Health
Understanding ‘Warning Strokes’: What to expect if you experience stroke symptoms, even if they disappear
Last Updated on September 28, 2025 by Daily News Staff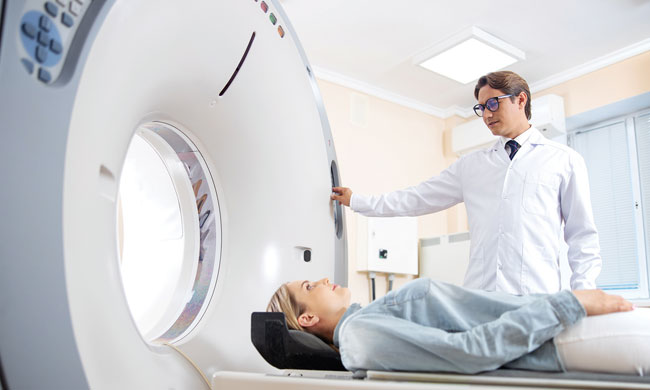
(Family Features) Diagnosing a transient ischemic attack (TIA), sometimes called a “warning stroke,” can be challenging because symptoms often disappear within an hour. However, it’s important to seek emergency assessment to help prevent a full-blown stroke.
While a TIA, which is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain, doesn’t cause permanent damage, nearly 1 in 5 people who have a suspected TIA will have a stroke within three months, according to a scientific statement published in the American Heart Association journal “Stroke.” Additionally, almost half will occur within two days – which is why TIAs are often described as warning strokes.
People with cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol and smoking, are at high risk for stroke and TIA. Other conditions that increase risk include peripheral artery disease, atrial fibrillation, obstructive sleep apnea and coronary artery disease. In addition, a person who has had a prior stroke is at high risk for TIA.
TIA symptoms are the same as stroke symptoms, only temporary. They begin suddenly and may have any or all these characteristics:
- Symptoms begin strong then fade
- Symptoms typically last less than an hour
- Facial droop
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Trouble finding the right words or slurred speech
- Dizziness, vision loss or trouble walking
The F.A.S.T. acronym for stroke symptoms can also be used to identify a TIA: F – face drooping or numbness; A – arm weakness; S – speech difficulty; T – time to call 9-1-1, even if the symptoms go away.
Given the appropriate scan, 2 in 5 people will learn they actually had a stroke rather than a TIA, according to the scientific statement, which highlights the importance of seeking prompt medical attention. Upon arrival to the emergency room, a series of tests may be completed after assessing symptoms and medical history, including a CT scan, MRI and blood tests.
- CT Scan – a non-contrast scan used to look at the blood vessels in the head and neck to rule out brain bleeding and TIA mimics (conditions that share some signs with TIAs but are due to other medical conditions such as low blood sugar, seizure or migraine). A CT scan may also be used to assess the neck arteries; nearly half of people with TIA symptoms have narrowing of the large arteries leading to the brain.
- MRI – The preferred way to rule out a brain injury, such as a stroke, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is typically done within 24 hours of symptoms beginning. Because some emergency rooms may not have access to an MRI scanner, patients may be admitted to the hospital or transferred to a center. About 40% of patients who go to the emergency room with TIA symptoms are diagnosed with a stroke based on MRI results.
- Blood Tests – Blood work will typically be completed to rule out conditions that may cause TIA-like symptoms, such as low blood sugar or infection, and check for cardiovascular risk factors like diabetes and high cholesterol.
Once a TIA is diagnosed, a cardiac checkup should be completed within a week of having a TIA, if not done in the emergency room. Consultation with a neurologist should also be completed within 48 hours (no longer than one week) after experiencing a TIA, as early consultation with a brain specialist is associated with lower death rates after a TIA.
To learn more and find additional resources, visit Stroke.org.
Photo courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
American Heart Association
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lifestyle
How to Practice Thoughtful Grief Etiquette Online
Grief experts advise caution in sharing condolences and loss-related information on social media, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing the grieving family’s needs. Thoughtful posting practices include waiting for family approval, reaching out privately first, and avoiding speculation about the cause of death. Compassionate communication is essential in these sensitive situations.

(Feature Impact) News of a death can spread online in seconds – often before families have notified close family members privately. That’s why grief experts urge people to rethink how they share condolences, tributes and loss-related information on social media, particularly during the winter months when grief can feel especially isolating.
“Grief etiquette is about putting the needs of the grieving family first, not our urge to say something publicly,” said Dr. Camelia L. Clarke, National Funeral Directors Association (NFDA) spokesperson, funeral director and grief educator with nearly 30 years of experience. “Just because information can be shared instantly doesn’t mean it should be.”
Social media has become a common place for sharing condolences, tributes and memories. However, grief experts caution that, without thoughtful consideration, online posts can unintentionally cause harm. Knowing when to post, what to say and when to remain silent can make a meaningful difference for families experiencing loss.
Consider this advice from the experts at the NFDA.
