Space and Tech
Jupiter’s moons hide giant subsurface oceans − Europa Clipper is one of 2 missions on their way to see if these moons could support life
NASA’s Europa Clipper and ESA’s JUICE missions aim to explore Jupiter’s icy moons, focusing on the potential habitability of their underground oceans, particularly Europa’s, by gathering vital scientific data.
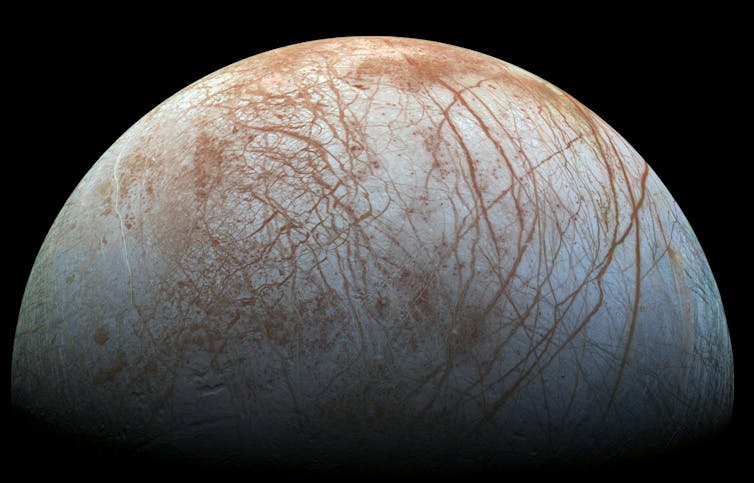

On Oct. 14, 2024, NASA launched a robotic spacecraft named Europa Clipper to Jupiter’s moons. Clipper will reach the ice-covered Jovian moon Europa in 2030 and spend several years collecting and sending valuable data on the moon’s potential habitability back to Earth.
Clipper isn’t the only mission highlighting researchers’ interest in Jupiter and its moons.
On April 13, 2023, the European Space Agency launched a rocket carrying a spacecraft destined for Jupiter. The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer – or JUICE – will spend at least three years on Jupiter’s moons after it arrives in 2031.
I’m a planetary scientist who studies the structure and evolution of solid planets and moons in the solar system.
There are many reasons my colleagues and I are looking forward to getting the data that Europa Clipper and JUICE will hopefully be sending back to Earth in the 2030s. But perhaps the most exciting information will have to do with water. Three of Jupiter’s moons – Europa, Ganymede and Callisto – are home to large, underground oceans of liquid water that could support life.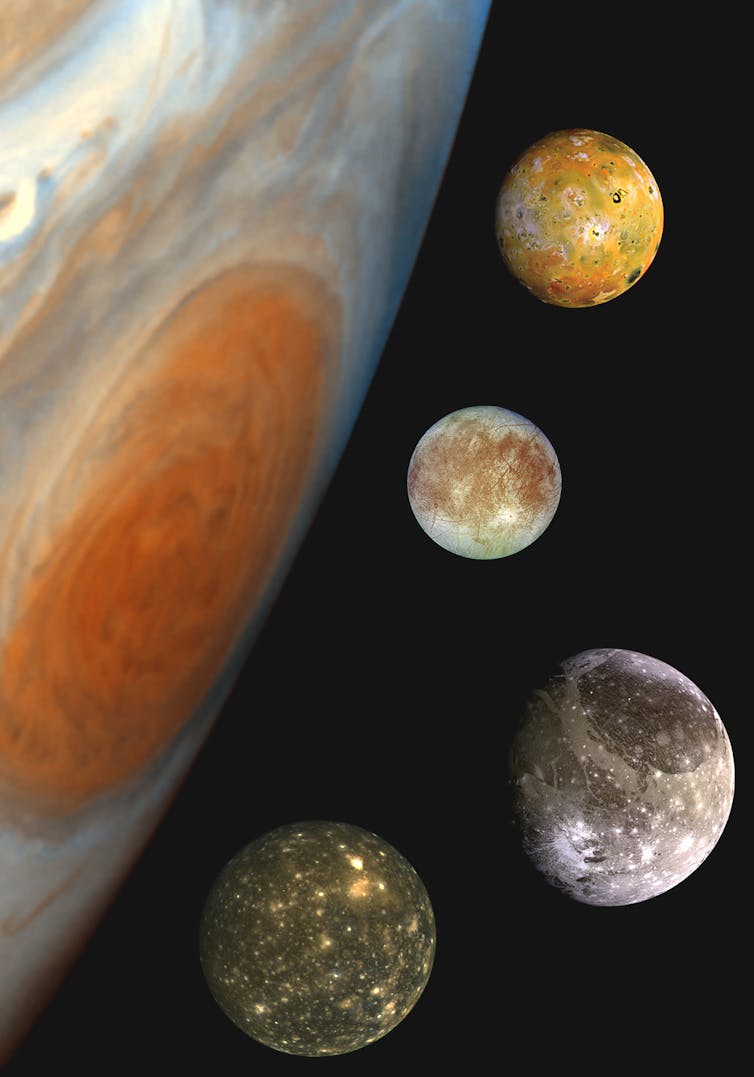
Meet Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto
Jupiter has dozens of moons. Four of them in particular are of interest to planetary scientists.
Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto are, like Earth’s Moon, relatively large, spherical complex worlds. Two previous NASA missions have sent spacecraft to orbit the Jupiter system and collected data on these moons. The Galileo mission orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003 and led to geological discoveries on all four large moons. The Juno mission is still orbiting Jupiter today and has provided scientists with an unprecedented view into Jupiter’s composition, structure and space environment.
These missions and other observations revealed that Io, the closest of the four to its host planet, is abuzz with geological activity, including lava lakes, volcanic eruptions and tectonically formed mountains. But it is not home to large amounts of water.
Europa, Ganymede and Callisto, in contrast, have icy landscapes. Europa’s surface is a frozen wonderland with a young but complex history, possibly including icy analogs of plate tectonics and volcanoes. Ganymede, the largest moon in the entire solar system, is bigger than Mercury and has its own magnetic field generated internally from a liquid metal core. Callisto appears somewhat inert compared to the others, but serves as a valuable time capsule of an ancient past that is no longer accessible on the youthful surfaces of Europa and Io.
Most exciting of all: Europa, Ganymede and Callisto all almost certainly possess underground oceans of liquid water.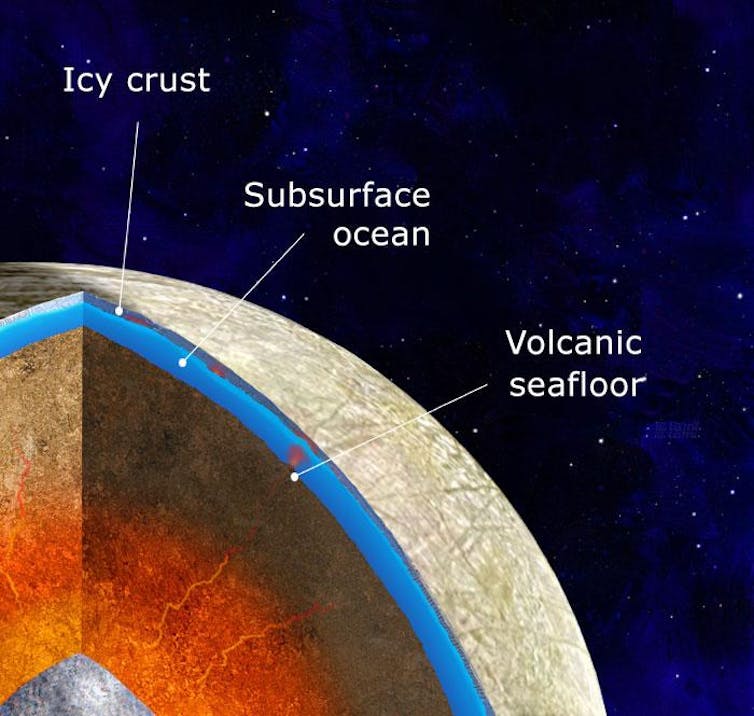
Ocean worlds
Europa, Ganymede and Callisto have chilly surfaces that are hundreds of degrees below zero. At these temperatures, ice behaves like solid rock.
