The Knowledge
Population Density: How Los Angeles Compares to New York and Chicago
How dense are America’s biggest cities? A clear breakdown of population density in Los Angeles, New York City, and Chicago—city limits vs metro areas—and why it matters.
![]()
Population Density: How Los Angeles Compares to New York and Chicago
When people think of crowded American cities, New York City usually comes to mind first. Los Angeles, by contrast, is often labeled as “sprawling,” while Chicago is seen as a middle ground. But population density tells a more nuanced story—especially when comparing city proper numbers versus metro-area density.
City Proper: How Dense Are the Cities Themselves?
Looking only at official city boundaries, the differences are stark:
New York City averages about 27,000–28,000 people per square mile, making it by far the most densely populated major city in the United States.
Chicago comes in at roughly 12,000 people per square mile, dense but far more spread out than New York.
Los Angeles, despite being the nation’s second-largest city by population, averages just 8,400–8,500 people per square mile.
This gap reflects development patterns. New York grew upward with dense apartment buildings and extensive transit. Los Angeles expanded outward with single-family neighborhoods and car-oriented planning.
Metro Areas Tell a Different Story
When the lens widens to include surrounding suburbs and commuter communities, the rankings shift:
Los Angeles Metro Area: ~7,000 people per square mile
New York Metro Area: ~5,300 people per square mile
Chicago Metro Area: ~3,500 people per square mile
This surprises many readers. While New York’s core is extremely dense, its metro region stretches across a vast, lower-density area spanning parts of New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. Los Angeles, on the other hand, has a metro region that is more consistently built-up, with fewer truly rural gaps.
Why Density Feels Different in Each City
Population density doesn’t always match perception:
New York feels crowded because density is concentrated vertically and transit funnels millions into compact areas.
Los Angeles feels congested not because of extreme density, but because people are spread out and heavily reliant on cars.
Chicago balances both, with dense neighborhoods near the core and more traditional suburban sprawl outward.
Hollywood vs. Reality: How LA’s Wilshire Subway Was Really Built
Why This Matters
Density shapes:
Transportation planning
Housing affordability
Infrastructure costs
Environmental impact
For cities like Los Angeles—now reinvesting in rail, buses, and transit-oriented development—understanding density is critical. As coverage on LA Metro and urban revival continues, these numbers explain why transit challenges in Southern California differ so sharply from those in New York or Chicago.
The Big Picture
Most dense city: New York City
Most dense metro area: Los Angeles
Most balanced: Chicago
Density isn’t just about how many people live in a place—it’s about how they live, move, and interact with the city around them.
Further Reading: Population Density & Urban Development
- U.S. Census Bureau – Urban vs. Rural and Urbanized Area Density
- U.S. Census Bureau – Population and Density Data for U.S. Cities
- New Geography – Density Rankings of Major U.S. Urban Areas
- Brookings Institution – Urban and Metropolitan Policy Research
- Planetizen – What Population Density Means in Urban Planning
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Entertainment
Byron Allen’s Starz Stake Signals Bigger Moves in the Streaming Industry
Byron Allen’s Starz: Byron Allen has acquired a 10.7% stake in Starz Entertainment for approximately $25 million, signaling his long-term media strategy amidst industry consolidation. This investment positions him influentially in the evolving streaming market despite intense competition.

Byron Allen’s Starz investment
Media entrepreneur Byron Allen has taken another step toward expanding his growing media empire. Through his family office, Allen recently acquired a 10.7% stake in Starz Entertainment, purchasing the shares from a fund managed by former U.S. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin.
The transaction, valued at approximately $25 million, gives Allen a significant minority position in the premium cable and streaming platform. While the investment itself may seem modest compared to the billion-dollar deals common in Hollywood, analysts say the move could signal a larger strategy unfolding in the rapidly evolving streaming industry.
Why the Starz Deal Matters
The shares were sold by Mnuchin’s Liberty 77 Capital fund, which previously invested in the company when Starz was still connected to its former parent, Lionsgate.
In 2025, Lionsgate completed a corporate restructuring that separated its operations into two distinct companies:
- Lionsgate Studios – responsible for film and television production
- Starz – focused on premium cable and streaming services
Following the spin-off, Starz became an independent publicly traded company. As a result, investors are still determining the platform’s long-term value in an increasingly crowded streaming marketplace.
A Streaming Platform With Loyal Audiences
Despite facing intense competition from larger platforms such as Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime Video, Starz continues to maintain a strong subscriber base and recognizable content franchises.
- Outlander – historical drama series
- The Power franchise created by Courtney A. Kemp and executive produced by 50 Cent
Byron Allen’s Long-Term Media Strategy
Allen’s investment strategy has long focused on owning media distribution and infrastructure rather than simply producing content.
