News
Thousands are feared dead in Myanmar’s quake. Trump’s USAID cuts will cause even more unnecessary deaths
Adam Simpson, University of South Australia
In early 2021, after a decade of political and economic reforms, Myanmar looked like it was finally beginning to shake off the hangover of decades of military rule. Foreign investment was growing, and standards of living were gradually improving.
In February that year, however, the military again grabbed power after ousting Aung San Suu Kyi’s democratically elected government in a coup. This sent the country spiralling towards civil war and social and economic collapse.
In the latest addition to the daily misery of Myanmar’s long-suffering people, a huge 7.7-magnitude earthquake hit the centre of the country on Friday. Its epicentre was just outside Mandalay, the county’s second-largest city.
The Thai capital of Bangkok, more than 1,000 kilometres from the epicentre, experienced extensive damage too. Video images showed a collapsing building under construction and sloshing rooftop infinity pools causing waterfalls down high-rise condominiums.
Information on the extent of the damage in Myanmar was slower to emerge, given the junta has largely banned social media and communications apps, such as Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Signal and X.
The death toll has now passed 1,000 at the time of writing. US Geological Survey modelling, however, suggests there could be more than 10,000 deaths and economic losses potentially exceeding the country’s gross domestic product (GDP).
Unusually for the isolationist military juntas of Myanmar, its leader, Min Aung Hlaing, immediately issued a call for international assistance.
The junta, however, has full control of as little as 21% of the country in the ongoing civil war, with the rest contested or controlled by ethnic armed groups and resistance fighters. This indicates some hard-hit areas of the country may be inaccessible to international aid.
Compounding these difficulties, the Trump administration has decimated the US Agency for International Development (USAID) activities in the country. This will make it far more challenging to determine the areas most in need and distribute any aid on the ground.
Natural disasters in Myanmar
Along with its history of brutal and authoritarian military rule since gaining independence in 1948, Myanmar is also regularly afflicted by natural disasters.
At least 430 people are believed to have died in floods last September due to the remnants of Typhoon Yagi. In 2023, Cyclone Mocha reportedly killed about 460 of the Rohingya ethnic minority, who are largely confined to government camps in Rakhine state in inhuman conditions.
The worst natural disaster in living memory, however, was Cyclone Nargis in 2008, which left at least 140,000 dead. On that occasion, the military junta resisted international assistance, likely resulting in many unnecessary deaths.
At that time, there was no independent media in Myanmar and it was almost impossible to find out what was actually happening on the ground.
Fortunately, the proliferation of mobile phones in the last decade has allowed information to spread much more widely, even with the junta’s internet blocks and other methods of censorship currently in place.
When Cyclone Nargis occurred – the year after the iPhone was launched – only around 1% of the Myanmar’s population had mobile phones. By the time of the coup in 2021, Myanmar had a smartphone penetration rate of 114%. (This means the country has more smartphones than people.)
Foreign assistance has been compromised
While Min Aung Hlaing has gone farther than his predecessor in 2008 in asking for international help, US President Donald Trump’s actions have ensured that any aid will be far less effective than it would have been two months ago.
On Friday, the same day the earthquake hit, the Trump administration told Congress it would cut nearly all remaining jobs at USAID and shut the agency, closing all USAID missions worldwide.
Jeremy Konyndyk, the president of Refugees International and a former USAID official, called the move “a total abdication of decades of US leadership in the world”. He argued the firings would cut “the last remnants of the team that would have mobilised a USAID disaster response” to the earthquake.
In 2024, USAID spent US$240 million (A$380 million) in Myanmar, around one-third of all multilateral humanitarian assistance to the country.
However, since Trump’s inauguration in January, the number of USAID programs in Myanmar has shrunk from 18 to just three. Several NGOs and at least seven US-funded hospitals operating along Myanmar’s border with Thailand have been shut down.
Myanmar’s exiled independent media outlets, which shine a light on the military’s atrocities, have also seen their funding slashed by the Trump administration’s USAID cuts.
What happens now?
The day before the earthquake, Min Aung Hlaing addressed troops at the 80th anniversary of Armed Forces Day Parade. He announced national elections would go ahead in December – a vote that human rights groups are already calling a “sham”.
There is no conceivable way elections of any integrity can be held in the country under military rule or while the civil war continues to rage.
Military-backed parties have been overwhelmingly rejected by Myanmar’s electorate in every remotely free or fair election over the last four decades. This includes the most recent elections held in 2020, won by the National League of Democracy (NLD), led by Aung San Suu Kyi.
