News
AI gives nonprogrammers a boost in writing computer code

Leo Porter, University of California, San Diego and Daniel Zingaro, University of Toronto
What do you think there are more of: professional computer programmers or computer users who do a little programming?
It’s the second group. There are millions of so-called end-user programmers. They’re not going into a career as a professional programmer or computer scientist. They’re going into business, teaching, law, or any number of professions – and they just need a little programming to be more efficient. The days of programmers being confined to software development companies are long gone.
If you’ve written formulas in Excel, filtered your email based on rules, modded a game, written a script in Photoshop, used R to analyze some data, or automated a repetitive work process, you’re an end-user programmer.
As educators who teach programming, we want to help students in fields other than computer science achieve their goals. But learning how to program well enough to write finished programs can be hard to accomplish in a single course because there is so much to learn about the programming language itself. Artificial intelligence can help.
Lost in the weeds
Learning the syntax of a programming language – for example, where to place colons and where indentation is required – takes a lot of time for many students. Spending time at the level of syntax is a waste for students who simply want to use coding to help solve problems rather than learn the skill of programming.
As a result, we feel our existing classes haven’t served these students well. Indeed, many students end up barely able to write small functions – short, discrete pieces of code – let alone write a full program that can help make their lives better.
Tools built on large language models such as GitHub Copilot may allow us to change these outcomes. These tools have already changed how professionals program, and we believe we can use them to help future end-user programmers write software that is meaningful to them.
These AIs almost always write syntactically correct code and can often write small functions based on prompts in plain English. Because students can use these tools to handle some of the lower-level details of programming, it frees them to focus on bigger-picture questions that are at the heart of writing software programs. Numerous universities now offer programming courses that use Copilot.
At the University of California, San Diego, we’ve created an introductory programming course primarily for those who are not computer science students that incorporates Copilot. In this course, students learn how to program with Copilot as their AI assistant, following the curriculum from our book. In our course, students learn high-level skills such as decomposing large tasks into smaller tasks, testing code to ensure its correctness, and reading and fixing buggy code.
Freed to solve problems
In this course, we’ve been giving students large, open-ended projects and couldn’t be happier with what they have created.
For example, in a project where students had to find and analyze online datasets, we had a neuroscience major create a data visualization tool that illustrated how age and other factors affected stroke risk. Or, for example, in another project, students were able to integrate their personal art into a collage, after applying filters that they had created using the programming language Python. These projects were well beyond the scope of what we could ask students to do before the advent of large language model AIs.
Given the rhetoric about how AI is ruining education by writing papers for students and doing their homework, you might be surprised to hear educators like us talking about its benefits. AI, like any other tool people have created, can be helpful in some circumstances and unhelpful in others.
In our introductory programming course with a majority of students who are not computer science majors, we see firsthand how AI can empower students in specific ways – and promises to expand the ranks of end-user programmers.
Leo Porter, Teaching Professor of Computer Science and Engineering, University of California, San Diego and Daniel Zingaro, Associate Professor of Mathematical and Computational Sciences, University of Toronto
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
unknown
Why people tend to believe UFOs are extraterrestrial
Last Updated on March 13, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Barry Markovsky, University of South Carolina
Most of us still call them UFOs – unidentified flying objects. NASA recently adopted the term “unidentified anomalous phenomena,” or UAP. Either way, every few years popular claims resurface that these things are not of our world, or that the U.S. government has some stored away.
I’m a sociologist who focuses on the interplay between individuals and groups, especially concerning shared beliefs and misconceptions. As for why UFOs and their alleged occupants enthrall the public, I’ve found that normal human perceptual and social processes explain UFO buzz as much as anything up in the sky.
Historical context
Like political scandals and high-waisted jeans, UFOs trend in and out of collective awareness but never fully disappear. Thirty years of polling find that 25%-50% of surveyed Americans believe at least some UFOs are alien spacecraft. Today in the U.S., over 100 million adults think our galactic neighbors pay us visits.
It wasn’t always so. Linking objects in the sky with visiting extraterrestrials has risen in popularity only in the past 75 years. Some of this is probably market-driven. Early UFO stories boosted newspaper and magazine sales, and today they are reliable clickbait online.
