that UFOs are of extraterrestrial origin – other than the occasional meteor or misidentification of Venus.
But the U.S. Navy’s 2017 Gimbal video continues to appear in the media. It shows strange objects filmed by fighter jets, often interpreted as evidence of alien spacecraft. And in June 2023, an otherwise credible Air Force veteran and former intelligence officer made the stunning claim that the U.S. government is storing numerous downed alien spacecraft and their dead occupants. https://www.youtube.com/embed/2TumprpOwHY?wmode=transparent&start=0 UFO videos released by the U.S. Navy, often taken as evidence of alien spaceships.
Human factors contributing to UFO beliefs
Only a small percentage of UFO believers are eyewitnesses. The rest base their opinions on eerie images and videos strewn across both social media and traditional mass media. There are astronomical and biological reasons to be skeptical of UFO claims. But less often discussed are the psychological and social factors that bring them to the popular forefront.
Many people would love to know whether or not we’re alone in the universe. But so far, the evidence on UFO origins is ambiguous at best. Being averse to ambiguity, people want answers. However, being highly motivated to find those answers can bias judgments. People are more likely to accept weak evidence or fall prey to optical illusions if they support preexisting beliefs.
For example, in the 2017 Navy video, the UFO appears as a cylindrical aircraft moving rapidly over the background, rotating and darting in a manner unlike any terrestrial machine. Science writer Mick West’s analysis challenged this interpretation using data displayed on the tracking screen and some basic geometry. He explained how the movements attributed to the blurry UFO are an illusion. They stem from the plane’s trajectory relative to the object, the quick adjustments of the belly-mounted camera, and misperceptions based on our tendency to assume cameras and backgrounds are stationary.
West found the UFO’s flight characteristics were more like a bird’s or a weather balloon’s than an acrobatic interstellar spacecraft. But the illusion is compelling, especially with the Navy’s still deeming the object unidentified.
West also addressed the former intelligence officer’s claim that the U.S. government possesses crashed UFOs and dead aliens. He emphasized caution, given the whistleblower’s only evidence was that people he trusted told him they’d seen the alien artifacts. West noted we’ve heard this sort of thing before, along with promises that the proof will soon be revealed. But it never comes.
Anyone, including pilots and intelligence officers, can be socially influenced to see things that aren’t there. Research shows that hearing from others who claim to have seen something extraordinary is enough to induce similar judgments. The effect is heightened when the influencers are numerous or higher in status. Even recognized experts aren’t immune from misjudging unfamiliar images obtained under unusual conditions.
Group factors contributing to UFO beliefs
“Pics or it didn’t happen” is a popular expression on social media. True to form, users are posting countless shaky images and videos of UFOs. Usually they’re nondescript lights in the sky captured on cellphone cameras. But they can go viral on social media and reach millions of users. With no higher authority or organization propelling the content, social scientists call this a bottom-up social diffusion process.
In contrast, top-down diffusion occurs when information emanates from centralized agents or organizations. In the case of UFOs, sources have included social institutions like the military, individuals with large public platforms like U.S. senators, and major media outlets like CBS.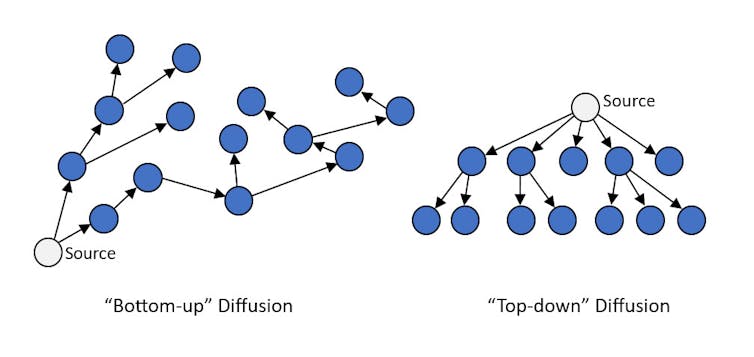
Amateur organizations also promote active personal involvement for many thousands of members, the Mutual UFO Network being among the oldest and largest. But as Sharon A. Hill points out in her book “Scientifical Americans,” these groups apply questionable standards, spread misinformation and garner little respect within mainstream scientific communities.