While the world should welcome – and urgently respond to – Min Aung Hlaing’s invitation for international assistance, this doesn’t mean the past is forgotten. Thousands of innocent lives have been lost as a result of the military’s unnecessary and destructive 2021 coup.
If the NLD had remained in government, the country would be infinitely more prepared to deal with consequences of this earthquake. Once again, the military’s brutal rule – and Trump’s draconian aid cuts – will no doubt cause more unnecessary suffering and deaths.
Adam Simpson, Senior Lecturer, International Studies, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Community
What if universal rental assistance were implemented to deal with the housing crisis?
A significant number of American families facing unaffordable rents are living in motels. While many believe a housing shortage causes high rents, experts suggest that expanding rental assistance is more effective. Making subsidies available to all eligible low-income households could tackle this affordability crisis significantly.
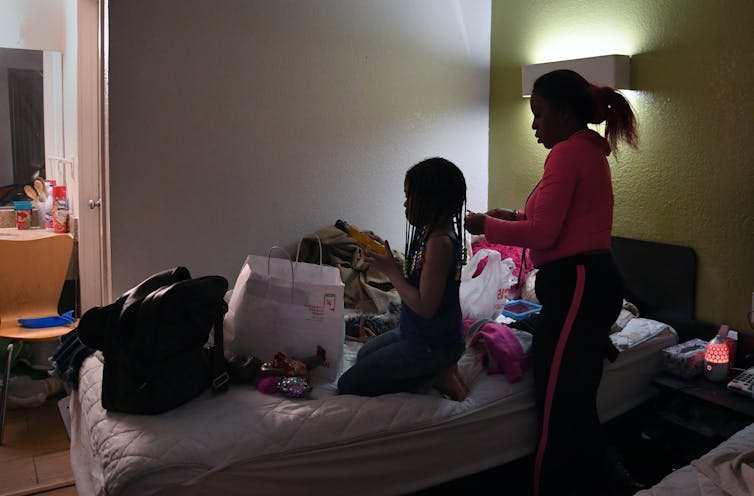
What if universal rental assistance were implemented to deal with the housing crisis?
Alex Schwartz, The New School and Kirk McClure, University of Kansas
If there’s one thing that U.S. politicians and activists from across the political spectrum can agree on, it’s that rents are far too high.
Many experts believe that this crisis is fueled by a shortage of housing, caused principally by restrictive regulations.
Rents and home prices would fall, the argument goes, if rules such as minimum lot- and house-size requirements and prohibitions against apartment complexes were relaxed. This, in turn, would make it easier to build more housing.
As experts on housing policy, we’re concerned about housing affordability. But our research shows little connection between a shortfall of housing and rental affordability problems. Even a massive infusion of new housing would not shrink housing costs enough to solve the crisis, as rents would likely remain out of reach for many households.
However, there are already subsidies in place that ensure that some renters in the U.S. pay no more than 30% of their income on housing costs. The most effective solution, in our view, is to make these subsidies much more widely available.
A financial sinkhole
Just how expensive are rents in the U.S.?
According to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, a household that spends more than 30% of its income on housing is deemed to be cost-burdened. If it spends more than 50%, it’s considered severely burdened. In 2023, 54% of all renters spent more than 30% of their pretax income on housing. That’s up from 43% of renters in 1999. And 28% of all renters spent more than half their income on housing in 2023.
Renters with low incomes are especially unlikely to afford their housing: 81% of renters making less than $30,000 spent more than 30% of their income on housing, and 60% spent more than 50%.
Estimates of the nation’s housing shortage vary widely, reaching up to 20 million units, depending on analytic approach and the time period covered. Yet our research, which compares growth in the housing stock from 2000 to the present, finds no evidence of an overall shortage of housing units. Rather, we see a gap between the number of low-income households and the number of affordable housing units available to them; more affluent renters face no such shortage. This is true in the nation as a whole and in nearly all large and small metropolitan areas.
Would lower rents help? Certainly. But they wouldn’t fix everything.
We ran a simulation to test an admittedly unlikely scenario: What if rents dropped 25% across the board? We found it would reduce the number of cost-burdened renters – but not by as much as you might think.
Even with the reduction, nearly one-third of all renters would still spend more than 30% of their income on housing. Moreover, reducing rents would help affluent renters much more than those with lower incomes – the households that face the most severe affordability challenges.
The proportion of cost-burdened renters earning more than $75,000 would fall from 16% to 4%, while the share of similarly burdened renters earning less than $15,000 would drop from 89% to just 80%. Even with a rent rollback of 25%, the majority of renters earning less than $30,000 would remain cost-burdened.
