Food and Beverage
Reducing Food Insecurity in Infants and Toddlers
Last Updated on June 10, 2024 by Daily News Staff
(Family Features) Food insecurity isn’t a new problem in the United States, but the economic upheaval created by the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the problem.
During the pandemic, households in the United States with children experienced an increase in food insecurity, despite overall rates of food insecurity staying the same. In 2019, 13.6% of households with children were food insecure, but by 2020, that number increased to 14.8%, according to data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
In general, child food insecurity rates are higher than overall food insecurity rates, according to the annual Map the Meal Gap study conducted by Feeding America, a nationwide nonprofit network of food banks. According to data from the Children’s Defense Fund, this is particularly prevalent among low-income families, single mother households and Black and Hispanic households.
What Food Insecurity Means for Children
Food insecurity and hunger are closely related but not quite the same. People who are food insecure don’t have reliable, ongoing access to an adequate supply of affordable, nutritious food. Hunger is a physical condition; food insecurity reflects barriers to obtaining food such as finances, physical location and transportation.
Infants and toddlers are particularly vulnerable to nutrient deficiencies because their nutrient needs are high, especially in relation to the size of their stomachs and appetites. Caregivers in food-insecure households may have little choice but to settle for cheaper, energy-dense but nutrient-poor foods. As a result, food-insecure infants and toddlers are not receiving adequate nutrition even when they may be receiving enough calories to satisfy hunger.
Even if a child isn’t physically starving, inadequate nutrition can negatively affect health in numerous ways, including immune system function, low weight, learning and developmental delays, vitamin deficiencies and more.
Ways to Help Promote Better Nutrition
Support good nutrition during infancy and toddlerhood for your own children and others in the community with these practical tips:
- Participate in (or introduce those in need to) aid programs. Government nutrition assistance programs help provide essential nutrition needs during infant and toddler years. One example is the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children (WIC), which provides a variety of resources including food and health care referrals to support mothers and young children at nutritional risk, including pregnant, breastfeeding and post-partum women, as well as infants and children up to age 5.
Another example is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), which provides benefits low-income families can use to purchase nutritious foods. For children and adults who are enrolled in certain care programs, the Child and Adult Care Food Program (CACFP) helps ensure they have access to nutritious meals and snacks. - Make purchases that work extra hard. In addition to producing foods that encourage better nutrition for children, some brands also make contributions that help offset food insecurity. For example, for every box of Plum Organics Super Smoothies purchased, the company donates a pouch to a child in need through its “The Full Effect” program. The smoothie is a specially formulated blend of fruits, vegetables, legumes and grains with no added sugars designed to fight malnutrition and help fortify the diets of children who don’t have access to regular, healthy meals.
- Act as a role model for healthy choices. Children learn by example, so be sure your little ones see you enjoying nutritious snacks, filling your plate with appropriate portions and preparing well-rounded meals. When kids are exposed to a wide range of healthy options early in life, those food choices become the norm as they grow older.
- Volunteer at a food bank. Getting hands-on by donating your time at a local food bank can help you understand the complexity of food insecurity. Many nutritious selections are perishable, and transporting and storing perishable goods is costly. Volunteers help offset a food bank’s operational expenses by contributing labor to sort donated items, prepare deliveries and more.
To find more information about foods that provide infants and toddlers the nutrients they need, visit plumorganics.com. Photos courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
Plum Organics
https://stmdailynews.com/category/food-and-drink/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Food and Beverage
Unwrap the Holidays: Whataburger Launches 12 Days of Whatacheer With Daily App Deals
Celebrate the holidays with Whataburger’s 12 Days of Whatacheer! Discover daily in-app deals, exclusive to Rewards members, from December 12–23. Unwrap new menu favorites, BOGO offers, and festive savings—only on the Whataburger App.
12 Days of Whatacheer: Festive Deals for Rewards Members
How It Works
- Who: Whataburger Rewards members (sign up in the app if you’re not already!)
- When: December 12–23, with a new offer every day
- How: Open the Whataburger App, claim the day’s deal, and enjoy with your next order
Holiday-themed graphic reading ‘12 Days of WhataCheer’ on a red background with white dots. Below the text are images of Whataburger menu items: a Cinnamon Roll, Onion Rings, a Whataburger, a Whatafresher, a Honey Butter Chicken Biscuit, and a Strawberry Shake.
Why Join the Whataburger Rewards Fun?
