Blog
NASA Astronaut Jonny Kim to Share Insights from Eight-Month Space Station Mission
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim will discuss his eight-month International Space Station mission during a live news conference on Dec. 19. Discover the science, technology, and teamwork behind his groundbreaking journey, streaming live via NASA and covered by STM Daily News.
Last Updated on December 19, 2025 by Daily News Staff
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim poses inside the International Space Station’s cupola as it orbits 265 miles above the Indian Ocean near Madagascar. Credit: NASA
NASA Astronaut Jonny Kim Recaps Eight-Month International Space Station Mission in Live News Conference
- What: Jonny Kim’s ISS Mission Recap News Conference
- When: Friday, Dec. 19, 3:30 p.m. EST
- Where: NASA’s YouTube channel (also available on other NASA streaming platforms)
A Mission Marked by Discovery
Advancing Medicine and Technology
- Bioprinted Tissues in Microgravity: Kim helped study the behavior of bioprinted tissues containing blood vessels, a step forward in space-based tissue production that could one day revolutionize patient care on Earth.
- Remote Robotics Operations: Through the Surface Avatar study, Kim tested the remote command of multiple robots in space—work that could lead to more advanced robotic assistants for future missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- Nanomaterials for Medicine: Kim contributed to the development of DNA-mimicking nanomaterials, opening doors for improved drug delivery and regenerative medicine both in space and at home.
How to Watch and Participate
NASA’s ISS Page
Why This Matters
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Knowledge
2025 was hotter than it should have been – 5 influences and a dirty surprise offer clues to what’s ahead
The past three years recorded unprecedented global heat, with 2025 being particularly warm. Factors such as greenhouse gas emissions and a decline in solar activity influenced temperatures and extreme weather patterns.

Michael Wysession, Washington University in St. Louis
The past three years have been the world’s hottest on record by far, with 2025 almost tied with 2023 for second place. With that energy came extreme weather, from flash flooding to powerful hurricanes and severe droughts. Yet, by most indicators, the planet should have been cooler in 2025 than it was.
So, what happened, and what does that say about the year ahead?
As an earth and environmental scientist, I study influences that affect global temperatures year to year, such as El Niño, wildfires and solar cycles. Some make Earth hotter. Some make it cooler. And one particularly unhealthy influence has been quietly hiding a large amount of global warming – until now.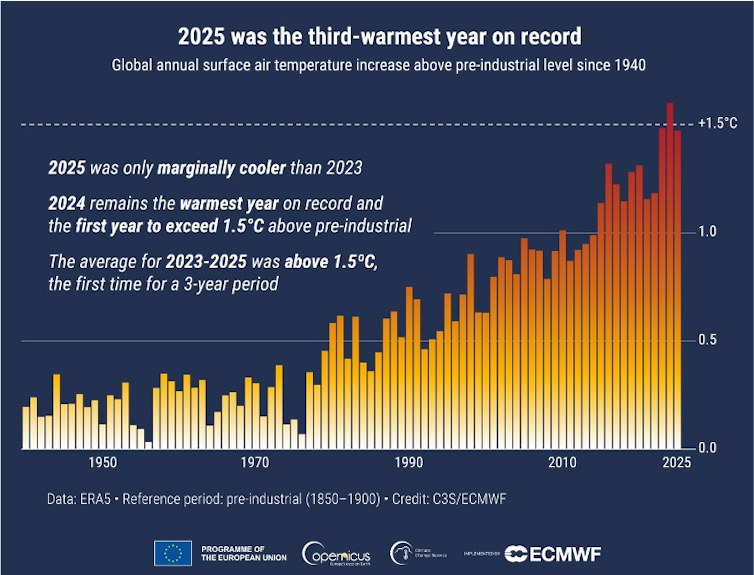
Factors that made 2025 cooler than 2024
The Earth’s climate is the result of many factors that change from year to year. Some that helped make 2025 cooler than 2024 include:
La Niña’s arrival: La Niña is part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, a natural climate pattern that fluctuates between warm El Niño conditions and cooler La Niña conditions. During El Niño, the Pacific Ocean heats up along the equator, influencing the atmosphere in ways that can cause intense storms, droughts and heat waves around the planet. La Niña does the opposite; it’s like putting an ice pack on the atmosphere.