Top-down and bottom-up diffusion processes can combine into self-reinforcing loops. Mass media spreads UFO content and piques worldwide interest in UFOs. More people aim their cameras at the skies, creating more opportunities to capture and share odd-looking content. Poorly documented UFO pics and videos spread on social media, leading media outlets to grab and republish the most intriguing. Whistleblowers emerge periodically, fanning the flames with claims of secret evidence.
Despite the hoopla, nothing ever comes of it.
For a scientist familiar with the issues, skepticism that UFOs carry alien beings is wholly separate from the prospect of intelligent life elsewhere in the universe. Scientists engaged in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence have a number of ongoing research projects designed to detect signs of extraterrestrial life. If intelligent life is out there, they’ll likely be the first to know.
As astronomer Carl Sagan wrote, “The universe is a pretty big place. If it’s just us, seems like an awful waste of space.”
Barry Markovsky, Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Sociology, University of South Carolina
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Community
Arizona Scholarships 2026: $1,500 Awards + Free ACF Virtual Workshops
Arizona scholarships 2026: Arizona scholarships are open through ACF: one application for 160+ awards, plus ARAC’s $1,500 Ashby-Herring scholarships due April 6, 2026.
Last Updated on March 11, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Arizona Scholarships 2026: $1,500 Awards + Free ACF Virtual Workshops
Scholarship season moves fast, and for a lot of Arizona families, the hardest part isn’t writing the essay or gathering transcripts—it’s simply finding the right opportunities in time.
The Archer Ragsdale Arizona Chapter (ARAC), Tuskegee Airmen, Inc. is encouraging students and the community to take advantage of scholarship resources through the Arizona Community Foundation (ACF), including an easy online application that can match applicants with 160+ scholarships—plus virtual workshops where students can get help directly from ACF’s scholarship team.
Whether you’re a high school senior, a current college student, or an adult re-entry student, ACF’s scholarship portal is designed to meet people where they are.
The Big Picture: One Application, 160+ Scholarships
According to the flyer, ACF awarded $6.3 million in scholarships last year, with over 160 scholarships available through a single, easy application.
- Application opens: January 1
- Most deadlines: March and April
- Where to start: https://azfoundation.org/scholarships
- ACF scholarship email: scholarship@azfoundation.org
What to watch for: Even if a student is only targeting one scholarship, completing the ACF application can surface additional matches they didn’t know existed.
ARAC Tuskegee Airmen Scholarship: Ashby-Herring Scholarships ($1,500) — Deadline April 6, 2026
ARAC (Tuskegee Airmen, Inc.) awards two or more scholarships to deserving Arizona students who are college-bound. The flyer highlights the Ashby-Herring scholarships, named in honor of late founding ARAC members who were original Tuskegee Airmen.
Award: Two Ashby-Herring scholarships (each $1,500)
Deadline:April 6, 2026
Apply here:https://www.azfoundation.org/archer-ragsdale
Eligibility:
- Graduating high school senior from Arizona
- Attending a 2-year or 4-year college/university
- African-American
- 3.0 GPA or higher
- Demonstrated financial need
Free Virtual Workshops (Zoom): Get Help With Your Application
If you’ve ever watched a student stall out halfway through an application, these workshops are a smart fix: they’re designed so applicants can work on their scholarship application with support from ACF’s scholarship team.
Workshop dates (Zoom):
- February 12, 2026 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m.
- March 5, 2026 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m.
- March 26 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m. (date listed on flyer; confirm year when registering)
Register here:https://acf.cventevents.com/acfscholarships2026
View the flyer here: https://stmdailynews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/Deadline-updated-12.29.2025-Archer-Ragsdale-Flyer-FINAL.pdf
Download Flyer (PDF)
What to watch for: Register for the dates you can attend and come prepared with what you already have (basic info, activities list, questions). One hour of guided progress can save days of procrastination.
Why This Matters (and Why Sharing Helps)
The Tuskegee Airmen legacy is rooted in excellence, discipline, and breaking barriers—and scholarships tied to that legacy are meant to elevate futures for the next generation.
If you’re a parent, teacher, coach, mentor, or neighbor, consider this your nudge: forward the link, post it in a group chat, or share it with a student who might qualify. Deadlines hit quickly, and the easiest scholarship to win is often the one you actually apply for.