Vouchers offer more breathing room
Meanwhile, there’s a proven way of making housing more affordable: rental subsidies.
In 2024, the U.S. provided what are known as “deep” housing subsidies to about 5 million households, meaning that rent payments are capped at 30% of their income.
These subsidies take three forms: Housing Choice Vouchers that enable people to rent homes in the private market; public housing; and project-based rental assistance, in which the federal government subsidizes the rents for all or some of the units in properties under private and nonprofit ownership.
The number of households participating in these three programs has increased by less than 2% since 2014, and they constitute only 25% of all eligible households. Households earning less than 50% of their area’s median family income are eligible for rental assistance. But unlike Social Security, Medicare or food stamps, rental assistance is not an entitlement available to all who qualify. The number of recipients is limited by the amount of funding appropriated each year by Congress, and this funding has never been sufficient to meet the need.
By expanding rental assistance to all eligible low-income households, the government could make huge headway in solving the rental affordability crisis. The most obvious option would be to expand the existing Housing Choice Voucher program, also known as Section 8.
The program helps pay the rent up to a specified “payment standard” determined by each local public housing authority, which can set this standard at between 80% and 120% of the HUD-designated fair market rent. To be eligible for the program, units must also satisfy HUD’s physical quality standards.
Unfortunately, about 43% of voucher recipients are unable to use it. They are either unable to find an apartment that rents for less than the payment standard, meets the physical quality standard, or has a landlord willing to accept vouchers.
Renters are more likely to find housing using vouchers in cities and states where it’s illegal for landlords to discriminate against voucher holders. Programs that provide housing counseling and landlord outreach and support have also improved outcomes for voucher recipients.
However, it might be more effective to forgo the voucher program altogether and simply give eligible households cash to cover their housing costs. The Philadelphia Housing Authority is currently testing out this approach.
The idea is that landlords would be less likely to reject applicants receiving government support if the bureaucratic hurdles were eliminated. The downside of this approach is that it would not prevent landlords from renting out deficient units that the voucher program would normally reject.
Homeowners get subsidies – why not renters?
Expanding rental assistance to all eligible low-income households would be costly.
The Urban Institute, a nonpartisan think tank, estimates it would cost about $118 billion a year.
However, Congress has spent similar sums on housing subsidies before. But they involve tax breaks for homeowners, not low-income renters. Congress forgoes billions of dollars annually in tax revenue it would otherwise collect were it not for tax deductions, credits, exclusions and exemptions. These are known as tax expenditures. A tax not collected is equivalent to a subsidy payment.
For example, from 1998 through 2017 – prior to the tax changes enacted by the first Trump administration in 2017 – the federal government annually sacrificed $187 billion on average, after inflation, in revenue due to mortgage interest deductions, deductions for state and local taxes, and for the exemption of proceeds from the sale of one’s home from capital gains taxes. In fiscal year 2025, these tax expenditures totaled $95.4 billion.
Moreover, tax expenditures on behalf of homeowners flow mostly to higher-income households. In 2024, for example, over 70% of all mortgage-interest tax deductions went to homeowners earning at least $200,000.
Broadening the availability of rental subsidies would have other benefits. It would save federal, state and local governments billions of dollars in homeless services. Moreover, automatic provision of rental subsidies would reduce the need for additional subsidies to finance new affordable housing. Universal rental assistance, by guaranteeing sufficient rental income, would allow builders to more easily obtain loans to cover development costs.
Of course, sharply raising federal expenditures for low-income rental assistance flies in the face of the Trump administration’s priorities. Its budget proposal for the next fiscal year calls for a 44% cut of more than $27 billion in rental assistance and public housing.
On the other hand, if the government supported rental assistance in amounts commensurate with the tax benefits given to homeowners, it would go a long way toward resolving the rental housing affordability crisis.
This article is part of a series centered on envisioning ways to deal with the housing crisis.
Alex Schwartz, Professor of Urban Policy, The New School and Kirk McClure, Professor of Urban Planning, University of Kansas
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Daily News
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl Halftime Show Fits the NFL’s Long Game to Win Latin America
The NFL aims to expand its reach into Latin America through strategic marketing and high-profile performers like Bad Bunny at the Super Bowl halftime show. While the choice has sparked controversy, particularly among conservatives, the league sees it as a business move to attract more fans, particularly in Mexico and Brazil.
Last Updated on February 7, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Jared Bahir Browsh, University of Colorado Boulder
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl show is part of long play drawn up by NFL to score with Latin America
Donald Trump, it is fair to assume, will be switching channels during this year’s Super Bowl halftime show.