Both 2023 and 2024 were El Niño years, but in 2025 conditions shifted to neutral and then to La Niña starting in September.
The solar cycle: The Sun reached its solar maximum near the end of 2024, the peak of its energy output in an approximately 11-year cycle, and began declining in 2025. So, while the sun’s output was still stronger than average in 2025, it was less than in 2024.
Fewer wildfires: Despite some destructive blazes, the world also saw fewer wildfires during 2025 than 2024, which put less carbon dioxide – a planet-warming greenhouse gas – into the atmosphere.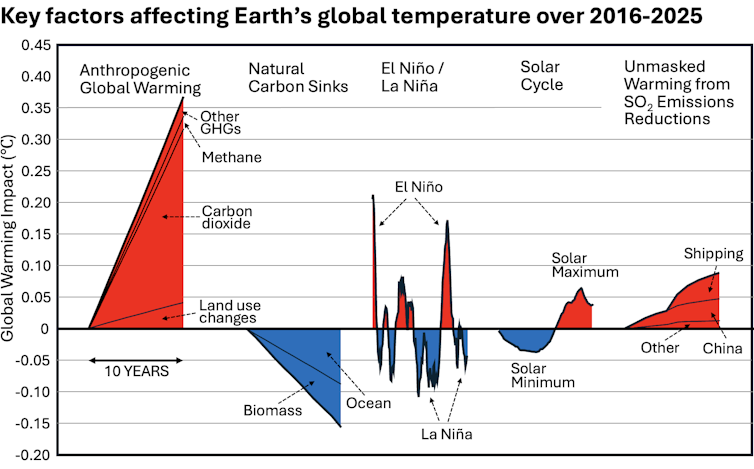
Despite those points, 2025 still ended up as the third-hottest year in over 175 years of record-keeping and likely one of the warmest in at least several thousand years. It was nearly as warm as 2023, at 2.6 degrees Fahrenheit (1.47 Celsius) above the 1850-1900 average, according to the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service. It also had the second-highest average land temperature recorded, up 3.6 F (2 C) compared to preindustrial years, with more than 10% of the land experiencing record-high temperatures.
Factors that made 2025 warmer than expected
Several other factors made 2025 warmer than expected, and some are likely to continue to increase in 2026. They include:
Greenhouse gas emissions: The big driver of global warming is excess greenhouse gas emissions, largely from burning fossil fuels, and 2025 had plenty.
Greenhouse gases trap heat near Earth’s surface like a blanket, raising the temperature. They also linger in the atmosphere for years to centuries, meaning gases released today will continue to warm the planet well into the future. The levels of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere all increased in 2025.
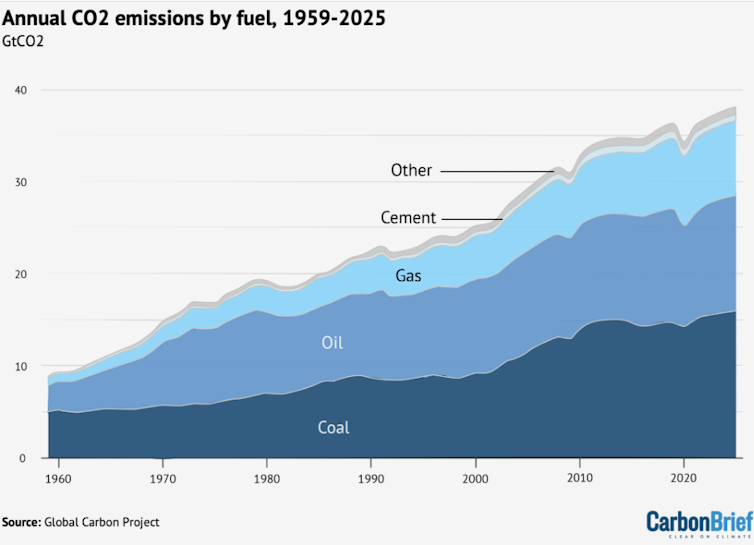
Rising energy demand drove an increase in fossil fuel use. About 80% of the increasing electric power demand came from emerging economies, largely for rising air conditioning demands as the world gets hotter. In the U.S., the rapid growth of data centers for AI and cryptocurrency mining helped boost U.S. carbon dioxide emissions by 2.4%.
