Julie Deshaies/iStock via Getty Images
How pecans went from ignored trees to a holiday staple – the 8,000-year history of America’s only native major nut crop
Shelley Mitchell, Oklahoma State University
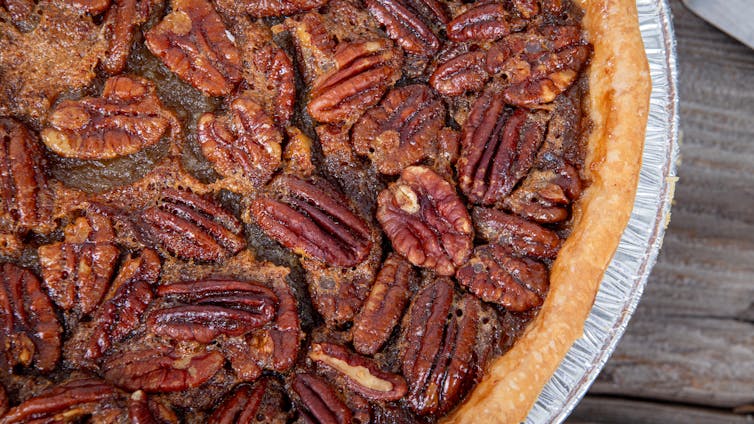
Pecans have a storied history in the United States. Today, American trees produce hundreds of million of pounds of pecans – 80% of the world’s pecan crop. Most of that crop stays here. Pecans are used to produce pecan milk, butter and oil, but many of the nuts end up in pecan pies.
Throughout history, pecans have been overlooked, poached, cultivated and improved. As they have spread throughout the United States, they have been eaten raw and in recipes. Pecans have grown more popular over the decades, and you will probably encounter them in some form this holiday season.
I’m an extension specialist in Oklahoma, a state consistently ranked fifth in pecan production, behind Georgia, New Mexico, Arizona and Texas. I’ll admit that I am not a fan of the taste of pecans, which leaves more for the squirrels, crows and enthusiastic pecan lovers.
The spread of pecans
The pecan is a nut related to the hickory. Actually, though we call them nuts, pecans are actually a type of fruit called a drupe. Drupes have pits, like the peach and cherry.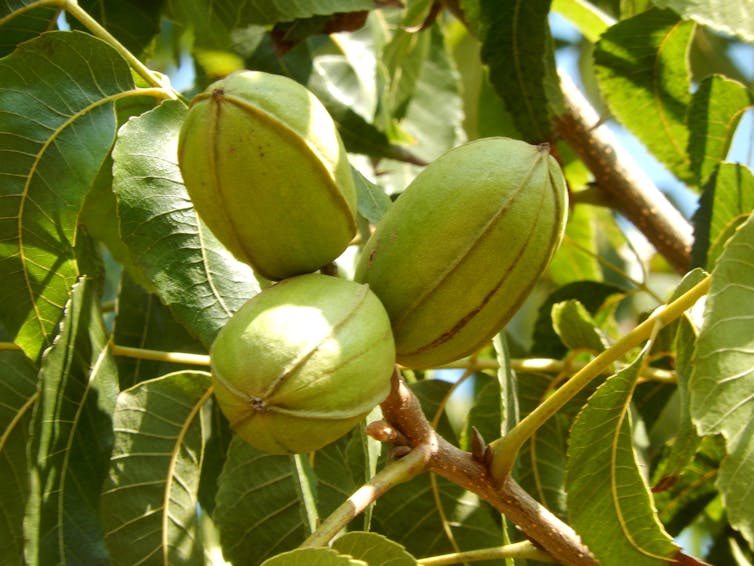
IAISI/Moment via Getty Images
The pecan nuts that look like little brown footballs are actually the seed that starts inside the pecan fruit – until the fruit ripens and splits open to release the pecan. They are usually the size of your thumb, and you may need a nutcracker to open them. You can eat them raw or as part of a cooked dish.
