STM Daily News
Oil and gas communities are a blind spot in America’s climate and economic policies
Rangely, Colorado, like many U.S. towns, relies heavily on the oil and gas industry. However, transitioning away from fossil fuels poses economic risks.
Last Updated on September 21, 2024 by Daily News Staff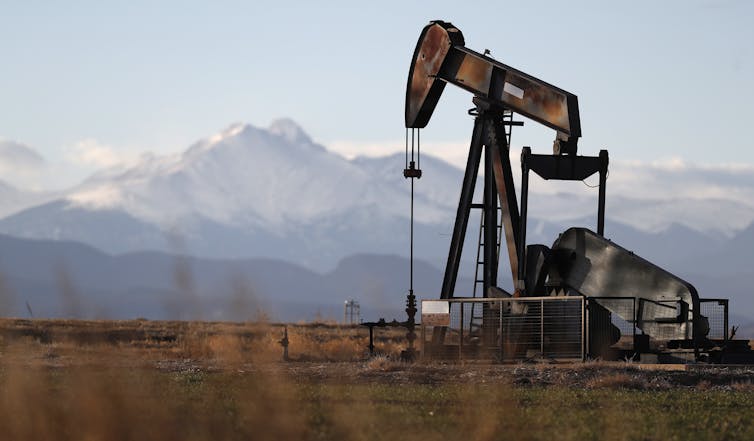
Noah Kaufman, Columbia University
On a recent visit to Rangely, a small town in northwest Colorado, my colleagues and I met with the administrators of a highly regarded community college to discuss the town’s economy. Leaving the scenic campus, we saw families driving into the mountains in off-road vehicles, a favorite activity for this outdoors-loving community. With a median household income above US$70,000 and a low cost of living, Rangely does not have the signs of a town in economic distress.
But an existential risk looms over Rangely. The town is here because of an oil boom during World War II. Today, the oil and gas industry contributes over half of the county’s economic output.
Rangely is not unique in the United States, which is the world’s largest producer of oil and natural gas. There are towns across the country that depend on the oil and gas industry for well-paying jobs and public revenues that fund their schools and other critical services.
A heavy dependence on any single industry is risky, and the oil industry is prone to booms and busts. But the economies of oil- and gas-dependent towns face a unique threat from global efforts to address the risks of climate change, which is fueled by the burning of oil and natural gas. Any serious strategy to halt global warming involves policies that will, over time, sharply reduce demand for all fossil fuels.
Early signs of this transformation can be seen in last year’s international agreement to “transition away from fossil fuels” and in the spread of electric vehicles that are starting to displace gasoline- and diesel-powered cars, trucks and buses.
As an economist who worked at the White House during the Obama administration and early Biden administration, I contributed to detailed strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to support communities in economic distress. But we did not have a plan to prepare oil and gas towns like Rangely for future economic challenges.
Why oil and gas towns are overlooked
Congress has prioritized support for small towns in recent legislation. However, oil- and gas-dependent towns were largely absent from these strategies for three primary reasons.
First is a perceived lack of urgency. The attention to a “just transition” as the nation moves away from fossil fuels has been disproportionately directed to coal-dependent communities. U.S. coal production has declined for 15 years, and a continued transition away from coal appears imminent and inevitable.
In contrast, U.S. production of oil and natural gas continues to grow. To be sure, some oil and gas communities are already struggling. But the widespread economic risks of a shift away from oil and gas may feel more like a problem for future decades.
Second, politicians downplay risks to oil and gas communities.
Most Republicans are not planning for a future decline in oil and gas production at all, and that includes many local politicians in oil and gas-dependent communities. For their part, most Democratic politicians prefer to focus on how climate action can be an engine of future economic growth. President Joe Biden likes to say, “When I think about climate change, I think jobs.”
He is not wrong to highlight the economic opportunities of climate solutions. But clean energy jobs rarely offer one-for-one replacements for the high-paying jobs in the oil and gas industries and the public revenues those industries bring local communities.
Third, economists’ policy toolbox is poorly suited to the challenges facing oil and gas communities.
Proposals to support local economic development commonly suggest targeting persistently distressed local economies with measures such as wage subsidies that have the potential to rapidly put more people to work.
A different prescription is needed for oil and gas communities, which are not generally struggling today. Over the 15-year period prior to the pandemic, the U.S. counties with oil and gas production experienced average annual GDP growth of 2.4% per year, compared with 1.9% nationwide.