- The Weather Channel
- Dozens of local television stations across the United States
- Multiple niche cable networks and digital platforms
Over the past several years, Allen has also pursued larger acquisitions, reportedly exploring deals involving companies such as Paramount Global and BET Media Group. While those deals did not materialize, they signaled his ambition to expand Allen Media Group into a major force in global media ownership.
The Bigger Picture: Industry Consolidation
Allen’s investment arrives during a time of significant disruption in the entertainment business. Traditional cable television continues to decline as audiences migrate toward streaming platforms. At the same time, major studios and media companies are struggling to make streaming services consistently profitable.
Industry observers believe these pressures could lead to a new wave of consolidation across Hollywood and the streaming sector. Smaller platforms like Starz could become attractive acquisition targets for larger companies seeking additional subscribers and content libraries.
A Potential Hidden Opportunity
For now, Allen’s 10.7% stake does not give him control of Starz. However, it does provide influence as one of the company’s larger shareholders and leaves open the possibility of increasing his ownership in the future.
If consolidation accelerates and streaming platforms begin merging or forming partnerships, assets like Starz could become significantly more valuable. For Byron Allen—whose career began as a stand-up comedian before evolving into one of the most prominent independent media owners in America—the investment may represent another calculated step in a decades-long strategy built around media ownership and long-term growth.
Related Coverage
- Byron Allen Acquires Stake in Starz – Hollywood Reporter
- Starz Spin-Off from Lionsgate: What It Means for Streaming – Variety
- Byron Allen’s Media Acquisitions: Building a Modern Empire – Forbes
- Starz in the Streaming Wars: How It Compares – CNBC
- Why Byron Allen is Betting on Streaming Platforms – Deadline
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
News
Valley Metro to Exit CAPEX Capitol Extension After Phoenix Council Shifts Focus to Indian School Road Corridor
Valley Metro is shifting its focus on high-capacity transit planning in west Phoenix following a City Council vote, prioritizing a new corridor along Indian School Road while exiting the Capitol Extension project, CAPEX, and seeking community engagement.
Last Updated on March 6, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Valley Metro is officially shifting gears on high-capacity transit planning in west Phoenix following a Phoenix City Council vote earlier this year.
In a message to the public, Valley Metro said that after the Jan. 27, 2026 City Council decision to re-evaluate high-capacity transit options and prioritize a proposed West Phoenix corridor along Indian School Road, the agency will exit project development and the Federal Transit Administration Capital Investment Grant (CIG) process for the Capitol Extension (CAPEX) project.

What the City Council voted to do
According to Valley Metro, the Phoenix City Council voted to take another look at high-capacity transit options for west Phoenix and to prioritize studying a new corridor alignment along Indian School Road.
What Valley Metro is doing next
Valley Metro emphasized it still supports expanding high-capacity transit in west Phoenix, citing demand and mobility needs in the corridor. But the agency says it will now pivot away from CAPEX and toward the new study effort.
Key next steps Valley Metro outlined include:
- Exiting the CAPEX project development process and the federal CIG pipeline
- Advancing planning for the West Phoenix study along Indian School Road
- Centering comprehensive community engagement, including outreach to residents, business owners, and stakeholders along the corridor
- Working closely with the City of Phoenix on project development
- Coordinating with the Federal Transit Administration to explore funding opportunities
How to stay engaged
Valley Metro is encouraging residents to sign up for updates as the next phase moves forward at valleymetro.org/notices.
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
2025 was hotter than it should have been – 5 influences and a dirty surprise offer clues to what’s ahead
The past three years recorded unprecedented global heat, with 2025 being particularly warm. Factors such as greenhouse gas emissions and a decline in solar activity influenced temperatures and extreme weather patterns.

Michael Wysession, Washington University in St. Louis
The past three years have been the world’s hottest on record by far, with 2025 almost tied with 2023 for second place. With that energy came extreme weather, from flash flooding to powerful hurricanes and severe droughts. Yet, by most indicators, the planet should have been cooler in 2025 than it was.
So, what happened, and what does that say about the year ahead?