In 1980, a popular book called “The Roswell Incident” by Charles Berlitz and William L. Moore described an alleged flying saucer crash and government cover-up 33 years prior near Roswell, New Mexico. The only evidence ever to emerge from this story was a small string of downed weather balloons. Nevertheless, the book coincided with a resurgence of interest in UFOs. From there, a steady stream of UFO-themed TV shows, films, and pseudo-documentaries has fueled public interest. Perhaps inevitably, conspiracy theories about government cover-ups have risen in parallel.
Some UFO cases inevitably remain unresolved. But despite the growing interest, multiple investigations have found no evidence that UFOs are of extraterrestrial origin – other than the occasional meteor or misidentification of Venus.
But the U.S. Navy’s 2017 Gimbal video continues to appear in the media. It shows strange objects filmed by fighter jets, often interpreted as evidence of alien spacecraft. And in June 2023, an otherwise credible Air Force veteran and former intelligence officer made the stunning claim that the U.S. government is storing numerous downed alien spacecraft and their dead occupants. https://www.youtube.com/embed/2TumprpOwHY?wmode=transparent&start=0 UFO videos released by the U.S. Navy, often taken as evidence of alien spaceships.
Human factors contributing to UFO beliefs
Only a small percentage of UFO believers are eyewitnesses. The rest base their opinions on eerie images and videos strewn across both social media and traditional mass media. There are astronomical and biological reasons to be skeptical of UFO claims. But less often discussed are the psychological and social factors that bring them to the popular forefront.
Many people would love to know whether or not we’re alone in the universe. But so far, the evidence on UFO origins is ambiguous at best. Being averse to ambiguity, people want answers. However, being highly motivated to find those answers can bias judgments. People are more likely to accept weak evidence or fall prey to optical illusions if they support preexisting beliefs.
For example, in the 2017 Navy video, the UFO appears as a cylindrical aircraft moving rapidly over the background, rotating and darting in a manner unlike any terrestrial machine. Science writer Mick West’s analysis challenged this interpretation using data displayed on the tracking screen and some basic geometry. He explained how the movements attributed to the blurry UFO are an illusion. They stem from the plane’s trajectory relative to the object, the quick adjustments of the belly-mounted camera, and misperceptions based on our tendency to assume cameras and backgrounds are stationary.
West found the UFO’s flight characteristics were more like a bird’s or a weather balloon’s than an acrobatic interstellar spacecraft. But the illusion is compelling, especially with the Navy’s still deeming the object unidentified.
West also addressed the former intelligence officer’s claim that the U.S. government possesses crashed UFOs and dead aliens. He emphasized caution, given the whistleblower’s only evidence was that people he trusted told him they’d seen the alien artifacts. West noted we’ve heard this sort of thing before, along with promises that the proof will soon be revealed. But it never comes.
Anyone, including pilots and intelligence officers, can be socially influenced to see things that aren’t there. Research shows that hearing from others who claim to have seen something extraordinary is enough to induce similar judgments. The effect is heightened when the influencers are numerous or higher in status. Even recognized experts aren’t immune from misjudging unfamiliar images obtained under unusual conditions.
Group factors contributing to UFO beliefs
“Pics or it didn’t happen” is a popular expression on social media. True to form, users are posting countless shaky images and videos of UFOs. Usually they’re nondescript lights in the sky captured on cellphone cameras. But they can go viral on social media and reach millions of users. With no higher authority or organization propelling the content, social scientists call this a bottom-up social diffusion process.
In contrast, top-down diffusion occurs when information emanates from centralized agents or organizations. In the case of UFOs, sources have included social institutions like the military, individuals with large public platforms like U.S. senators, and major media outlets like CBS.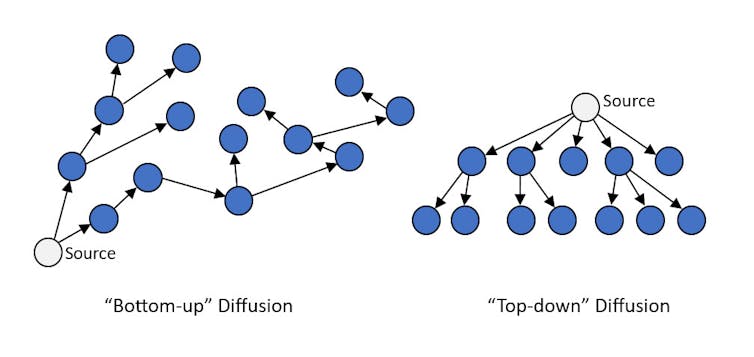
Amateur organizations also promote active personal involvement for many thousands of members, the Mutual UFO Network being among the oldest and largest. But as Sharon A. Hill points out in her book “Scientifical Americans,” these groups apply questionable standards, spread misinformation and garner little respect within mainstream scientific communities.
