
Joel Kowsky/NASA via AP
AI Spacecraft Propulsion: Machine Learning’s Role in Space Travel
Marcos Fernandez Tous, University of North Dakota; Preeti Nair, University of North Dakota; Sai Susmitha Guddanti, University of North Dakota, and Sreejith Vidhyadharan Nair, University of North Dakota
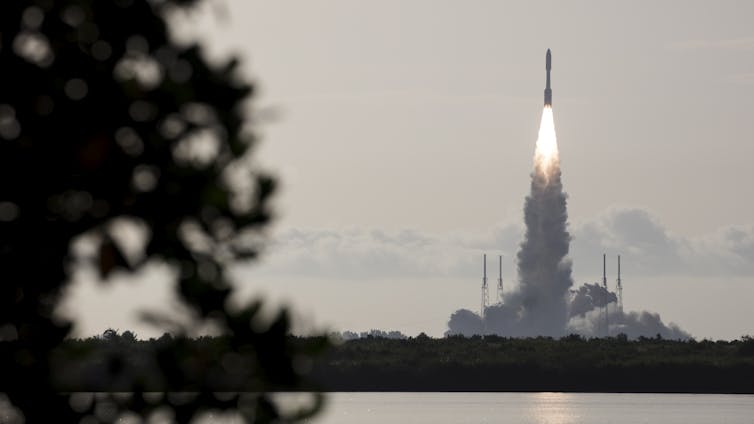
Every year, companies and space agencies launch hundreds of rockets into space – and that number is set to grow dramatically with ambitious missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond. But these dreams hinge on one critical challenge: propulsion – the methods used to push rockets and spacecraft forward.
To make interplanetary travel faster, safer and more efficient, scientists need breakthroughs in propulsion technology. Artificial intelligence is one type of technology that has begun to provide some of these necessary breakthroughs.
We’re a team of engineers and graduate students who are studying how AI in general, and a subset of AI called machine learning in particular, can transform spacecraft propulsion. From optimizing nuclear thermal engines to managing complex plasma confinement in fusion systems, AI is reshaping propulsion design and operations. It is quickly becoming an indispensable partner in humankind’s journey to the stars.
Machine learning and reinforcement learning
Machine learning is a branch of AI that identifies patterns in data that it has not explicitly been trained on. It is a vast field with its own branches, with a lot of applications. Each branch emulates intelligence in different ways: by recognizing patterns, parsing and generating language, or learning from experience. This last subset in particular, commonly known as reinforcement learning, teaches machines to perform their tasks by rating their performance, enabling them to continuously improve through experience.
As a simple example, imagine a chess player. The player does not calculate every move but rather recognizes patterns from playing a thousand matches. Reinforcement learning creates similar intuitive expertise in machines and systems, but at a computational speed and scale impossible for humans. It learns through experiences and iterations by observing its environment. These observations allows the machine to correctly interpret each outcome and deploy the best strategies for the system to reach its goal.
Reinforcement learning can improve human understanding of deeply complex systems – those that challenge the limits of human intuition. It can help determine the most efficient trajectory for a spacecraft heading anywhere in space, and it does so by optimizing the propulsion necessary to send the craft there. It can also potentially design better propulsion systems, from selecting the best materials to coming up with configurations that transfer heat between parts in the engine more efficiently.
Reinforcement learning for propulsion systems
In regard to space propulsion, reinforcement learning generally falls into two categories: those that assist during the design phase – when engineers define mission needs and system capabilities – and those that support real-time operation once the spacecraft is in flight.
Among the most exotic and promising propulsion concepts is nuclear propulsion, which harnesses the same forces that power atomic bombs and fuel the Sun: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Fission works by splitting heavy atoms such as uranium or plutonium to release energy – a principle used in most terrestrial nuclear reactors. Fusion, on the other hand, merges lighter atoms such as hydrogen to produce even more energy, though it requires far more extreme conditions to initiate.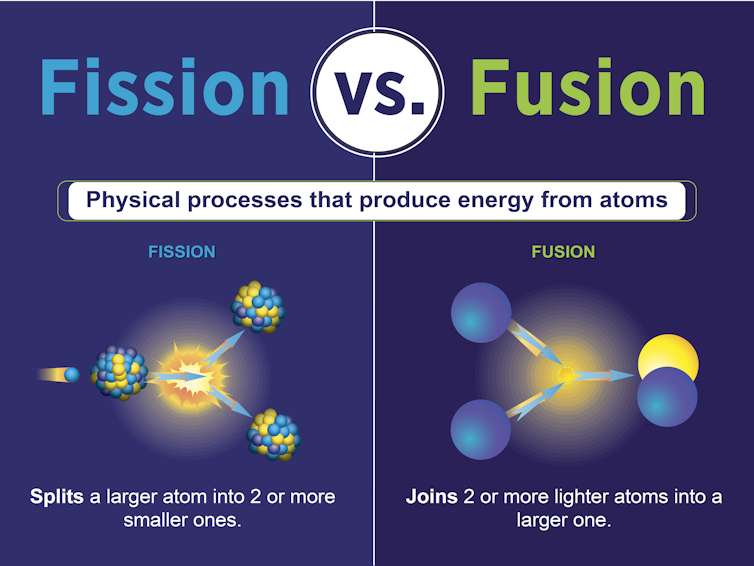
Sarah Harman/U.S. Department of Energy
Fission is a more mature technology that has been tested in some space propulsion prototypes. It has even been used in space in the form of radioisotope thermoelectric generators, like those that powered the Voyager probes. But fusion remains a tantalizing frontier.