The pecan derives its name from the Algonquin “pakani,” which means “a nut too hard to crack by hand.” Rich in fat and easy to transport, pecans traveled with Native Americans throughout what is now the southern United States. They were used for food, medicine and trade as early as 8,000 years ago.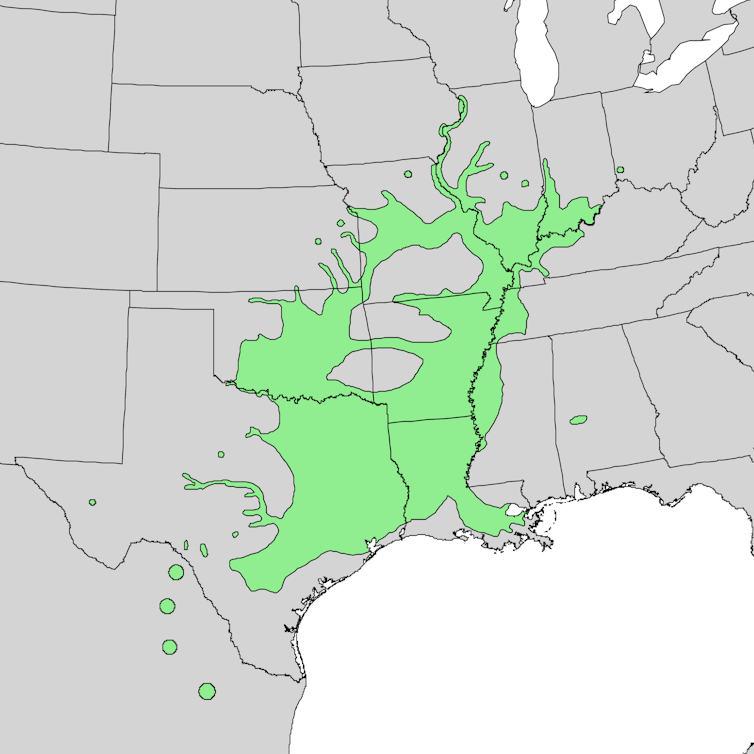
Elbert L. Little Jr. of the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service
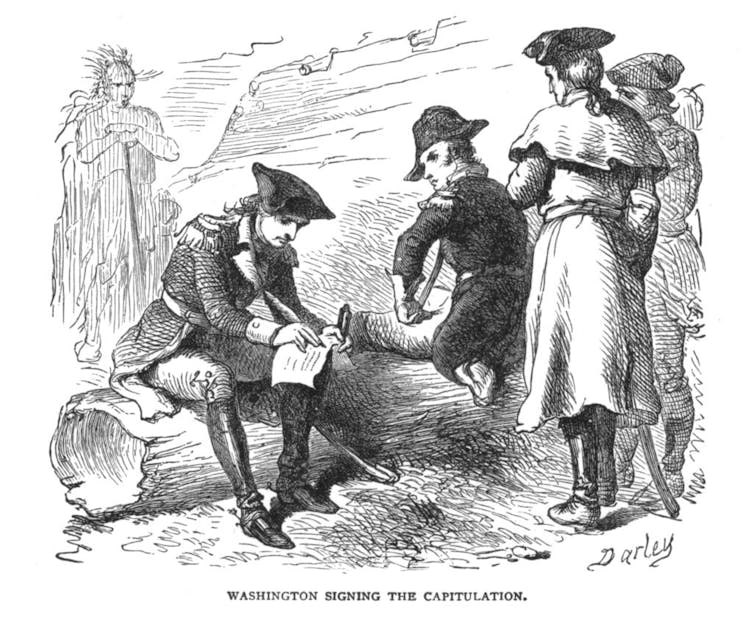
Pecans are native to the southern United States, and while they had previously spread along travel and trade routes, the first documented purposeful planting of a pecan tree was in New York in 1722. Three years later, George Washington’s estate, Mount Vernon, had some planted pecans. Washington loved pecans, and Revolutionary War soldiers said he was constantly eating them.