Get Started
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
recipes
A Sweet, Seasonal Spice Cake
Pumpkin spice may be all the rage this time of year, but don’t forget another fruit that’s sure to please: sweet, delicious apples. For an ooey-gooey breakfast, office snack or potluck dessert, turn to this Apple Spice Cake.

A Sweet, Seasonal Spice Cake
(Family Features) Pumpkin spice may be all the rage this time of year, but don’t forget another fruit that’s sure to please: sweet, delicious apples. For an ooey-gooey breakfast, office snack or potluck dessert, turn to this Apple Spice Cake that looks and tastes like it’s made for the season. Visit Culinary.net to discover more recipe inspiration.
Apple Spice Cake
Recipe courtesy of “Cookin’ Savvy”- 2 apples
- 3 tablespoons brown sugar
- 1 tablespoon cinnamon
- 1 tablespoon flour (optional)
- 1 box spice cake mix
- 1 stick butter, melted
- 4 eggs
- 1 cup milk
- 1 1/2 cups powdered sugar
- 2-3 tablespoons milk
- 1 cup chopped pecans
- Heat oven to 350 F.
- Peel, core and chop apples into bite-sized pieces. In bowl, mix apples with brown sugar, cinnamon and flour, if desired, which helps keep apples from sinking to bottom. Set aside.
- In large mixing bowl, mix spice cake mix, butter, eggs and milk. Mix in apples and pour into 9-by-13-inch pan. Bake 30-35 minutes, or until toothpick inserted in center comes out clean.
- Let cool.
- To make glaze: Mix powdered sugar and milk; pour over cooled cake.
- Top with pecans.
The fate of Lucky Supermarkets in SoCalLink: https://stmdailynews.com/the-fate-of-lucky-supermarkets-in-socal/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Recipe of the Week
Holiday Desserts Just Got a Dairy-Forward Upgrade
Holiday Desserts: From festive cookies to indulgent dips, these delicious desserts bring people together to create memories that will last a lifetime. If you’re looking to impress guests, Santa Cookies are the ultimate treat. For a unique twist, try Gingerbread Dip, featuring vanilla Greek yogurt made with 100% grass-fed organic milk.
Last Updated on December 17, 2025 by Rod Washington

Holiday Desserts Just Got a Dairy-Forward Upgrade
(Family Features) Holiday desserts set the stage for seasonal delight and add a touch of joy to gatherings. From festive cookies to indulgent dips, these delicious desserts bring people together to create memories that will last a lifetime. If you’re looking to impress guests, Santa Cookies are the ultimate treat. Made with Maple Hill Salted Butter, they’re rich, soft and full of festive spirit. For a unique twist, try Gingerbread Dip, featuring vanilla Greek yogurt made with 100% grass-fed organic milk. Whether you’re hosting or deciding what to bring to the potluck, Maple Hill’s 100% grass-fed organic dairy makes it easy to whip up desserts that are as wholesome as they are delicious. Rich in nutrients and free from GMOs, hormones and antibiotics, each product comes from farms that prioritize regenerative practices as nature intended. With a 40% healthier ratio of omega 3:6 and 40% higher levels of CLA fatty acids compared to traditional organic dairy, you can feel good about sweet treats at the holiday table. To find more recipes, visit MapleHill.com.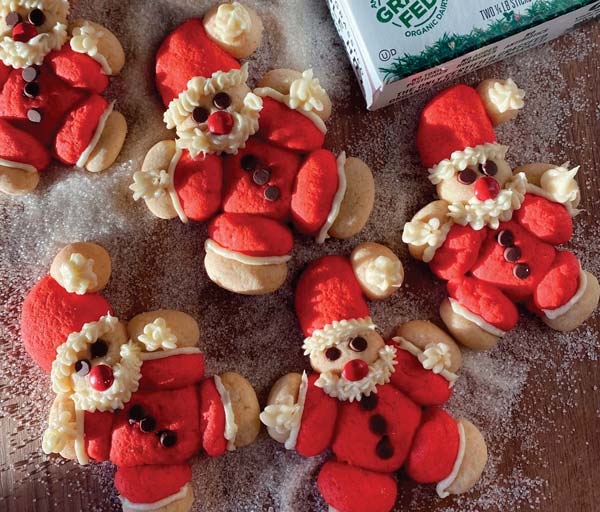
Santa Cookies
Yield: 14 cookies- 1 cup (2 sticks) Maple Hill Salted Butter, at room temperature
- 1/2 cup brown sugar
- 1 tablespoon vanilla extract
- 1 large egg, at room temperature
- 2 1/4 cups all-purpose flour
- 1/4 teaspoon salt
- 1 teaspoon red food coloring
- mini chocolate chips
- mini red chocolate-coated candies
- 1/2 cup (1 stick) Maple Hill Salted Butter, at room temperature
- 4 ounces cream cheese, at room temperature
- 1 teaspoon vanilla extract
- 2 1/2 cups powdered sugar
- Preheat oven to 350 F and line two baking sheets with parchment paper.