View the press release: https://stmdailynews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/FOR-IMMEDIATE-RELEASE.pdf
Related Links:
- https://azfoundation.org/scholarships
- https://acf.cventevents.com/acfscholarships2026
- https://www.azfoundation.org/archer-ragsdale
College Life
College isn’t just classes and credits — it’s learning how to manage your time, money, health, and relationships while you build a future that actually fits. In our College Life coverage, STM Daily News shares practical, real-world guides for students and families: campus living tips, study and productivity habits, career prep, budgeting basics, mental wellness check-ins, and smart ways to make the most of college in Arizona and beyond.
Expect quick reads, useful takeaways, and “what to do next” advice — whether you’re a first-year student, a transfer, or heading back to school.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Travel Advisory
Traveling to Mexico this spring? Here’s what to know about current advisories
Traveling to Mexico this spring? Visitors should be aware of state-specific travel advisories, as safety concerns in one region do not affect major resort areas like Cancun and Los Cabos, currently rated Level 2, which encourages increased caution. Monitoring official updates is essential for informed travel decisions amidst evolving conditions.
Last Updated on March 10, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Traveling to Mexico this spring? Here’s what to know about current advisories
(Tiffany Miller for ALG Vacations) For some travelers counting down to spring break, recent headlines about violence in parts of Mexico have sparked a new question: Should I cancel my trip? Travel advisors say they are seeing a surge in calls and emails from clients trying to determine whether developments in one region affect major resort areas elsewhere.
The questions follow several days of unrest in parts of Mexico after security operations targeting organized crime leaders prompted temporary flight disruptions and shelter-in-place guidance for U.S. government personnel in areas including Puerto Vallarta and Guadalajara. In this article, ALG Vacations explains what current travel advisories mean for spring break travelers heading to Mexico.
The U.S. State Department evaluates Mexico state by state, not as a single destination, and advisory levels vary by region. Many major beach destinations, including Cancun, Riviera Maya, Tulum and Los Cabos, are currently under a Level 2 advisory, which encourages travelers to exercise increased caution. It does not discourage travel.
Part of the confusion stems from geography. Puerto Vallarta, on the Pacific coast, is roughly 1,300 miles from Cancun and the Riviera Maya on the Caribbean side, about the distance between New York and Miami. Because advisories are assigned state by state, developments in one region do not automatically alter another.
In recent days, that uncertainty has translated into additional inquiries about whether specific resort areas are experiencing disruptions. U.S. Embassy security alerts issued this week indicate that temporary shelter-in-place guidance affecting Puerto Vallarta was lifted and that flight operations resumed. The advisory level for the Mexican state of Quintana Roo remains unchanged.
Some clients are asking about alternatives, advisors say, but many are continuing with their plans after reviewing official updates. Travel patterns often shift in response to breaking headlines, they add, before stabilizing as clearer information becomes available.
The State Department assigns travel advisories on a four-tier scale ranging from Level 1, exercise normal precautions, to Level 4, do not travel. While Level 2 encourages increased awareness, Level 3 and Level 4 carry stronger language discouraging or restricting travel.
Advisories are reviewed regularly and can be updated as conditions evolve. The State Department’s Mexico advisory page breaks down conditions by state, reflecting the country’s federal structure rather than issuing a single national designation. Travelers can also enroll in the State Department’s Smart Traveler Enrollment Program, which provides real-time security updates and allows U.S. officials to contact citizens in an emergency.
Embassy notices state that airports, hotels and tourism services in Quintana Roo are operating normally. Security conditions across Mexico vary widely by state, with some regions carrying higher advisories and others designated Level 1. Most destinations popular with U.S. travelers are currently classified as Level 2.
As spring break approaches, advisors say informed decision-making depends on reviewing the advisories assigned to a specific destination and monitoring official updates, rather than reacting to national headlines alone. Travel decisions ultimately depend on individual comfort levels, they add, but advisory levels are assigned regionally and should be evaluated accordingly.
Photo courtesy of Shutterstock
![]()
SOURCE:
Welcome to the Consumer Corner section of STM Daily News, your ultimate destination for savvy shopping and informed decision-making! Dive into a treasure trove of insights and reviews covering everything from the hottest toys that spark joy in your little ones to the latest electronic gadgets that simplify your life. Explore our comprehensive guides on stylish home furnishings, discover smart tips for buying a home or enhancing your living space with creative improvement ideas, and get the lowdown on the best cars through our detailed auto reviews. Whether you’re making a major purchase or simply seeking inspiration, the Consumer Corner is here to empower you every step of the way—unlock the keys to becoming a smarter consumer today!
https://stmdailynews.com/category/consumer-corner
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