Meanwhile, no one needed to plant pecans in the South, since they naturally grew along riverbanks and in groves. Pecan trees are alternate bearing: They will have a very large crop one year, followed by one or two very small crops. But because they naturally produced a harvest with no input from farmers, people did not need to actively cultivate them. Locals would harvest nuts for themselves but otherwise ignored the self-sufficient trees.
It wasn’t until the late 1800s that people in the pecan’s native range realized the pecan’s potential worth for income and trade. Harvesting pecans became competitive, and young boys would climb onto precarious tree branches. One girl was lifted by a hot air balloon so she could beat on the upper branches of trees and let them fall to collectors below. Pecan poaching was a problem in natural groves on private property.
Pecan cultivation begins
Even with so obvious a demand, cultivated orchards in the South were still rare into the 1900s. Pecan trees don’t produce nuts for several years after planting, so their future quality is unknown.
Jon Frederick/iStock via Getty Images
To guarantee quality nuts, farmers began using a technique called grafting; they’d join branches from quality trees to another pecan tree’s trunk. The first attempt at grafting pecans was in 1822, but the attempts weren’t very successful.
Grafting pecans became popular after an enslaved man named Antoine who lived on a Louisiana plantation successfully produced large pecans with tender shells by grafting, around 1846. His pecans became the first widely available improved pecan variety.

Orest Lyzhechka/iStock via Getty Images
The variety was named Centennial because it was introduced to the public 30 years later at the Philadelphia Centennial Expedition in 1876, alongside the telephone, Heinz ketchup and the right arm of the Statue of Liberty.
This technique also sped up the production process. To keep pecan quality up and produce consistent annual harvests, today’s pecan growers shake the trees while the nuts are still growing, until about half of the pecans fall off. This reduces the number of nuts so that the tree can put more energy into fewer pecans, which leads to better quality. Shaking also evens out the yield, so that the alternate-bearing characteristic doesn’t create a boom-bust cycle.
US pecan consumption
The French brought praline dessert with them when they immigrated to Louisiana in the early 1700s. A praline is a flat, creamy candy made with nuts, sugar, butter and cream. Their original recipe used almonds, but at the time, the only nut available in America was the pecan, so pecan pralines were born.
Jupiterimages/The Image Bank via Getty Images
During the Civil War and world wars, Americans consumed pecans in large quantities because they were a protein-packed alternative when meat was expensive and scarce. One cup of pecan halves has about 9 grams of protein.
After the wars, pecan demand declined, resulting in millions of excess pounds at harvest. One effort to increase demand was a national pecan recipe contest in 1924. Over 21,000 submissions came from over 5,000 cooks, with 800 of them published in a book.
Pecan consumption went up with the inclusion of pecans in commercially prepared foods and the start of the mail-order industry in the 1870s, as pecans can be shipped and stored at room temperature. That characteristic also put them on some Apollo missions. Small amounts of pecans contain many vitamins and minerals. They became commonplace in cereals, which touted their health benefits.
In 1938, the federal government published the pamphlet Nuts and How to Use Them, which touted pecans’ nutritional value and came with recipes. Food writers suggested using pecans as shortening because they are composed mostly of fat.
The government even put a price ceiling on pecans to encourage consumption, but consumers weren’t buying them. The government ended up buying the surplus pecans and integrating them into the National School Lunch Program.
Christine_Kohler/iStock via Getty Images
While you are sitting around the Thanksgiving table this year, you can discuss one of the biggest controversies in the pecan industry: Are they PEE-cans or puh-KAHNS?
Editor’s note: This article was updated to include the amount of protein in a cup of pecans.
Shelley Mitchell, Senior Extension Specialist in Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Oklahoma State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.