- In large mixing bowl, beat butter, sugar and vanilla until light and fluffy. Add egg and beat until combined. Add flour and salt; mix until dough begins to form ball.
- Remove 1 cup dough and set aside. Add red food coloring to remaining dough.
- From red cookie dough, make one 1-inch ball and five 1/2-inch balls. From plain cookie dough, make one 3/4-inch ball and five 1/4-inch balls.
- On prepared baking sheet, place red 1-inch ball and gently flatten until 1/2-inch thick. Attach four red 1/2-inch balls for arms and legs. Attach plain 3/4-inch ball for head and gently flatten until 1/2-inch thick. Attach plain 1/4-inch balls for hands and feet. Shape remaining red 1/2-inch ball into triangle for hat and attach. Repeat with remaining dough, arranging cookies 2 inches apart on baking sheet. Add chocolate candies for eyes and buttons.
- Bake 12-15 minutes, or until lightly golden.
- To make frosting: In medium bowl, beat butter and cream cheese until light and fluffy, about 3 minutes. Add vanilla and powdered sugar; mix until combined.
- To decorate: Place half of frosting in piping bag with small tip to line Santa’s arms and legs. Place other half in second piping bag with small star tip to add Santa’s beard, hat and hands. Put small dot of icing between eyes and beard and place red mini chocolate-coated candy on face for nose.
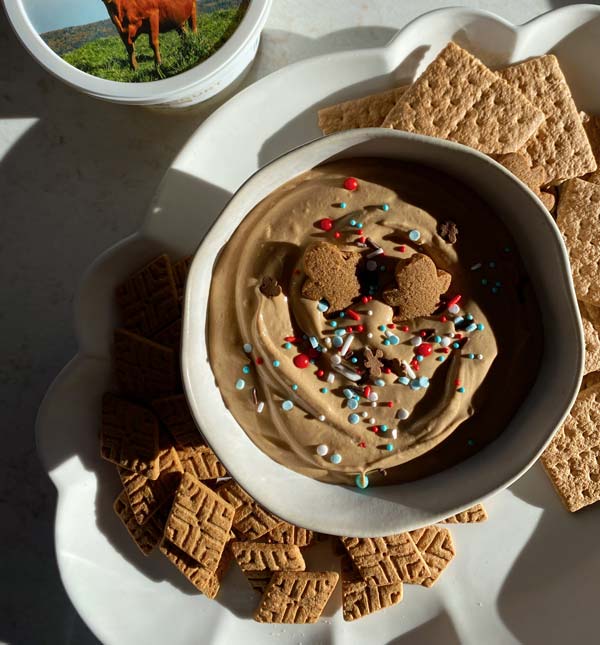
Gingerbread Dip
Servings: 8-12- 4 ounces cream cheese, at room temperature
- 1/4 cup brown sugar
- 1/4 cup powdered sugar
- 3 tablespoons molasses
- 1 container (16 ounces) Maple Hill Vanilla Greek Yogurt
- 1 teaspoon ground ginger
- 1 teaspoon ground cinnamon
- 1 teaspoon ground nutmeg
- 2 cups whipped cream
- graham crackers
- fruit
- In medium bowl using electric mixer on medium speed, beat cream cheese and sugars about 1 minute. Add molasses and mix until combined.
- Add Greek yogurt, ginger, cinnamon and nutmeg; beat until combined. Fold in whipped cream and mix until fully incorporated. Refrigerate 1 hour before serving or overnight.
- Serve with graham crackers and fruit.
At our core, we at STM Daily News, strive to keep you informed and inspired with the freshest content on all things food and beverage. From mouthwatering recipes to intriguing articles, we’re here to satisfy your appetite for culinary knowledge.
Visit our Food & Drink section to get the latest on Foodie News and recipes, offering a delightful blend of culinary inspiration and gastronomic trends to elevate your dining experience. https://stmdailynews.com/food-and-drink/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