Most oil and gas communities do not need economic stimulus policies that provide immediate relief. What they need are holistic economic development strategies that can cultivate new industries – building on their existing strengths – that will enable them to prosper into the future.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/NL6to/1
Solutions to help oil and gas towns prepare
Harvard economist Ricardo Hausmann compares the challenge of developing new economic capabilities to the game of Scrabble, where each additional letter enables the creation of more words. He cites the Finish economy as an example: It evolved from harvesting lumber to making tools that cut wood to producing automated cutting machines. From there, it evolved to sophisticated automated machines, including those used by global corporations such as telecommunications giant Nokia.
Such economic evolutions must be tailored to the characteristics of individual places. But the initial step is to recognize the problem and invest in solutions.
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe is doing this in southwest Colorado. It devotes oil and gas revenues to a Permanent Fund, which promotes fiscal sustainability by ensuring the tribe’s assets are aligned with its long-term financial goals, and a Growth Fund that diversifies the tribe’s revenue sources by investing in a range of businesses.
At the national level, a recent National Academies panel proposed the creation of a federally chartered corporation to help communities facing acute economic threats, including a future decline in oil and gas. This corporation could provide funding for displaced workers, critical public infrastructure and programs that ensure access to economic opportunities.
Colorado’s state Office of Just Transition has started to serve this role. Currently, it focuses only on the transition away from coal, with the goals of helping communities develop new economic opportunities and helping workers transition to new jobs. But its mission could be expanded in the future. In fact, Rangely is already receiving some support due to coal closures nearby.
No one-size-fits-all solution
Small, rural towns like Rangely illustrate how oil- and gas-reliant regions will need unique strategies tailored to the strengths and limitations of individual places. No off-the-shelf playbook exists.
Our group of researchers who visited Rangely are part of the Resilient Energy Economies initiative, which was created by universities, research institutes and philanthropic organizations to ensure that policymakers have the information they need to help fossil fuel-dependent communities successfully navigate the energy transition.
The best time to build a more resilient economy is before a crisis arrives. Anyone familiar with the Bible – or Broadway – knows the story of Joseph, whose dreams foresaw seven years of abundance for Egypt followed by seven years of famine. The pharaoh acted on Joseph’s vision, using the boom to prepare for the bust.
The United States is experiencing abundant oil and gas production today. Policymakers know risks are coming. But so far, the country is failing to prepare communities for harder days to come.
Noah Kaufman, Senior Research Scholar in Climate Economics, Columbia University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
STM Daily News is a vibrant news blog dedicated to sharing the brighter side of human experiences. Emphasizing positive, uplifting stories, the site focuses on delivering inspiring, informative, and well-researched content. With a commitment to accurate, fair, and responsible journalism, STM Daily News aims to foster a community of readers passionate about positive change and engaged in meaningful conversations. Join the movement and explore stories that celebrate the positive impacts shaping our world.
https://stmdailynews.com/category/stories-this-moment
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Making a Difference
Why Christian clergy see risk as part of their moral calling
As clergy join protests against harsh immigration enforcement, a religious ethics scholar explains why many Christian Clergy view personal risk—arrest, backlash, even violence—as part of their vocation to protect vulnerable neighbors.

Laura E. Alexander, University of Nebraska Omaha
As Christian clergy across the United States participate in ongoing protests against harsh immigration enforcement actions and further funding for U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement, many are still pondering the words of Rob Hirschfeld. On Jan. 18, 2026, Hirschfeld, Bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of New Hampshire, encouraged clergy in his diocese to “prepare for a new era of martyrdom” and put their wills and affairs in order.
He asserted that “it may be that now is no longer the time for statements, but for us with our bodies to stand between the powers of this world and the most vulnerable.”
Hirschfeld’s words attracted a lot of attention, with clergy generally responding positively, though at least one priest argued that he “did not sign up to be a martyr” and had a family and church relying on him.
Other clergy have willingly faced arrest for their advocacy on behalf of immigrants, seeing it as a moral calling. Rev. Karen Larson was arrested while protesting at the Minneapolis airport. She stated that when people are being separated from their families and taken to unknown detention centers, “this is our call” to protest on their behalf.
As a scholar of religious ethics, I am interested in how Christian clergy and thinkers consider personal risk when they feel called to engage in social action.