But just like Earth, the deeper underground you go on these moons, the hotter it gets. Go down far enough and you eventually reach the temperature where ice melts into water. Exactly how far down this transition occurs on each of the moons is a subject of debate that scientists hope to resolve with JUICE and Europa Clipper. While the exact depths are still uncertain, scientists are confident that these oceans exist.
The best evidence of these oceans comes from Jupiter’s magnetic field. Saltwater is electrically conductive. So as these moons travel through Jupiter’s magnetic field, they generate a secondary, smaller magnetic field that signals to researchers the presence of an underground ocean. Using this technique, planetary scientists have been able to show that the three moons contain underground oceans. And these oceans are not small – Europa’s ocean alone might have more than double the water of all of Earth’s oceans combined.
An obvious and tantalizing next question is whether these oceans can support extraterrestrial life. Liquid water is an important piece of what makes for a habitable world, but far from the only requirement for life. Life also needs energy and certain chemical compounds in addition to water to flourish. Because these oceans are hidden beneath miles of solid ice, sunlight and photosynthesis are out. But it’s possible other sources could provide the needed ingredients.
On Europa, for example, the liquid water ocean overlays a rocky interior. That rocky seafloor could provide energy and chemicals through underwater volcanoes that could make Europa’s ocean habitable. But it is also possible that Europa’s ocean is a sterile, inhospitable place – scientists need more data to answer these questions.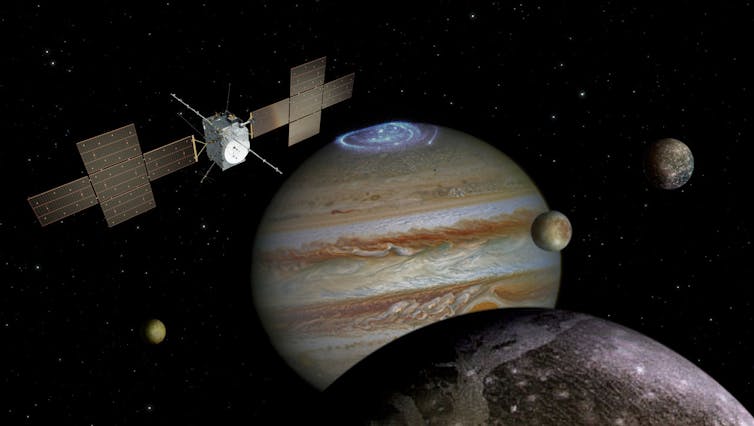
Upcoming missions from ESA and NASA
Europa Clipper and JUICE are set up to give scientists game-changing information about the potential habitability of Jupiter’s moons. While both missions will gather data on multiple moons, JUICE will spend time orbiting and focusing on Ganymede, and Europa Clipper will make dozens of close flybys of Europa.
Both of the spacecraft will carry a suite of scientific instruments built specifically to investigate the oceans. Onboard radar will allow Europa Clipper and JUICE to probe into the moons’ outer layers of solid ice. Radar could reveal any small pockets of liquid water in the ice, or, in the case of Europa, which has a thinner outer ice layer than Ganymede and Callisto, hopefully detect the larger ocean.
Magnetometers will also be on both missions. These tools will give scientists the opportunity to study the secondary magnetic fields produced by the interaction of conductive oceans with Jupiter’s field in great detail and will hopefully give researchers clues to salinity and volumes of the oceans.
Scientists will also observe small variations in the moons’ gravitational pulls by tracking subtle movements in both spacecrafts’ orbits, which could help determine if Europa’s seafloor has volcanoes that provide the needed energy and chemistry for the ocean to support life.
Finally, both craft will carry a host of cameras and light sensors that will provide unprecedented images of the geology and composition of the moons’ icy surfaces.