Earth’s energy imbalance: Other sources can disrupt the natural balance between the amount of sunlight that reaches Earth and the lesser amount radiated back to space. A recent study found that Earth’s energy uptake surged and temperatures rose quickly when a rare three-year La Niña in 2020-2022 shifted to El Niño in 2023-2024.
Declining polar ice, which efficiently reflects sunlight back into space, also affects the energy balance. As sea ice declines, it leaves dark ocean water that absorbs most of the sunlight that reaches it. In a spiraling feedback, warmer water melts sea ice, allowing more sunlight into the ocean, warming it faster; 2025 had the lowest winter peak of Arctic sea ice on record and the third-lowest minimum extent of Antarctic ice.
https://datawrapper.dwcdn.net/t0SSd/1
Air pollution: Sulfate aerosol pollution from coal combustion and burning heavy fuel oil in shipping has also been affecting Earth’s energy balance. It has been masking the full effects of human-caused greenhouse gases for years by reflecting sunlight back into space, creating a cooling effect. But sulfate aerosol pollution is also a serious health hazard, blamed for about 8 million human deaths per year from lung diseases.
Recent reductions in sulfate pollution – now 40% less than 20 years ago – have meant about a 0.2 F (0.13 C) increase in global temperatures. Much of the reduction was from China’s efforts to reduce its notoriously bad air pollution in recent years and international shipping rules in effect since 2020 that have reduced sulfur emissions from large ships by 85%.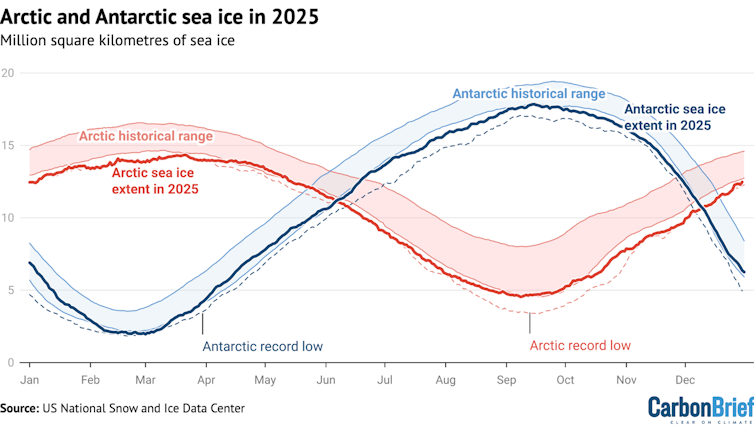
Taking all factors together, humans are now warming the planet at a faster rate than at any point in human history: at about 0.5 F (0.27 C) per decade. That extra heat can fuel extreme weather, including flash floods, heat waves, extended droughts, wildfires and coastal flooding, affecting human lives and economies.
Predictions for 2026
Most climate models predict 2026 will be about as hot as 2025, depending on whether a Pacific El Niño develops, which forecasters give about a 60% chance of happening. The planet is already starting the year out warm, even if it doesn’t feel like that everywhere. While January was very cold in parts of the U.S., globally, Earth saw its fifth-warmest January on record, and much of the western U.S. saw one of its warmest winters on record.
Solar output will continue to decrease slowly in 2026. However, the International Monetary Fund projects strong global economic growth at about 3.3%, suggesting electricity demand will also continue to grow. The International Energy Agency expects global electricity demand to increase by 3.6% per year through at least 2030.
Even though global renewable energy use is growing quickly, it isn’t growing fast enough to meet rising demand, meaning more fossil fuel use in the coming years. More fossil fuels burned means more emissions and more warming, while the ability of the ocean and land to absorb carbon dioxide continues to decrease. As a result, the atmosphere and oceans heat up, increasing the risks of passing tipping points – glaciers disappear, Atlantic Ocean circulation shuts down, permafrost thaws, coral reefs die.
If greenhouse gas emissions continue at a high rate, humanity may look back at 2025 as one the coolest years globally in the rest of our lives.