Ethics of risk
There are many examples of Christian leaders who have taken on risks out of a religious and moral obligation to provide spiritual care for people in need or advocate for oppressed communities.
Most data on the risks that clergy face in their roles as religious leaders comes from studies of religious leaders in institutional settings, such as hospitals or prisons.
Scholarship on clergy and chaplains in medical settings points to a professional obligation to take on risks. Similar to medical providers who often see risking exposure to infection as part of their professional responsibility, many clergy and chaplains in medical settings understand their vocation to include such a risk.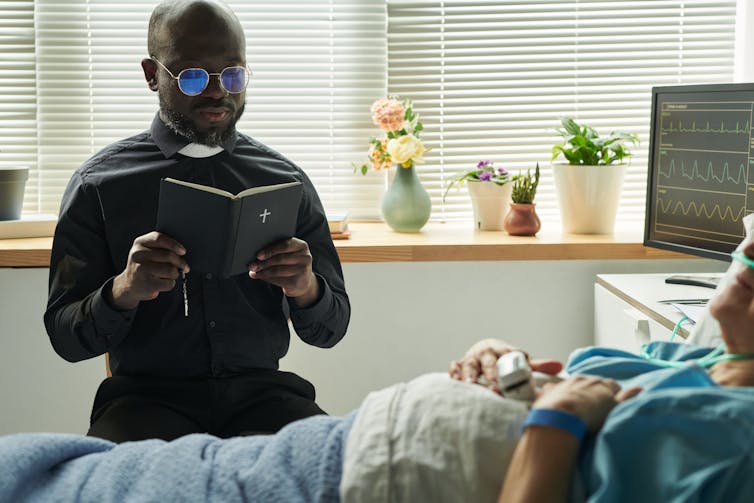
Questions about professional risks became particularly acute during the early years of the HIV/AIDS crisis, when researchers were uncertain exactly how the disease was spread and caregivers feared they might acquire HIV through their bedside work.
In her memoir about chaplaincy with HIV patients, Audrey Elisa Kerr notes that Riverside Church in New York continued to organize funerals, ministries and support groups for HIV/AIDS patients despite “terror” in the wider community about contagion.
As a chaplain herself, Kerr says this story of “radical hospitality” inspired her to set aside her own fears and embrace her professional role caring for people who were ill and dying.
Priests and nuns of the Catholic Church who cared for HIV/AIDS patients in the 1980s risked both the fear of contagion and the disapproval of their bishops and communities, since many of the people they cared for were men who had sex with men.
Some felt, however, that they must care for those at the margins as part of their role in the church or their monastic order. Sister Carol of the Hospital Sisters of Saint Francis felt that it was simply her moral duty as a sister to “go where she was needed,” despite potential risk.
Examination of the ethical obligations of chaplains and clergy ramped up during the COVID-19 pandemic when at least some priest, pastors and hospital chaplains felt an obligation to continue visiting patients for spiritual care.
In a reflection from 2020, Rev. David Hottinger, then working at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, noted that chaplains “felt privileged” to use their professional skills, even though they took on extra risk because they did not always have access to adequate protective equipment.
Risks in other institutional settings are not such a matter of life and death. Because of their professional preaching function, however, clergy in church settings do accept the risk of alienating church members when they feel religiously called to speak about social issues. Rev. Teri McDowell Ott has written about taking risks when discussing LGBTQ+ inclusion and starting a prison ministry.
Risk-taking during social protest
For many clergy, religious and ethical obligations extend beyond their work in institutions like churches and hospitals and include their witness in public life.
Many feel an obligation to preach on issues of moral importance, even topics that are considered controversial and might elicit strong disagreement. It is common for priests and pastors in conservative churches to include messages against legalized abortion in their sermons.
Tom Ascol of the Center for Baptist Leadership urged Baptist pastors to preach about abortion in the lead-up to the 2024 presidential election.
Rev. Leah Schade, a Lutheran minister and scholar, has argued that since 2017, mainline pastors have preached more often on issues like racism, environmental justice or gun violence. Schade says pastors are inspired to speak more bluntly about social issues because of their religious concern for people who are at risk of harm from injustice or government policies.