Maybe one day, a spacecraft will be able to drill through the miles of solid ice on Europa, Ganymede or Callisto and explore oceans directly. Until then, observations from spacecraft like Europa Clipper and JUICE are scientists’ best bet for learning about these ocean worlds.
When Galileo discovered these moons in 1609, they were the first objects known to directly orbit another planet. Their discovery was the final nail in the coffin of the theory that Earth – and humanity – resides at the center of the universe. Maybe these worlds have another humbling surprise in store.
This article, originally published April 10, 2023, has been updated with details about the Europa Clipper launch.
Mike Sori, Assistant Professor of Planetary Science, Purdue University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Forgotten Genius Fridays
Valerie Thomas: NASA Engineer, Inventor, and STEM Trailblazer
Last Updated on February 10, 2026 by Daily News Staff![]()
Valerie Thomas is a true pioneer in the world of science and technology. A NASA engineer and physicist, she is best known for inventing the illusion transmitter, a groundbreaking device that creates 3D images using concave mirrors. This invention laid the foundation for modern 3D imaging and virtual reality technologies.
Beyond her inventions, Thomas broke barriers as an African American woman in STEM, mentoring countless young scientists and advocating for diversity in science and engineering. Her work at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center helped advance satellite technology and data visualization, making her contributions both innovative and enduring.
In our latest short video, we highlight Valerie Thomas’ remarkable journey—from her early passion for science to her groundbreaking work at NASA. Watch and be inspired by a true STEM pioneer whose legacy continues to shape the future of space and technology.
🎥 Watch the video here: https://youtu.be/P5XTgpcAoHw
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Forgotten Genius Fridays
https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge-2/forgotten-genius-fridays/
🧠 Forgotten Genius Fridays
A Short-Form Series from The Knowledge by STM Daily News
Every Friday, STM Daily News shines a light on brilliant minds history overlooked.
Forgotten Genius Fridays is a weekly collection of short videos and articles dedicated to inventors, innovators, scientists, and creators whose impact changed the world—but whose names were often left out of the textbooks.
From life-saving inventions and cultural breakthroughs to game-changing ideas buried by bias, our series digs up the truth behind the minds that mattered.
Each episode of The Knowledge runs 30–90 seconds, designed for curious minds on the go—perfect for YouTube Shorts, TikTok, Reels, and quick reads.
Because remembering these stories isn’t just about the past—it’s about restoring credit where it’s long overdue.
🔔 New episodes every Friday
📺 Watch now at: stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge
🧠 Now you know.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
Beneath the Waves: The Global Push to Build Undersea Railways
Undersea railways are transforming transportation, turning oceans from barriers into gateways. Proven by tunnels like the Channel and Seikan, these innovations offer cleaner, reliable connections for passengers and freight. Ongoing projects in China and Europe, alongside future proposals, signal a new era of global mobility beneath the waves.

For most of modern history, oceans have acted as natural barriers—dividing nations, slowing trade, and shaping how cities grow. But beneath the waves, a quiet transportation revolution is underway. Infrastructure once limited by geography is now being reimagined through undersea railways.
Undersea rail tunnels—like the Channel Tunnel and Japan’s Seikan Tunnel—proved decades ago that trains could reliably travel beneath the ocean floor. Today, new projects are expanding that vision even further.
Around the world, engineers and governments are investing in undersea railways—tunnels that allow high-speed trains to travel beneath oceans and seas. Once considered science fiction, these projects are now operational, under construction, or actively being planned.

Undersea Rail Is Already a Reality
Japan’s Seikan Tunnel and the Channel Tunnel between the United Kingdom and France proved decades ago that undersea railways are not only possible, but reliable. These tunnels carry passengers and freight beneath the sea every day, reshaping regional connectivity.
Undersea railways are cleaner than short-haul flights, more resilient than bridges, and capable of lasting more than a century. As climate pressures and congestion increase, rail beneath the sea is emerging as a practical solution for future mobility.