Nuclear thermal propulsion could one day take spacecraft to Mars and beyond at a lower cost than that of simply burning fuel. It would get a craft there faster than electric propulsion, which uses a heated gas made of charged particles called plasma.
Unlike these systems, nuclear propulsion relies on heat generated from atomic reactions. That heat is transferred to a propellant, typically hydrogen, which expands and exits through a nozzle to produce thrust and shoot the craft forward.
So how can reinforcement learning help engineers develop and operate these powerful technologies? Let’s begin with design.
Idaho National Laboratory, CC BY
Reinforcement learning’s role in design
Early nuclear thermal propulsion designs from the 1960s, such as those in NASA’s NERVA program, used solid uranium fuel molded into prism-shaped blocks. Since then, engineers have explored alternative configurations – from beds of ceramic pebbles to grooved rings with intricate channels.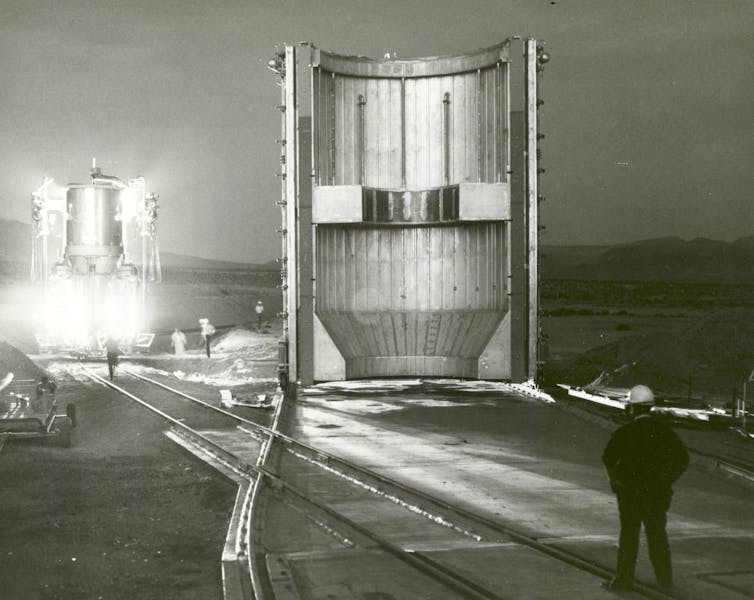
NASA/Wikipedia
Why has there been so much experimentation? Because the more efficiently a reactor can transfer heat from the fuel to the hydrogen, the more thrust it generates.
This area is where reinforcement learning has proved to be essential. Optimizing the geometry and heat flow between fuel and propellant is a complex problem, involving countless variables – from the material properties to the amount of hydrogen that flows across the reactor at any given moment. Reinforcement learning can analyze these design variations and identify configurations that maximize heat transfer. Imagine it as a smart thermostat but for a rocket engine – one you definitely don’t want to stand too close to, given the extreme temperatures involved.
Reinforcement learning and fusion technology
Reinforcement learning also plays a key role in developing nuclear fusion technology. Large-scale experiments such as the JT-60SA tokamak in Japan are pushing the boundaries of fusion energy, but their massive size makes them impractical for spaceflight. That’s why researchers are exploring compact designs such as polywells. These exotic devices look like hollow cubes, about a few inches across, and they confine plasma in magnetic fields to create the conditions necessary for fusion.
Controlling magnetic fields within a polywell is no small feat. The magnetic fields must be strong enough to keep hydrogen atoms bouncing around until they fuse – a process that demands immense energy to start but can become self-sustaining once underway. Overcoming this challenge is necessary for scaling this technology for nuclear thermal propulsion.
Reinforcement learning and energy generation
However, reinforcement learning’s role doesn’t end with design. It can help manage fuel consumption – a critical task for missions that must adapt on the fly. In today’s space industry, there’s growing interest in spacecraft that can serve different roles depending on the mission’s needs and how they adapt to priority changes through time.
Military applications, for instance, must respond rapidly to shifting geopolitical scenarios. An example of a technology adapted to fast changes is Lockheed Martin’s LM400 satellite, which has varied capabilities such as missile warning or remote sensing.
But this flexibility introduces uncertainty. How much fuel will a mission require? And when will it need it? Reinforcement learning can help with these calculations.
From bicycles to rockets, learning through experience – whether human or machine – is shaping the future of space exploration. As scientists push the boundaries of propulsion and intelligence, AI is playing a growing role in space travel. It may help scientists explore within and beyond our solar system and open the gates for new discoveries.
Marcos Fernandez Tous, Assistant Professor of Space Studies, University of North Dakota; Preeti Nair, Master’s Student in Aerospace Sciences, University of North Dakota; Sai Susmitha Guddanti, Ph.D. Student in Aerospace Sciences, University of North Dakota, and Sreejith Vidhyadharan Nair, Research Assistant Professor of Aviation, University of North Dakota
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