Some clergy view their moral obligations as going beyond preaching and leading them to on-the-ground advocacy and protest. Rev. Brandy Daniels of the Disciples of Christ denomination examines these obligations in an article on her participation in a group of interfaith clergy in Portland, Oregon. The group was convened by a local rabbi and supported protesters for racial justice in Portland in 2017. In Daniels’ analysis, clergy took on the risk of staying in the middle of protests and facing a violent police response in order to “bear moral witness,” something they were both empowered and obligated to do as religious leaders.
Risking their lives
There are more extreme cases in which clergy who challenged government leaders or policies were killed for their words and actions of protest.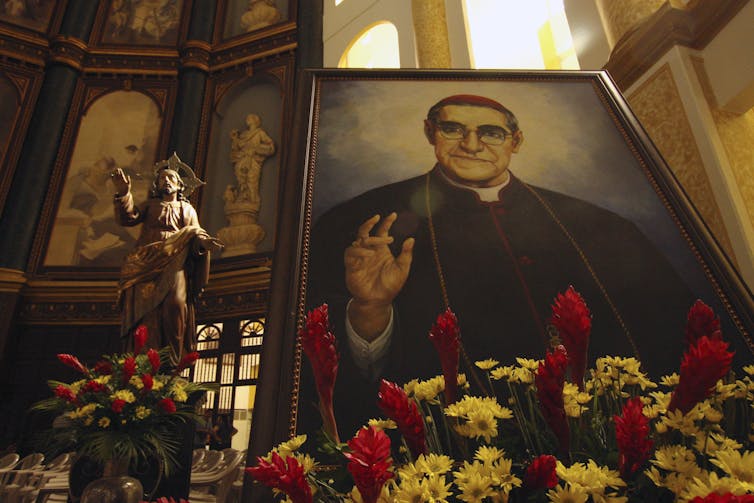
In a well-known historical example, Bishop Oscar Romero, canonized as a martyred saint by the Roman Catholic Church in 2018, was assassinated in 1980 after speaking out against human rights violations against poor and Indigenous communities committed by the government of El Salvador. Romero viewed himself, in his priestly role, as a representative of God who was obliged to “give voice to the voiceless.”
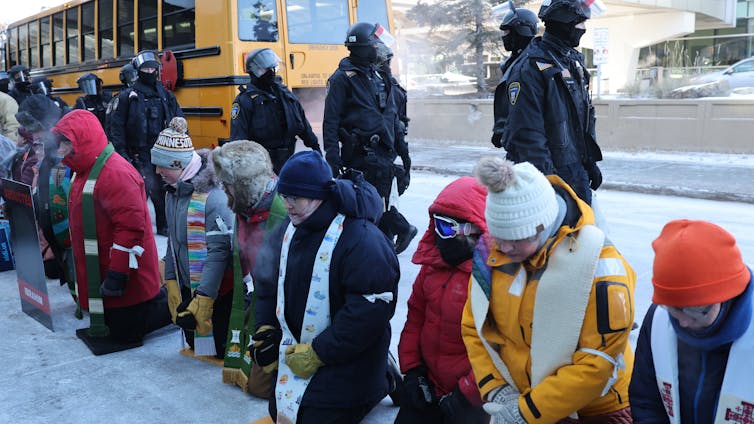
During recent protests against ICE in Minneapolis and elsewhere, many clergy risked arrest and bodily harm. Rev. Kenny Callaghan, a Metropolitan Community Church pastor, who says that ICE agents in Minneapolis pointed a gun in his face and handcuffed him as he tried to help a woman they were questioning, said, “It’s in my DNA; I have to speak up for marginalized people.”
On Jan. 23, 2026, over 100 clergy were arrested at the Minneapolis-St. Paul airport as they protested and prayed against ICE actions. Rev. Mariah Furness Tollgaard said that she and others accepted being arrested as a way of demonstrating public support for migrants who are afraid to leave their homes.
In Chicago, ministers have been hit with projectiles and violently arrested. Presbyterian pastor David Black was shot in the head with a pepper spray projectile while protesting outside an immigration detention center in October 2025.
The clergy have told reporters that they feel a particular call to be out in public and to protect and support their vulnerable neighbors against ICE raids, at a time when families are afraid to go to school or work and U.S. citizens have been swept up in enforcement tactics as well.
As I see it, for these and many Christian clergy and ethicists, the call to ministry includes an obligation to express their values of care for vulnerable neighbors precisely through a public willingness to accept personal risk.