What’s Being Built Right Now
China is currently constructing the Jintang Undersea Railway Tunnel as part of the Ningbo–Zhoushan high-speed rail line, while Europe’s Fehmarnbelt Fixed Link will soon connect Denmark and Germany beneath the Baltic Sea. These projects highlight how transportation and technology are converging to solve modern mobility challenges.
The Mega-Projects Still on the Drawing Board
Looking ahead, proposals such as the Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel and the long-studied Strait of Gibraltar rail tunnel could reshape global affairs by linking regions—and even continents—once separated by water.
Why Undersea Rail Matters
The future of transportation may not rise above the ocean—but run quietly beneath it.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Space and Tech
Blue Origin Launches First Human Spaceflight of 2026 with New Shepard NS-38
Blue Origin successfully completed its first human spaceflight of 2026 with New Shepard NS-38, carrying six private astronauts and marking 98 humans flown to space.

Blue Origin has officially kicked off its 2026 flight calendar, successfully completing the 38th mission of its New Shepard program and further solidifying its role in commercial human spaceflight.
The suborbital flight, known as NS-38, carried six private astronauts beyond the Kármán line, offering several minutes of weightlessness and sweeping views of Earth before a safe return to West Texas. The mission marks the first New Shepard launch of 2026 and another milestone for Blue Origin’s reusable spaceflight system.

Vegas High-Speed Rail Hits 99% Milestone – STM Daily News Podcast
The NS-38 Crew
The six-person crew aboard NS-38 included:
- Tim Drexler
- Dr. Linda Edwards
- Alain Fernandez
- Alberto Gutiérrez
- Jim Hendren
- Dr. Laura Stiles
With this flight, New Shepard has now flown 98 humans into space, representing 92 individual passengers. The growing total reflects Blue Origin’s emphasis on routine, repeatable access to space—once considered experimental, now becoming operational.
A Reliable Start to 2026
Blue Origin leadership emphasized reliability and customer trust as central priorities moving into the new year.
“As we enter 2026, we’re focused on continuing to deliver transformational experiences for our customers through the proven capability and reliability of New Shepard,” said Phil Joyce, Senior Vice President of New Shepard. “We are grateful for our astronaut customers who put their trust in our team to bring this experience into reality.”
The fully reusable New Shepard rocket and capsule system has demonstrated strong safety performance, autonomous operations, and consistent recovery—key elements in scaling human spaceflight.
Building Toward a Larger Vision
Beyond space tourism, New Shepard plays a foundational role in Blue Origin’s long-term goal of enabling millions of people to live and work in space for the benefit of Earth.
As the company’s first operational human spaceflight system, New Shepard supports:
- Reusable launch vehicle testing
- Human-rated safety system validation
- Increased launch cadence and manufacturing expertise
- Future Blue Origin programs and missions
Each successful flight expands operational confidence while helping normalize commercial access to space.
What’s Next for Aspiring Astronauts
Blue Origin continues to accept interest from future New Shepard passengers, with additional flights expected throughout 2026. The company also released commemorative merchandise from the NS-38 mission, now available through the Blue Origin Shop.
As commercial spaceflight matures, missions like NS-38 highlight the industry’s shift from novelty to normalcy—bringing space closer to scientists, explorers, and private citizens alike.
Related Articles & Information
- Blue Origin – New Shepard Program Overview
Official overview of Blue Origin’s reusable suborbital rocket and human spaceflight system. - Blue Origin – Human Spaceflight Missions
Details on past and upcoming crewed New Shepard missions. - NASA: Humans in Space
NASA’s overview of human spaceflight history and current programs. - Commercial Spaceflight: How Private Companies Are Changing Access to Space
STM Daily News coverage of the growing space tourism and commercial launch industry. - Reusable Rockets Explained: Why They Matter
An explainer on reusable rocket technology and its impact on space exploration.
For more updates, insights, and in-depth coverage of space exploration and commercial spaceflight, visit the STM Daily News blog at stmdailynews.com. From mission breakdowns to industry trends and technology explainers, STM Daily News keeps you informed about humanity’s journey beyond Earth.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