As an earth and environmental scientist, I study influences that affect global temperatures year to year, such as El Niño, wildfires and solar cycles. Some make Earth hotter. Some make it cooler. And one particularly unhealthy influence has been quietly hiding a large amount of global warming – until now.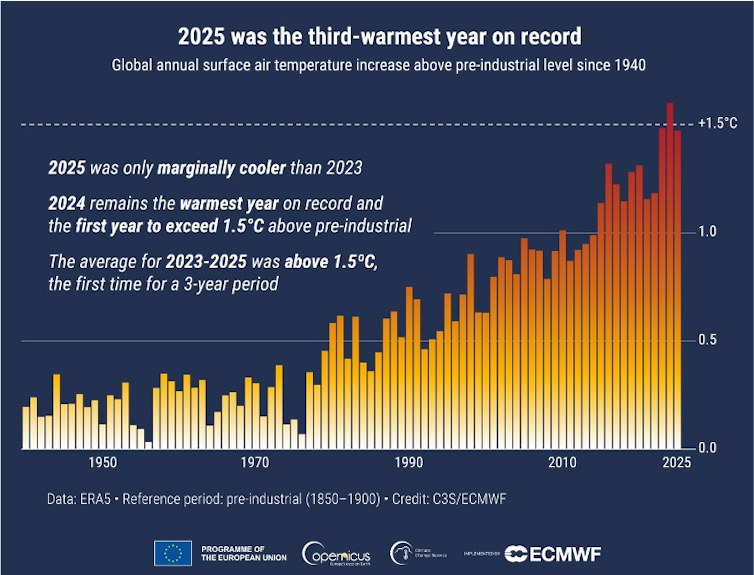
Factors that made 2025 cooler than 2024
The Earth’s climate is the result of many factors that change from year to year. Some that helped make 2025 cooler than 2024 include:
La Niña’s arrival: La Niña is part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, a natural climate pattern that fluctuates between warm El Niño conditions and cooler La Niña conditions. During El Niño, the Pacific Ocean heats up along the equator, influencing the atmosphere in ways that can cause intense storms, droughts and heat waves around the planet. La Niña does the opposite; it’s like putting an ice pack on the atmosphere.
Both 2023 and 2024 were El Niño years, but in 2025 conditions shifted to neutral and then to La Niña starting in September.
The solar cycle: The Sun reached its solar maximum near the end of 2024, the peak of its energy output in an approximately 11-year cycle, and began declining in 2025. So, while the sun’s output was still stronger than average in 2025, it was less than in 2024.
Fewer wildfires: Despite some destructive blazes, the world also saw fewer wildfires during 2025 than 2024, which put less carbon dioxide – a planet-warming greenhouse gas – into the atmosphere.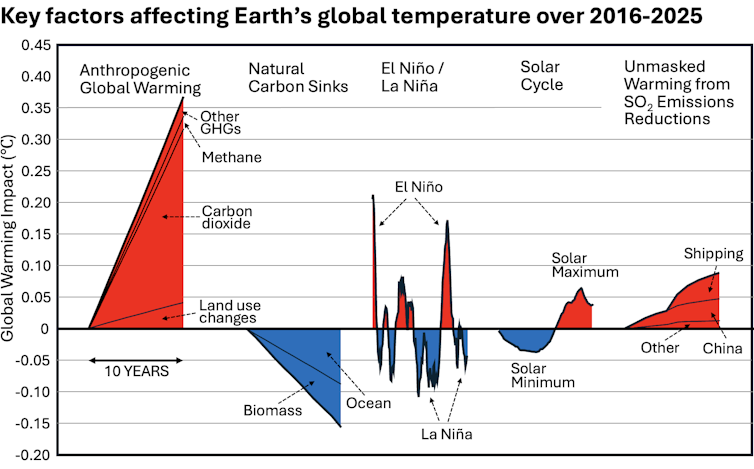
Despite those points, 2025 still ended up as the third-hottest year in over 175 years of record-keeping and likely one of the warmest in at least several thousand years. It was nearly as warm as 2023, at 2.6 degrees Fahrenheit (1.47 Celsius) above the 1850-1900 average, according to the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service. It also had the second-highest average land temperature recorded, up 3.6 F (2 C) compared to preindustrial years, with more than 10% of the land experiencing record-high temperatures.
Factors that made 2025 warmer than expected
Several other factors made 2025 warmer than expected, and some are likely to continue to increase in 2026. They include:
Greenhouse gas emissions: The big driver of global warming is excess greenhouse gas emissions, largely from burning fossil fuels, and 2025 had plenty.
Greenhouse gases trap heat near Earth’s surface like a blanket, raising the temperature. They also linger in the atmosphere for years to centuries, meaning gases released today will continue to warm the planet well into the future. The levels of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere all increased in 2025.
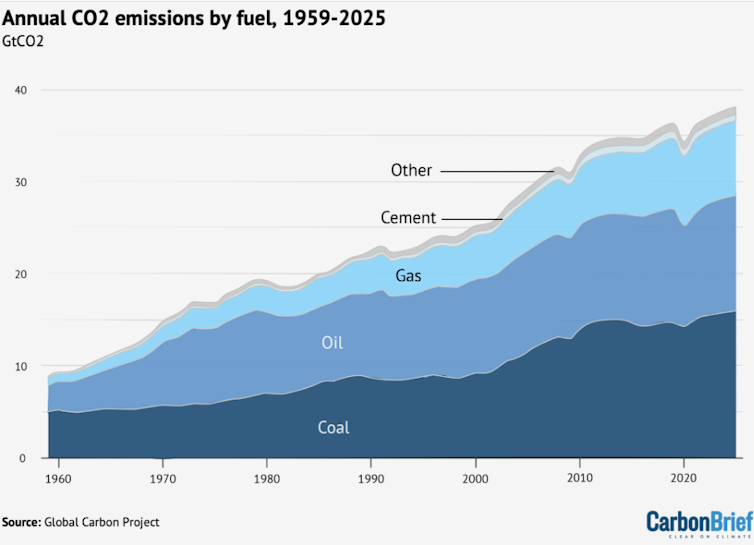
Rising energy demand drove an increase in fossil fuel use. About 80% of the increasing electric power demand came from emerging economies, largely for rising air conditioning demands as the world gets hotter. In the U.S., the rapid growth of data centers for AI and cryptocurrency mining helped boost U.S. carbon dioxide emissions by 2.4%.