The U.S. president has already said that he won’t be attending Super Bowl LX in person, suggesting that the venue, Levi’s Stadium in Santa Clara, California, was “just too far away.” But the choice of celebrity entertainment planned for the main break – Puerto Rican reggaeton star Bad Bunny and recently announced pregame addition Green Day – didn’t appeal. “I’m anti-them. I think it’s a terrible choice. All it does is sow hatred. Terrible,” Trump told the New York Post.
National Football League Commissioner Roger Goodell likely didn’t have the sensibilities of the U.S. president in mind when the choice of Bad Bunny was made.
One of the top artists in the world, Bad Bunny performs primarily in Spanish and has been critical of immigration enforcement, which factored into the backlash in some conservative circles to the choice. Bad Bunny’s anti-ICE comments at this year’s Grammy Awards will have only stoked the ire of some conservatives.
But for the NFL hierarchy, this was likely a business decision, not a political one. The league has its eyes on expansion into Latin America; Bad Bunny, they hope, will be a ratings-winning means to an end. It has made such bets in the past. In 2020, Shakira and Jennifer Lopez were chosen to perform, with Bad Bunny making an appearance. The choice then, too, was seen as controversial.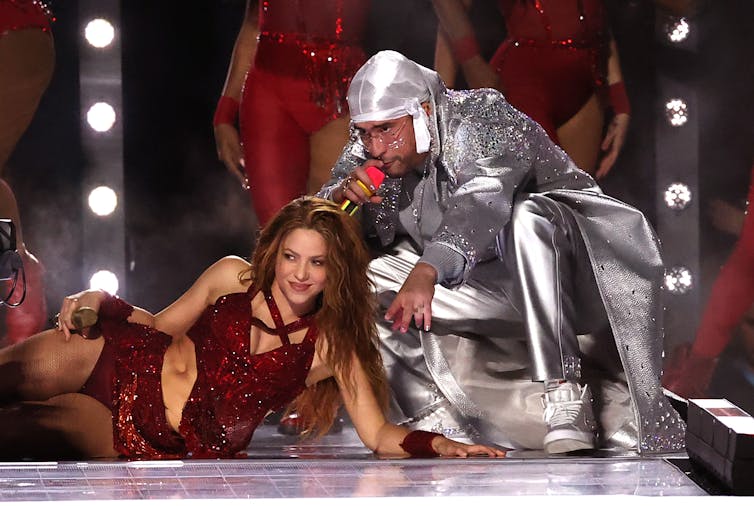
Raising the flag overseas
As a teacher and scholar of critical sports studies, I study the global growth of U.S.-based sports leagues overseas.
Some, like the National Basketball Association, are at an advantage. The sport is played around the globe and has large support bases in Asia – notably in the Philippines and China – as well as in Europe, Australia and Canada.
The NFL, by contrast, is largely entering markets that have comparatively little knowledge and experience with football and its players.
The league has opted for a multiprong approach to attracting international fans, including lobbying to get flag football into the 2028 Olympics in Los Angeles.
Playing the field
When it comes to the traditional tackle game, the NFL has held global aspirations for over three-quarters of a century. Between 1950-1961, before they merged, the NFL and American Football League played seven games against teams in Canada’s CFL to strengthen the relationship between the two nations’ leagues.
Developing a fan base south of the border has long been part of the plan.
The first international exhibition game between two NFL teams was supposed to take place in Mexico City in 1968. But Mexican protest over the economy and cost of staging the Olympics that year led the game, between the Detroit Lions and Philadelphia Eagles, to be canceled.
Instead, it was Montreal that staged the first international exhibition match the following year.
In 1986, the NFL added an annual international preseason game, the “American Bowl,” to reach international fans, including several games in Mexico City and one in Monterrey.
But the more concerted effort was to grow football in the potentially lucrative, and familiar, European market.
After several attempts by the NFL and other entities in the 1970s and ’80s to establish an international football league, the NFL-backed World League of Football launched in 1991. Featuring six teams from the United States, one from Canada and three from Europe, the spring league lost money but provided evidence that there was a market for American football in Europe, leading to the establishment of NFL Europe.
But NFL bosses have long had wider ambitions. The league staged 13 games in Tokyo, beginning in 1976, and planned exhibitions for 2007 and 2009 in China that were ultimately canceled. These attempts did not have the same success as in Europe.
Beyond exhibitions
The NFL’s outreach in Latin America has been decades in the making. After six exhibition matches in Mexico between 1978 and 2001, the NFL chose Mexico City as the venue of its first regular season game outside the United States.
In 2005, it pitted the Arizona Cardinals against the San Francisco 49ers at Estadio Azteca in Mexico City. Marketed as “Fútbol Americano,” it drew the largest attendance in NFL history, with over 103,000 spectators.