Michael Wysession, Professor of Earth, Environmental, and Planetary Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Dive into “The Knowledge,” where curiosity meets clarity. This playlist, in collaboration with STMDailyNews.com, is designed for viewers who value historical accuracy and insightful learning. Our short videos, ranging from 30 seconds to a minute and a half, make complex subjects easy to grasp in no time. Covering everything from historical events to contemporary processes and entertainment, “The Knowledge” bridges the past with the present. In a world where information is abundant yet often misused, our series aims to guide you through the noise, preserving vital knowledge and truths that shape our lives today. Perfect for curious minds eager to discover the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything around us. Subscribe and join in as we explore the facts that matter. https://stmdailynews.com/the-knowledge/
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Science
After the Blood Moon: Scientists and Skywatchers React to the March 3, 2026 Total Lunar Eclipse
The March 3, 2026 total lunar eclipse amazed skywatchers worldwide. Scientists and amateur astronomers share reactions and photos from the dramatic blood moon event.
Last Updated on March 5, 2026 by Daily News Staff
Millions of people around the world looked to the sky in the early hours of March 3, 2026 to witness one of the most striking astronomical events of the year — a total lunar eclipse, often referred to as a “Blood Moon.” As the Moon passed completely into Earth’s shadow, it transformed from its familiar silver glow into a deep copper-red color, captivating observers from North America to Asia and across the Pacific.
Blood Moon Aftermath: Scientists and Skywatchers React to the March 3, 2026 Total Lunar Eclipse
For viewers in the western United States, including Arizona and California, the eclipse occurred just before sunrise. The timing created a dramatic scene as the reddish Moon hovered low in the western sky while the eastern horizon began to brighten with dawn.
A Global Skywatching Event
Total lunar eclipses occur when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align so that Earth’s shadow completely covers the Moon. During the March 3 event, the Moon spent nearly an hour fully inside the darkest part of Earth’s shadow, known as the umbra. During this phase, sunlight filtered through Earth’s atmosphere projected reddish light onto the Moon’s surface, creating the dramatic “blood moon” effect.
Astronomers noted that the event was particularly significant because total lunar eclipses are relatively infrequent. While partial eclipses occur more often, a full eclipse visible across large portions of the globe remains a memorable experience for both scientists and casual observers.
Scientists Explain the Phenomenon
According to researchers at NASA, the reddish color seen during totality occurs because Earth’s atmosphere scatters shorter wavelengths of sunlight — such as blue — while allowing longer red wavelengths to pass through. This filtered light is then bent, or refracted, into Earth’s shadow and projected onto the Moon.
Planetary scientists say lunar eclipses provide a powerful visual demonstration of the geometry of the Earth–Moon–Sun system. The curved shadow moving across the Moon also historically served as one of the earliest pieces of evidence that Earth is spherical.
Researchers also point out that lunar eclipses offer opportunities to study Earth’s atmosphere. Variations in dust, volcanic particles, and atmospheric conditions can influence how dark or red the Moon appears during totality.
Amateur Astronomers Share Their Views
While professional observatories monitored the eclipse with precision instruments, amateur astronomers and astrophotographers helped document the event from countless locations worldwide. Social media platforms and astronomy forums quickly filled with images showing the Moon’s color shifting from pale gray to orange and deep red.
Many skywatchers in the southwestern United States described the experience as particularly dramatic because the eclipse occurred just before moonset. Observers reported seeing the Moon glowing red above desert landscapes and city skylines before gradually fading into the brightening morning sky.
Astrophotographers also emphasized that lunar eclipses are among the easiest astronomical events to capture. Unlike solar eclipses, they can be photographed safely without special filters, making them accessible to beginners using smartphones as well as professionals using telescopes and high-end cameras.
A Rare Pre-Dawn Sight
In parts of the western United States, some observers were able to witness a rare atmospheric phenomenon known as a selenelion, when both the eclipsed Moon and the rising Sun appear in the sky at the same time due to atmospheric refraction. The effect added an unusual visual element to an already impressive celestial event.
The combination of a deep red Moon and the approaching dawn created striking photographic opportunities and memorable moments for early-morning skywatchers.
When Is the Next Total Lunar Eclipse?
Although partial eclipses occur periodically, the next widely visible total lunar eclipse will not occur until late 2028. That makes the March 2026 eclipse one of the most notable skywatching events of the decade.
For many observers, the event served as a reminder that some of the most spectacular astronomical experiences require nothing more than stepping outside, looking up, and taking a moment to appreciate the universe above.