Grief Etiquette in the Digital Age
Grief etiquette refers to the unspoken guidelines for how individuals acknowledge death, loss and mourning, particularly online.
According to Clarke, one of the most important principles is restraint.
“When a death is shared online too quickly, families can feel exposed and overwhelmed at a moment when they’re still processing the loss themselves,” she said. “Waiting is an act of compassion.”
Best Practices for Posting About Loss Online
As social media continues to play a role in modern mourning, grief professionals encourage users to pause before posting and consider a few key guidelines:
- Let the family lead. Don’t post about a death until the immediate family has made it public.
- Ask permission. Obtain consent before sharing photos, stories or tributes.
- Reach out privately first. A direct message, call or handwritten note can be more meaningful than a public comment.
- Avoid speculation. Don’t ask about or share details regarding the cause of death.
- Offer ongoing support. Grief extends far beyond the first days or weeks after a loss.
What to Say (and Avoid)
When expressing condolences online, experts recommend simplicity, sincerity and sensitivity. Messages that acknowledge loss without attempting to explain or minimize it are often the most supportive.
Helpful phrases include:
- “I’m sorry for your loss.”
- “Thinking of you and your family.”
- “I’m here if you want to talk or need anything.”
By contrast, well-meaning cliches can unintentionally cause harm. Phrases such as “They’re in a better place” or “Everything happens for a reason” may reflect the speaker’s beliefs, but they can feel dismissive to someone grieving.
“Grieving people don’t need answers – they need presence,” Clarke said. “Listening matters more than saying the perfect thing.”
Resources for Families and Friends
As digital spaces continue to shape how people communicate during life’s most difficult moments, experts agree empathy, patience and respect remain timeless.
“Grief is deeply personal,” Clarke said. “When we slow down and lead with compassion, we honor both the person who has died and those who are left to grieve.”
To learn more about how to support a grieving person and access free, expert-reviewed resources for navigating grief, expressing condolences and supporting loved ones before, during and after a loss, visit RememberingALife.com, an initiative of the NFDA.
Photo courtesy of Shutterstock
<img src="https://ssl.google-analytics.com/collect?v=1&tid=UA-482330-7&cid=1955551e-1975-5e52-0cdb-8516071094cd&sc=start&t=pageview&dl=http%3A%2F%2Ftrack.familyfeatures.com%2F17832%2F10240&dt=HOW-TO-PRACTICE-THOUGHTFUL-GRIEF-ETIQUETTE-ONLINE" />
<img src="https://erp.featureimpact.com/api/v1/tracking/17832/10240/track.gif" />SOURCE:
National Funeral Directors Association
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Food and Beverage
Fresh Thinking About Frozen: Bring Quality Meals to the Table While Cutting Food Waste and Stretching Your Budget
For many families, the freezer is for last-minute meal options. However, new federal nutrition guidance and growing scientific consensus reveal a different reality: frozen foods can be the starting point for healthy eating, not a backup plan.
Last Updated on February 21, 2026 by Daily News Staff
(Feature Impact) The key to easy preparation of high-quality meals, wasting less food and saving money may already be sitting in your kitchen.
For many families, the freezer is for last-minute meal options. However, new federal nutrition guidance and growing scientific consensus reveal a different reality: frozen foods can be the starting point for healthy eating, not a backup plan. That’s why the American Frozen Food Institute (AFFI) is launching “Fresh Thinking About Frozen,” a campaign to help families discover these benefits of frozen foods.
Making Nutrition Achievable
The recently released 2025-2030 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, the nation’s top nutrition advice, emphasizes portion control and nutrient-dense foods. Frozen options deliver on both counts.
Families who keep frozen produce on hand tend to eat more fruits and vegetables overall. Pre-portioned frozen meals also help people eat what they need without overdoing it. Plus, the convenience factor matters: frozen berries are ready for a morning smoothie, pre-cut frozen vegetables can be added to tonight’s stir-fry and a balanced frozen meal can be quickly paired with a salad.
That isn’t cutting corners. It’s being smart on how best to feed a family well.
Freezing Hits the Pause Button on Fresh Foods
Freezing food only changes a food’s temperature, not its nutrition. Freezing keeps food close to its original state without requiring additives.
Produce begins to lose nutritional value right after it’s harvested. Freezing fruits and vegetables hours after harvest pauses nutrient degradation and locks in the vitamins and minerals, so the food remains farm fresh even as it travels across the country to your grocery store. Frozen meals are similarly made with real ingredients and turned into just-cooked recipes then frozen for families to eat when they’re ready.
The nutrition community understands this. A recent survey conducted by AFFI found 94% of registered dietitians agree frozen fruits and vegetables are just as nutritious as their fresh counterparts. Another 92% said frozen foods offer a variety of nutritious meal offerings. These findings are central to the “Fresh Thinking About Frozen” message: Frozen is not second-best. It’s simply smart.
Solving the Food Waste Problem
Nearly 40% of food in the United States gets thrown away, according to the nonprofit ReFED. That translates to roughly $1,500 per year per household, straight into the trash along with unused produce and forgotten leftovers.