Earth’s energy imbalance: Other sources can disrupt the natural balance between the amount of sunlight that reaches Earth and the lesser amount radiated back to space. A recent study found that Earth’s energy uptake surged and temperatures rose quickly when a rare three-year La Niña in 2020-2022 shifted to El Niño in 2023-2024.
Declining polar ice, which efficiently reflects sunlight back into space, also affects the energy balance. As sea ice declines, it leaves dark ocean water that absorbs most of the sunlight that reaches it. In a spiraling feedback, warmer water melts sea ice, allowing more sunlight into the ocean, warming it faster; 2025 had the lowest winter peak of Arctic sea ice on record and the third-lowest minimum extent of Antarctic ice.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/t0SSd/1
Air pollution: Sulfate aerosol pollution from coal combustion and burning heavy fuel oil in shipping has also been affecting Earth’s energy balance. It has been masking the full effects of human-caused greenhouse gases for years by reflecting sunlight back into space, creating a cooling effect. But sulfate aerosol pollution is also a serious health hazard, blamed for about 8 million human deaths per year from lung diseases.
Recent reductions in sulfate pollution – now 40% less than 20 years ago – have meant about a 0.2 F (0.13 C) increase in global temperatures. Much of the reduction was from China’s efforts to reduce its notoriously bad air pollution in recent years and international shipping rules in effect since 2020 that have reduced sulfur emissions from large ships by 85%.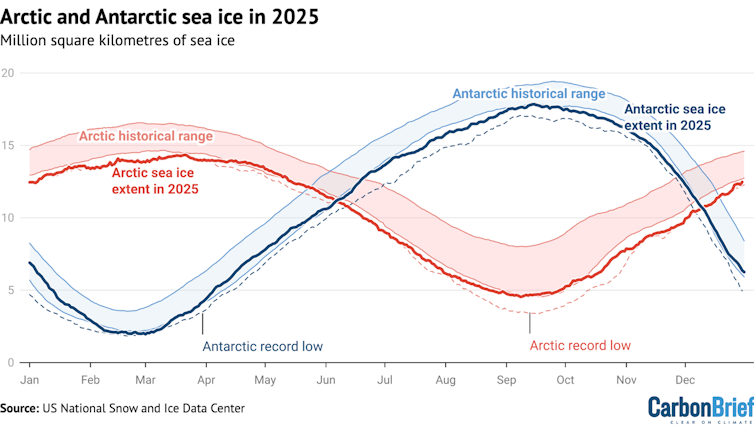
Taking all factors together, humans are now warming the planet at a faster rate than at any point in human history: at about 0.5 F (0.27 C) per decade. That extra heat can fuel extreme weather, including flash floods, heat waves, extended droughts, wildfires and coastal flooding, affecting human lives and economies.
Predictions for 2026
Most climate models predict 2026 will be about as hot as 2025, depending on whether a Pacific El Niño develops, which forecasters give about a 60% chance of happening. The planet is already starting the year out warm, even if it doesn’t feel like that everywhere. While January was very cold in parts of the U.S., globally, Earth saw its fifth-warmest January on record, and much of the western U.S. saw one of its warmest winters on record.
Solar output will continue to decrease slowly in 2026. However, the International Monetary Fund projects strong global economic growth at about 3.3%, suggesting electricity demand will also continue to grow. The International Energy Agency expects global electricity demand to increase by 3.6% per year through at least 2030.
Even though global renewable energy use is growing quickly, it isn’t growing fast enough to meet rising demand, meaning more fossil fuel use in the coming years. More fossil fuels burned means more emissions and more warming, while the ability of the ocean and land to absorb carbon dioxide continues to decrease. As a result, the atmosphere and oceans heat up, increasing the risks of passing tipping points – glaciers disappear, Atlantic Ocean circulation shuts down, permafrost thaws, coral reefs die.
If greenhouse gas emissions continue at a high rate, humanity may look back at 2025 as one the coolest years globally in the rest of our lives.
Michael Wysession, Professor of Earth, Environmental, and Planetary Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