Top-down and bottom-up diffusion processes can combine into self-reinforcing loops. Mass media spreads UFO content and piques worldwide interest in UFOs. More people aim their cameras at the skies, creating more opportunities to capture and share odd-looking content. Poorly documented UFO pics and videos spread on social media, leading media outlets to grab and republish the most intriguing. Whistleblowers emerge periodically, fanning the flames with claims of secret evidence.
Despite the hoopla, nothing ever comes of it.
For a scientist familiar with the issues, skepticism that UFOs carry alien beings is wholly separate from the prospect of intelligent life elsewhere in the universe. Scientists engaged in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence have a number of ongoing research projects designed to detect signs of extraterrestrial life. If intelligent life is out there, they’ll likely be the first to know.
As astronomer Carl Sagan wrote, “The universe is a pretty big place. If it’s just us, seems like an awful waste of space.”
Barry Markovsky, Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Sociology, University of South Carolina
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
Why can’t it always be summer? It’s all about the Earth’s tilt
Earth’s axial tilt causes the seasons. As Earth orbits the Sun, different hemispheres tilt toward or away, creating summer and winter depending on location.
Last Updated on March 13, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Stephanie Spera, University of Richmond
Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to curiouskidsus@theconversation.com.
Why can’t it always be summer? – Amanda, age 5, Chile
With its long days just itching to be spent by water doing nothing, summer really can be an enchanting season. As Jenny Han wrote in the young adult novel “The Summer I Turned Pretty”: “Everything good, everything magical happens between the months of June and August.”
But all good things must come to an end, and summer cannot last forever. There’s both a simple reason and a more complicated one. The simple reason is that it can’t always be summer because the Earth is tilted. The more complicated answer requires some geometry.
I’m a professor of geography and the environment who has studied seasonal changes on the landscape. Here’s what seasons have to do with our planet’s position as it moves through the solar system.
This animation shows why the Earth has seasons.
Closeness to the Sun doesn’t explain seasons
First, you need to know that the Earth is a sphere – technically, an oblate spheroid. That means Earth has a round shape a little wider than it is tall.
Every year, Earth travels in its orbit to make one revolution around the Sun. The Earth’s orbit is an ellipse, which is more like an oval than a circle. So there are times when Earth is closer to the Sun and times when it’s farther away.
A lot of people assume this distance is why we have seasons. But these people would be wrong. In the United States, the Earth is 3 million miles closer to the Sun during winter than in the summer.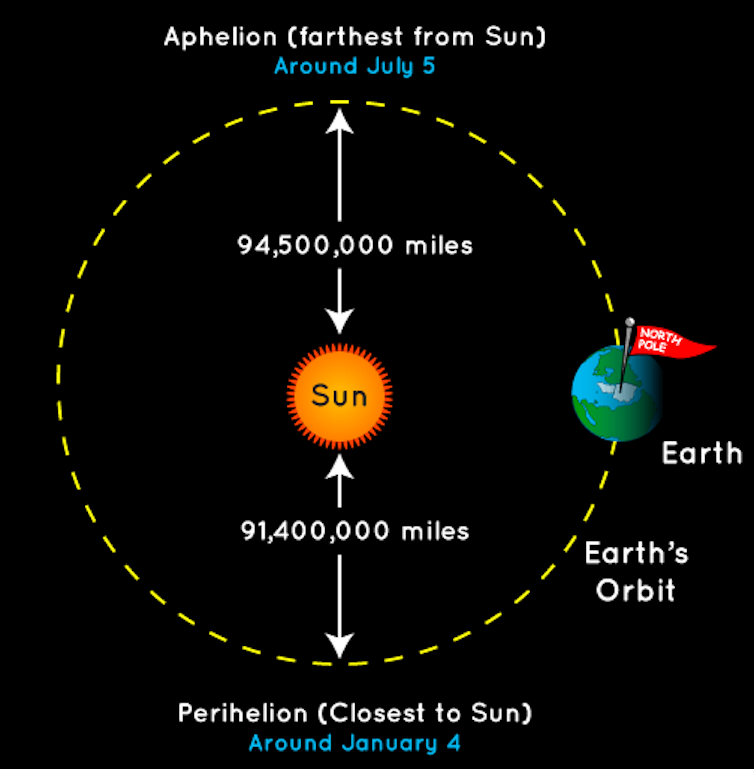
Spinning like a top
Now picture an imaginary line across Earth, right in the middle, at 0° latitude. This line is called the equator. If you drew it on a globe, the equator would pass through countries including Brazil, Kenya, Indonesia and Ecuador.