Frozen helps fix that problem. Eight in 10 consumers agree buying frozen helps reduce food waste at home, AFFI research finds. The reason is simple: You use what you need, when you need it and the rest stays perfectly preserved. No more dreading the refrigerator cleanouts and feeling guilty over the uneaten food going into the trashcan.
Time for Fresh Thinking
Families already making this shift aren’t settling for less. They’re strategic about nutrition, budget and time. They integrate the freezer into regular meal planning. They feel confident about providing quality foods that are simply frozen.
The freezer isn’t a place of last resort. It’s a tool for eating well in real life. Visit frozenadvantage.org/FTAF for tips, recipes and resources to make the most of your freezer.
Photos courtesy of Shutterstock
SOURCE:
American Frozen Food Institute
At our core, we at STM Daily News, strive to keep you informed and inspired with the freshest content on all things food and beverage. From mouthwatering recipes to intriguing articles, we’re here to satisfy your appetite for culinary knowledge.
Visit our Food & Drink section to get the latest on Foodie News and recipes, offering a delightful blend of culinary inspiration and gastronomic trends to elevate your dining experience. https://stmdailynews.com/food-and-drink/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
health and wellness
Stacking Healthy Habits for Progress, Not Perfection
Healthy Habits: Many struggle with building healthier habits due to unrealistic expectations rather than lack of motivation. The American Heart Association’s My Life Check tool offers personalized heart health insights, helping to set attainable goals. Simple lifestyle changes—focused on nutrition, movement, sleep, and stress management—can gradually lead to significant health improvements.

(Feature Impact) Despite the best of intentions, it’s common for plans to build healthier habits to fall flat. Often, the culprit isn’t a lack of motivation or discipline; rather, it’s unrealistic expectations.
Overhauling your lifestyle requires a level of commitment that isn’t always practical. Understanding your personal health needs and the challenges you need to overcome can help give you a more realistic roadmap toward better health.
Tools to Guide You
Every plan needs a starting point and there are many reputable sources that can help guide you toward a plan that addresses your personal health needs.
For example, the American Heart Association introduced My Life Check, a simple, free tool to help individuals understand their heart health and what’s driving it. Users answer simple questions about their daily habits and health factors to get a personalized Heart Health Score in minutes.
The results are private and downloadable, giving you full control of your information. The tool turns big goals into small, specific actions you can start right away. Knowing your numbers relative to your heart health (and where you are in comparison to target ranges for optimal health) can help you decide how to build a better map to get you where you want to be.
While the report is customized to each individual, no personal data is stored and answers are only used to calculate health scores and provide personalized recommendations and practical steps to improve your health, so you can use your results to focus on what matters most to you. Every small step you take, such as moving more, eating smarter, sleeping better or managing stress, can add up over time.
Finding Your Path
Once you’re armed with data and know where you stand on your heart health numbers, small steps become clearer and more manageable. That knowledge makes it easier to choose one area to focus on, such as getting more sleep, taking daily walks or adding more color to your meals.
Healthy changes don’t need to be expensive or complicated. The best habits are ones that fit real life when every action you take moves you closer to your goals.
Eat Smart
Choose foods that help you feel your best, one meal at a time. Add more color to your plate and focus on balance, not restriction. Simple, affordable swaps can make a real difference.
Move More
Find movement that fits your life, such as a walk, a stretch or dancing while you cook. Every bit of activity counts and it all supports your heart and mind. Move for joy, not just for results.
Sleep Well
Rest is a foundation of good health, not a reward. Protect your bedtime routine and give your body the recovery it deserves. Notice how good sleep makes everything else easier.
Manage Stress
Check in with yourself regularly, both mentally and emotionally. Create simple moments to pause, breathe, laugh or step outside. Connection, kindness and calm all support a healthy heart.
Staying motivated and on track is also easier when you can check back in, see your progress and realize the steps you’re taking are making an impact. Checking in every few months to see how you can grow gives you the chance to celebrate your progress, learn from challenges and keep building lasting habits that feel good.
To get started with personalized tips to set your own health goals, visit heart.org/mylifecheck.
Photos courtesy of Shutterstock
<img src="https://ssl.google-analytics.com/collect?v=1&tid=UA-482330-7&cid=1955551e-1975-5e52-0cdb-8516071094cd&sc=start&t=pageview&dl=http%3A%2F%2Ftrack.familyfeatures.com%2F17763%2F10236&dt=STACKING-HEALTHY-HABITS-FOR-PROGRESS-NOT-PERFECTION" />
<script src="https://erp.featureimpact.com/api/v1/tracking/17763/10236/track.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
(function () {
var image = new Image(1, 1);
image.src = 'https://erp.featureimpact.com/api/v1/tracking/17763/10236/track.gif?referrer=' + window.location.href;
image.id = 'feature-impact-content-tracking-pixel';
image.style.position = 'absolute';
image.style.top = 0;
image.style.left = 0;
document.body.appendChild(image);
})();
</script>SOURCE:
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