The following year, Goodell was named commissioner and announced that the NFL would focus future international efforts on regular-season games.
The U.K. was a safe bet due to the established stadium infrastructure and the country’s small but passionate fan base. The NFL International Series was played exclusively in London between 2007 and 2016.
But in 2016, the NFL finally returned to Mexico City, staging a regular-season game between the Oakland – now Las Vegas – Raiders and Houston Texans.
And after the completion of upgrades to Latin America’s largest stadium, Estadio Azteca, the NFL will return to Mexico City in 2026, along with games in Munich, Berlin and London. Future plans include expanding the series to include Sydney, Australia, and Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 2026.
The International Player Pathway program also offers players from outside the United States an opportunity to train and earn a roster spot on an NFL team. The hope is that future Latin American players could help expand the sport in their home countries, similar to how Yao Ming expanded the NBA fan base in China after joining the Houston Rockets, and Shohei Ohtani did the same for baseball in Japan while playing in Los Angeles.
Heading south of the border
The NFL’s strategy has gained the league a foothold in Latin America.
Mexico and Brazil have become the two largest international markets for the NFL, with nearly 40 million fans in each of the nations.
Although this represents a fraction of the overall sports fans in each nation, the raw numbers match the overall Latino fan base in the United States. In recent years the NFL has celebrated Latino Heritage Month through its Por La Cultura campaign, highlighting Latino players past and present.
Latin America also offers practical advantages. Mexico has long had access to NFL games as the southern neighbor to the United States, with the Dallas Cowboys among the most popular teams in Mexico.
For broadcasters, Central and South America offer less disruption in regards to time zones. Games in Europe start as early as 6:30 a.m. for West Coast fans, whereas Mexico City follows Central time, and Brasilia time is only one to two hours ahead of Eastern time.
The NFL’s expansion plans are not without criticism. Domestically, fans have complained that teams playing outside the U.S. borders means one less home game for season-ticket holders. And some teams have embraced international games more than others.
Another criticism is the league, which has reported revenues of over US$23 billion during the 2024-25 season – nearly double any other U.S.-based league – is using its resources to displace local sports. There are also those who see expansion of the league as a form of cultural imperialism. These criticisms often intersect with long-held ideas around the league promoting militarism, nationalism and American exceptionalism.
Bad Bunny: No Hail Mary attempt
For sure, the choice of Bad Bunny as the halftime pick is controversial, given the current political climate around immigration. The artist removed tour dates on the U.S. mainland in 2025 due to concerns about ICE targeting fans at his concerts, a concern reinforced by threats from the Department of Homeland Security that they would do just that at the Super Bowl.
But in sticking with Bad Bunny, the NFL is showing it is willing to face down a section of its traditional support and bet instead on Latin American fans not just tuning in for the halftime show but for the whole game – and falling in love with football, too.
Jared Bahir Browsh, Assistant Teaching Professor of Critical Sports Studies, University of Colorado Boulder
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
family fun
Jurassic Quest Brings Life-Size Dinosaurs to Phoenix in February 2026
Jurassic Quest is roaring back into Phoenix in February 2026 with towering life-size dinosaurs, interactive exhibits, and hands-on activities for kids and families at the Arizona State Fairgrounds.
Last Updated on February 7, 2026 by Daily News Staff

Phoenix, AZ — Jurassic Quest, billed as North America’s largest traveling dinosaur experience, is set to return to Arizona with a limited engagement at the Arizona State Fairgrounds from February 6–8, 2026.
The family-friendly attraction features life-size animatronic dinosaurs, immersive walk-through exhibits, and hands-on activities designed to blend entertainment with education. Guests will encounter towering recreations of iconic species such as Tyrannosaurus rex and Spinosaurus, along with interactive fossil digs, dinosaur rides, inflatables, and meet-and-greet opportunities with baby dinosaurs.
Jurassic Quest has become a popular touring event across the United States, particularly among families with young children. The experience combines museum-style displays with high-energy attractions, allowing visitors to explore at their own pace. Most attendees spend one to two hours navigating the exhibit.
The event will take place at the Arizona State Fairgrounds, located at 1826 W. McDowell Road in Phoenix, with multiple daily sessions scheduled throughout the weekend.
Tickets and additional event details are available through the official Jurassic Quest website.
- Jurassic Quest Phoenix 2026 – Official Event Page
- Arizona State Fairgrounds – Venue Information
- More Entertainment News from STM Daily News
- Family & Kid-Friendly Events on STM Daily News
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