Everything north of the equator, including the United States, is considered the Northern Hemisphere, and everything south of the equator is the Southern Hemisphere.
Now think of the Earth’s axis as another imaginary line that runs vertically through the middle of the Earth, going from the North Pole to the South Pole.
As it orbits, or revolves, around the Sun, the Earth also rotates. That means it spins on its axis, like a top. The Earth takes one full year to revolve around the Sun and takes 24 hours, or one day, to do one full rotation on its axis.
This axis is why we have day and night; during the day, we’re facing the Sun, and at night, we’re facing away.
But the Earth’s axis does not go directly up and down. Instead, its axis is always tilted at 23.5 degrees in the exact same direction, toward the North Star.
The Earth’s axis is tilted due to a giant object – perhaps an ancient planet – smashing into it billions of years ago. And it’s this tilt that causes seasons.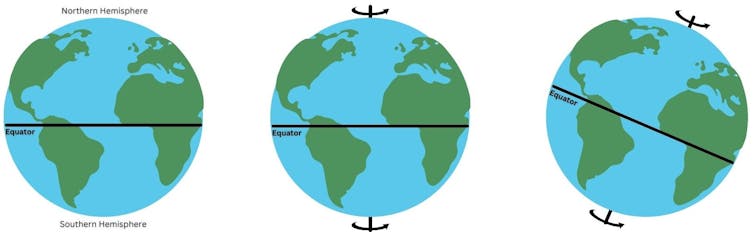
It’s all about the tilt
So that means in June, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun. That tilt means more sunlight, more solar energy, longer days – all the things that make summer, well, summer.
At the same time, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun. So countries such as Australia, Chile and Argentina are experiencing winter then.
To say it another way: As the Earth moves around the Sun throughout the year, the parts of the Earth getting the most sunlight are always changing.
Fast-forward to December, and Earth is on the exact opposite side of its orbit as where it was in June. It’s the Southern Hemisphere’s turn to be tilted toward the Sun, which means its summer happens in December, January and February.
If Earth were not tilted at all, there would be no seasons. If it were tilted more than it is, there would be even more extreme seasons and drastic swings in temperature. Summers would be hotter and winters would be colder.
Defining summer
Talk to a meteorologist, climate scientist or author Jenny Han, and they’ll tell you that for those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, summer is June, July and August, the warmest months of the year.
But there’s another way to define summer. Talk to astronomers, and they’ll tell you the first day of summer is the summer solstice – the day of the year with the longest amount of daylight and shortest amount of darkness.
The summer solstice occurs every year sometime between June 20 and June 22. And every day after, until the winter solstice in December, the Northern Hemisphere receives a little less daylight.
Summer officially ends on the autumnal equinox, the fall day when everywhere on Earth has an equal amount of daylight and night. The autumnal equinox happens every year on either September 22 or 23.
But whether you view summer like Jenny Han or like an astronomer, one thing is certain: Either way, summer must come to an end. But the season and the magic it brings with it will be back before you know it.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
Stephanie Spera, Assistant Professor of Geography and the Environment, University of Richmond
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
The science section of our news blog STM Daily News provides readers with captivating and up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries, breakthroughs, and innovations across various fields. We offer engaging and accessible content, ensuring that readers with different levels of scientific knowledge can stay informed. Whether it’s exploring advancements in medicine, astronomy, technology, or environmental sciences, our science section strives to shed light on the intriguing world of scientific exploration and its profound impact on our daily lives. From thought-provoking articles to informative interviews with experts in the field, STM Daily News Science offers a harmonious blend of factual reporting, analysis, and exploration, making it a go-to source for science enthusiasts and curious minds alike. https://stmdailynews.com/category/science/
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Community
Arizona Scholarships 2026: $1,500 Awards + Free ACF Virtual Workshops
Arizona scholarships 2026: Arizona scholarships are open through ACF: one application for 160+ awards, plus ARAC’s $1,500 Ashby-Herring scholarships due April 6, 2026.