Laura E. Alexander, Associate Professor of Religious Studies, University of Nebraska Omaha
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
STM Daily News is a vibrant news blog dedicated to sharing the brighter side of human experiences. Emphasizing positive, uplifting stories, the site focuses on delivering inspiring, informative, and well-researched content. With a commitment to accurate, fair, and responsible journalism, STM Daily News aims to foster a community of readers passionate about positive change and engaged in meaningful conversations. Join the movement and explore stories that celebrate the positive impacts shaping our world.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
STM Daily News
Chinamaxxing: The Viral Trend Turning Geopolitics Into Aesthetic Fantasy
A viral social media trend called “Chinamaxxing” is turning geopolitics into aesthetic comparison—revealing more about generational frustration than China itself.
Last Updated on February 11, 2026 by Daily News Staff
At first glance, the videos seem harmless enough.
Clean subways gliding into spotless stations. Neon skylines glowing at night. Clips of high-speed trains, cashless stores, orderly crowds. Overlaid text reads something like, “Meanwhile in China…” or “They figured it out.”
This is “Chinamaxxing,” a loosely defined but increasingly visible social media trend where mostly young users frame China as a model of efficiency, stability, and modernity—often in contrast to life in the West.
What makes the trend notable isn’t just its subject, but its tone. Chinamaxxing is rarely explicit political advocacy. It’s not a manifesto. It’s a mood. Aesthetic admiration blended with subtle critique, delivered through short, visually compelling clips that invite comparison without context.
And that’s precisely why it has sparked debate.
What Is “Chinamaxxing,” Really?
Despite the provocative name, Chinamaxxing isn’t a coordinated movement or ideology. It’s better understood as an algorithm-driven pattern—a recurring style of content that rewards certain visuals and emotional cues.
Most Chinamaxxing content emphasizes:
- Infrastructure and urban design
- Technology embedded in daily life
- Perceived order and efficiency
- Implicit contrast with Western dysfunction
What it typically omits:
- Political repression and censorship
- State surveillance
- Limits on speech and dissent
- The lived diversity of Chinese experiences
The result is a highly curated portrayal—less about China as a nation, and more about what viewers want to believe is possible somewhere else.
Why It’s Gaining Traction Now
The rise of Chinamaxxing says as much about the West as it does about China.
For many young users, particularly Gen Z, the backdrop is familiar: rising housing costs, student debt, healthcare anxiety, political polarization, and a growing sense that institutions no longer function as promised.
In that environment, visually persuasive content showing order and functionality carries emotional weight. It offers relief from chaos—real or perceived.
Social platforms amplify this effect. Short-form video rewards clarity, contrast, and immediacy. A clean subway platform communicates more in five seconds than a policy analysis ever could. Nuance does not trend well. Aesthetics do.
The Social and Political Criticism
Critics argue Chinamaxxing crosses a line from curiosity into distortion.
By focusing exclusively on infrastructure and surface-level efficiency, the trend risks:
- Normalizing authoritarian governance through lifestyle framing
- Reducing political systems to consumer experiences
- Ignoring the tradeoffs that make such systems possible
Supporters counter that Western media has long flattened China into a single negative narrative, and that admiration for specific aspects of another society is not the same as endorsing its government.
Both perspectives, however, miss something important.
What the Trend Actually Reveals
Chinamaxxing isn’t primarily about China. It’s about disillusionment.
It reflects a generation that:
- Feels let down by existing systems
- Engages politics emotionally rather than institutionally
- Uses visual culture to express dissatisfaction indirectly
In this context, China becomes a projection surface—not because it is perfect, but because it appears functional.
That distinction matters.
Why This Matters
Chinamaxxing highlights how political understanding is evolving in the digital age. Governance is increasingly consumed not through debate or civic participation, but through comparison clips, memes, and aesthetics.
The risk isn’t admiration. It’s oversimplification.
When complex societies are reduced to visuals alone, public discourse loses depth. But when those visuals resonate, they also signal real unmet needs: stability, competence, and trust in institutions.
Ignoring that signal would be a mistake.
The STM Daily News Perspective
Chinamaxxing is not an endorsement, a conspiracy, or a joke. It is a cultural artifact—one that reflects generational anxiety, algorithmic storytelling, and the widening gap between expectations and reality.
The question it raises isn’t whether China is better.
It’s why so many people feel their own systems are no longer working.