References and Further Reading
- NASA – Lunar Eclipse Science Overview
- Time and Date – March 3, 2026 Total Lunar Eclipse Details
- Sky & Telescope – Astronomy News and Observing Guides
- Space.com – Guide to Lunar Eclipses
- STM Daily News – Science Coverage
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
amusement and theme parks
Inside the Wait for Mattel Adventure Park & VAI Resort in Glendale, Arizona
Last Updated on March 4, 2026 by Daily News Staff
What was once pitched as one of the most exciting new additions to Arizona’s entertainment landscape — a world-class resort and theme park featuring some of Mattel’s most beloved brands — has become a long-anticipated project marked by persistent delays, evolving plans, and growing expectations.
A Vision Bigger Than a Theme Park
The centerpiece of the massive development near State Farm Stadium in Glendale, Arizona is VAI Resort, a 60-acre luxury entertainment destination designed to combine upscale hospitality with dynamic entertainment. Plans include:
- Over 1,100 luxury hotel rooms spread across multiple towers, catering to visitors of all types.
- A beach-style water oasis with white sand and temperature-controlled pools — a first for Arizona.
- A state-of-the-art concert amphitheater for national performers and DJ-driven nightlife.
- Dozens of restaurants, lounges, shopping experiences, and convention spaces. And anchored within this resort footprint is the long-awaited Mattel Adventure Park — a theme park bringing Hot Wheels™, Barbie™, Thomas & Friends™, and other iconic Mattel brands to life.
Construction Progress — Visible and Ongoing
The resort and park construction continue visibly along Cardinals Way and West Cardinals Way just south of the State Farm Stadium area. Over the past several years, crews have been steadily working on building structures for the resort’s hotels, water features, and entertainment venues.
For Mattel Adventure Park specifically:
- Core infrastructure and coaster track supports have been erected, including sections of the distinctive Hot Wheels-themed attractions, though construction has been slower than initially anticipated.
- The project’s official construction live-camera feed continues to stream real-time activity, underscoring that work is not abandoned even if progress isn’t tracking toward imminent completion.
In support of the wider development, the City of Glendale approved construction of a large parking garage designed to handle tens of thousands of visitors tied to future resort events and park operations.
Most recently, the resort’s developer expanded its footprint by acquiring an additional 33 acres of land to support future hospitality, residential, and commercial uses — a sign of long-term confidence in the destination despite timeline shifts.
Opening Date Ambiguity and Shifting Targets
From the outset, Mattel Adventure Park was slated to open in coordination with major regional events — originally pegged for 2022 and the Super Bowl LVII timeframe — then revised for 2023, 2024, and late 2025.
Similarly, VAI Resort itself has repeatedly shifted its projected debut:
- In April 2025, resort officials were targeting late 2025 for phased openings.
- By late 2025, that target had quietly dropped from public materials, and the official website no longer listed a specific opening date.
- As of early 2026, VAI Resort officials have refused to commit to any set opening date, saying they intend to announce a timeline only 9–12 months prior to launch — a stance that has left Arizona residents and visitors without concrete expectations.
There’s no public evidence yet that Mattel Adventure Park will open in early 2026, and some observers speculate the project may slide further into the future before doors open to the public.
What Guests Can Expect (When It Opens)
When ultimately completed, Mattel Adventure Park promises a unique experience distinct from traditional amusement parks:
- Hot Wheels™ Bone Shaker™ and Twin Mill™ Racer coasters
- Barbie™ Beach House with themed experiences
- Interactive zones featuring Thomas & Friends™ and other Mattel franchisesAll designed to appeal to families, children, and thrill seekers alike.
Beyond the park itself, the resort’s expansive amenities — including beaches, concert venues, fine dining, luxury spas, and convention space — intend to make Glendale a year-round entertainment hub for visitors from across the Southwest and beyond.
Looking Ahead
With additional land purchased and visible work continuing on multiple fronts, the broader VAI Resort and Mattel Adventure Park project is far from stalled, even if its opening dates have become increasingly uncertain.
Industry watchers and local residents alike will likely continue to track construction progress closely, waiting for the first official announcement of firm opening dates — a milestone the resort has said it’s now hesitant to set prematurely.
Track updates on the VAI Resort official website and the project’s construction live camera feed.
For more information about Mattel Adventure Park and VAI Resort, visit the Official website
Discover more from Daily News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