Last Updated on March 11, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Arizona Scholarships 2026: $1,500 Awards + Free ACF Virtual Workshops
Scholarship season moves fast, and for a lot of Arizona families, the hardest part isn’t writing the essay or gathering transcripts—it’s simply finding the right opportunities in time.
The Archer Ragsdale Arizona Chapter (ARAC), Tuskegee Airmen, Inc. is encouraging students and the community to take advantage of scholarship resources through the Arizona Community Foundation (ACF), including an easy online application that can match applicants with 160+ scholarships—plus virtual workshops where students can get help directly from ACF’s scholarship team.
Whether you’re a high school senior, a current college student, or an adult re-entry student, ACF’s scholarship portal is designed to meet people where they are.
The Big Picture: One Application, 160+ Scholarships
According to the flyer, ACF awarded $6.3 million in scholarships last year, with over 160 scholarships available through a single, easy application.
- Application opens: January 1
- Most deadlines: March and April
- Where to start: https://azfoundation.org/scholarships
- ACF scholarship email: scholarship@azfoundation.org
What to watch for: Even if a student is only targeting one scholarship, completing the ACF application can surface additional matches they didn’t know existed.
ARAC Tuskegee Airmen Scholarship: Ashby-Herring Scholarships ($1,500) — Deadline April 6, 2026
ARAC (Tuskegee Airmen, Inc.) awards two or more scholarships to deserving Arizona students who are college-bound. The flyer highlights the Ashby-Herring scholarships, named in honor of late founding ARAC members who were original Tuskegee Airmen.
Award: Two Ashby-Herring scholarships (each $1,500)
Deadline:April 6, 2026
Apply here:https://www.azfoundation.org/archer-ragsdale
Eligibility:
- Graduating high school senior from Arizona
- Attending a 2-year or 4-year college/university
- African-American
- 3.0 GPA or higher
- Demonstrated financial need
Free Virtual Workshops (Zoom): Get Help With Your Application
If you’ve ever watched a student stall out halfway through an application, these workshops are a smart fix: they’re designed so applicants can work on their scholarship application with support from ACF’s scholarship team.
Workshop dates (Zoom):
- February 12, 2026 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m.
- March 5, 2026 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m.
- March 26 — 4:00 to 5:00 p.m. (date listed on flyer; confirm year when registering)
Register here:https://acf.cventevents.com/acfscholarships2026
View the flyer here: https://stmdailynews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/Deadline-updated-12.29.2025-Archer-Ragsdale-Flyer-FINAL.pdf
Download Flyer (PDF)
What to watch for: Register for the dates you can attend and come prepared with what you already have (basic info, activities list, questions). One hour of guided progress can save days of procrastination.
Why This Matters (and Why Sharing Helps)
The Tuskegee Airmen legacy is rooted in excellence, discipline, and breaking barriers—and scholarships tied to that legacy are meant to elevate futures for the next generation.
If you’re a parent, teacher, coach, mentor, or neighbor, consider this your nudge: forward the link, post it in a group chat, or share it with a student who might qualify. Deadlines hit quickly, and the easiest scholarship to win is often the one you actually apply for.
View the press release: https://stmdailynews.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/FOR-IMMEDIATE-RELEASE.pdf
Related Links:
- https://azfoundation.org/scholarships
- https://acf.cventevents.com/acfscholarships2026
- https://www.azfoundation.org/archer-ragsdale
College Life
College isn’t just classes and credits — it’s learning how to manage your time, money, health, and relationships while you build a future that actually fits. In our College Life coverage, STM Daily News shares practical, real-world guides for students and families: campus living tips, study and productivity habits, career prep, budgeting basics, mental wellness check-ins, and smart ways to make the most of college in Arizona and beyond.
Expect quick reads, useful takeaways, and “what to do next” advice — whether you’re a first-year student, a transfer, or heading back to school.
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