Related Reading
- BBC News: China Coverage and Global Context
- The Atlantic: Technology, Media, and Internet Culture Analysis
- Pew Research Center: Global Attitudes and Political Perception
- The New York Times: China and International Affairs
- Brookings Institution: China Policy and Global Governance
More on This Topic from STM Daily News
Stay tuned to STM Daily News for more stories exploring internet culture, social media trends, and how digital platforms shape public perception. We’ll be publishing in-depth pieces that break down the societal impact of viral phenomena like Chinamaxxing, the psychology behind online political trends, and the evolving language of Gen Z culture.
Want alerts? Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter for the latest insights and analysis.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Community
What if universal rental assistance were implemented to deal with the housing crisis?
A significant number of American families facing unaffordable rents are living in motels. While many believe a housing shortage causes high rents, experts suggest that expanding rental assistance is more effective. Making subsidies available to all eligible low-income households could tackle this affordability crisis significantly.
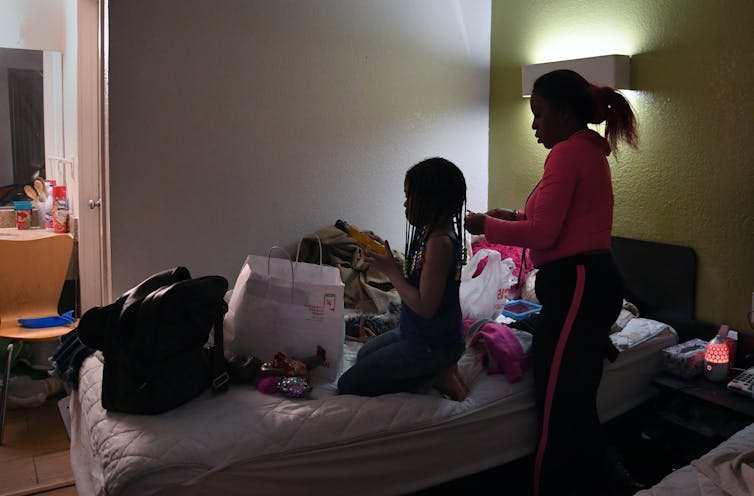
What if universal rental assistance were implemented to deal with the housing crisis?
Alex Schwartz, The New School and Kirk McClure, University of Kansas
If there’s one thing that U.S. politicians and activists from across the political spectrum can agree on, it’s that rents are far too high.
Many experts believe that this crisis is fueled by a shortage of housing, caused principally by restrictive regulations.
Rents and home prices would fall, the argument goes, if rules such as minimum lot- and house-size requirements and prohibitions against apartment complexes were relaxed. This, in turn, would make it easier to build more housing.
As experts on housing policy, we’re concerned about housing affordability. But our research shows little connection between a shortfall of housing and rental affordability problems. Even a massive infusion of new housing would not shrink housing costs enough to solve the crisis, as rents would likely remain out of reach for many households.
However, there are already subsidies in place that ensure that some renters in the U.S. pay no more than 30% of their income on housing costs. The most effective solution, in our view, is to make these subsidies much more widely available.
A financial sinkhole
Just how expensive are rents in the U.S.?
According to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, a household that spends more than 30% of its income on housing is deemed to be cost-burdened. If it spends more than 50%, it’s considered severely burdened. In 2023, 54% of all renters spent more than 30% of their pretax income on housing. That’s up from 43% of renters in 1999. And 28% of all renters spent more than half their income on housing in 2023.
Renters with low incomes are especially unlikely to afford their housing: 81% of renters making less than $30,000 spent more than 30% of their income on housing, and 60% spent more than 50%.
Estimates of the nation’s housing shortage vary widely, reaching up to 20 million units, depending on analytic approach and the time period covered. Yet our research, which compares growth in the housing stock from 2000 to the present, finds no evidence of an overall shortage of housing units. Rather, we see a gap between the number of low-income households and the number of affordable housing units available to them; more affluent renters face no such shortage. This is true in the nation as a whole and in nearly all large and small metropolitan areas.
Would lower rents help? Certainly. But they wouldn’t fix everything.
We ran a simulation to test an admittedly unlikely scenario: What if rents dropped 25% across the board? We found it would reduce the number of cost-burdened renters – but not by as much as you might think.
Even with the reduction, nearly one-third of all renters would still spend more than 30% of their income on housing. Moreover, reducing rents would help affluent renters much more than those with lower incomes – the households that face the most severe affordability challenges.
The proportion of cost-burdened renters earning more than $75,000 would fall from 16% to 4%, while the share of similarly burdened renters earning less than $15,000 would drop from 89% to just 80%. Even with a rent rollback of 25%, the majority of renters earning less than $30,000 would remain cost-burdened.
Vouchers offer more breathing room
Meanwhile, there’s a proven way of making housing more affordable: rental subsidies.
In 2024, the U.S. provided what are known as “deep” housing subsidies to about 5 million households, meaning that rent payments are capped at 30% of their income.
These subsidies take three forms: Housing Choice Vouchers that enable people to rent homes in the private market; public housing; and project-based rental assistance, in which the federal government subsidizes the rents for all or some of the units in properties under private and nonprofit ownership.
The number of households participating in these three programs has increased by less than 2% since 2014, and they constitute only 25% of all eligible households. Households earning less than 50% of their area’s median family income are eligible for rental assistance. But unlike Social Security, Medicare or food stamps, rental assistance is not an entitlement available to all who qualify. The number of recipients is limited by the amount of funding appropriated each year by Congress, and this funding has never been sufficient to meet the need.
By expanding rental assistance to all eligible low-income households, the government could make huge headway in solving the rental affordability crisis. The most obvious option would be to expand the existing Housing Choice Voucher program, also known as Section 8.
The program helps pay the rent up to a specified “payment standard” determined by each local public housing authority, which can set this standard at between 80% and 120% of the HUD-designated fair market rent. To be eligible for the program, units must also satisfy HUD’s physical quality standards.
Unfortunately, about 43% of voucher recipients are unable to use it. They are either unable to find an apartment that rents for less than the payment standard, meets the physical quality standard, or has a landlord willing to accept vouchers.
Renters are more likely to find housing using vouchers in cities and states where it’s illegal for landlords to discriminate against voucher holders. Programs that provide housing counseling and landlord outreach and support have also improved outcomes for voucher recipients.
However, it might be more effective to forgo the voucher program altogether and simply give eligible households cash to cover their housing costs. The Philadelphia Housing Authority is currently testing out this approach.
The idea is that landlords would be less likely to reject applicants receiving government support if the bureaucratic hurdles were eliminated. The downside of this approach is that it would not prevent landlords from renting out deficient units that the voucher program would normally reject.
Homeowners get subsidies – why not renters?
Expanding rental assistance to all eligible low-income households would be costly.
The Urban Institute, a nonpartisan think tank, estimates it would cost about $118 billion a year.
However, Congress has spent similar sums on housing subsidies before. But they involve tax breaks for homeowners, not low-income renters. Congress forgoes billions of dollars annually in tax revenue it would otherwise collect were it not for tax deductions, credits, exclusions and exemptions. These are known as tax expenditures. A tax not collected is equivalent to a subsidy payment.
For example, from 1998 through 2017 – prior to the tax changes enacted by the first Trump administration in 2017 – the federal government annually sacrificed $187 billion on average, after inflation, in revenue due to mortgage interest deductions, deductions for state and local taxes, and for the exemption of proceeds from the sale of one’s home from capital gains taxes. In fiscal year 2025, these tax expenditures totaled $95.4 billion.
Moreover, tax expenditures on behalf of homeowners flow mostly to higher-income households. In 2024, for example, over 70% of all mortgage-interest tax deductions went to homeowners earning at least $200,000.
Broadening the availability of rental subsidies would have other benefits. It would save federal, state and local governments billions of dollars in homeless services. Moreover, automatic provision of rental subsidies would reduce the need for additional subsidies to finance new affordable housing. Universal rental assistance, by guaranteeing sufficient rental income, would allow builders to more easily obtain loans to cover development costs.
Of course, sharply raising federal expenditures for low-income rental assistance flies in the face of the Trump administration’s priorities. Its budget proposal for the next fiscal year calls for a 44% cut of more than $27 billion in rental assistance and public housing.
On the other hand, if the government supported rental assistance in amounts commensurate with the tax benefits given to homeowners, it would go a long way toward resolving the rental housing affordability crisis.
This article is part of a series centered on envisioning ways to deal with the housing crisis.
Alex Schwartz, Professor of Urban Policy, The New School and Kirk McClure, Professor of Urban Planning, University of Kansas
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
